Table of Contents
Eco-Sensitive Zones (ESZs) are specifically demarcated areas surrounding national parks and wildlife sanctuaries in India. They are governed and designated under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986. The primary objective of establishing ESZs is to regulate human activities that could potentially harm the delicate ecosystem and wildlife habitats within these protected areas. These zones serve as a buffer between human habitation and the core protected area, ensuring a balance between conservation efforts and sustainable development practices.
ESZs play a crucial role in minimizing negative impacts on biodiversity while allowing for certain activities that are deemed compatible with ecological conservation. This strategic approach aims to preserve natural resources and maintain the ecological integrity of these sensitive habitats.

Eco Sensitive Zones in India
Ecologically Sensitive Zones in India are designated by the Central Government through the Ministry of Environment, Forests, and Climate Change under the Environment Protection Act, 1986. There are over 600 such zones spread across different states. Key ESZs include Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Karnataka.
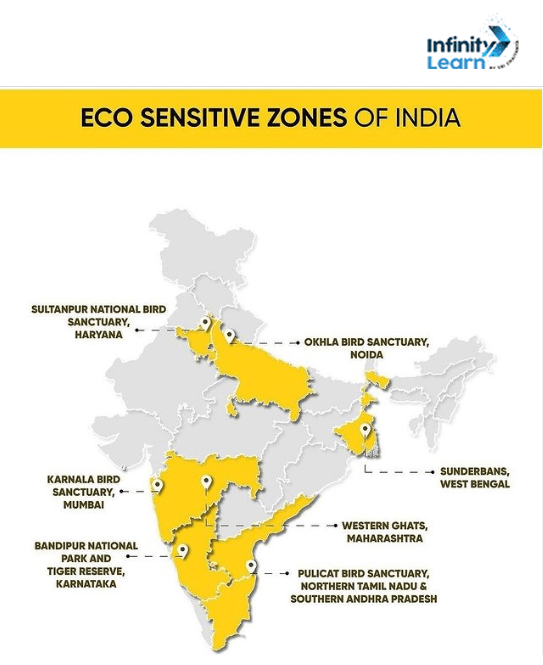
These zones impose strict restrictions on activities like commercial wood usage, industrial setups, mining, and tourism. Additionally, the discharge of waste and production of hazardous substances that cause pollution are strictly prohibited. Protecting these areas surrounding forests and wildlife corridors is crucial for maintaining ecological balance, safeguarding biodiversity, and preserving natural habitats for flora and fauna to thrive.
Also Read: National Parks in India
Eco Sensitive Zone List
Here’s a tabular representation of some major Eco-Sensitive Zones in India, including additional relevant information:
| State | Number of ESZs | Key Features |
| Uttar Pradesh | 35 | Includes areas around Dudhwa National Park and Hastinapur Wildlife Sanctuary. |
| Haryana | 20 | ESZs around Sultanpur National Park and Asola Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary. |
| West Bengal | 28 | Covers Sundarbans Biosphere Reserve and Buxa Tiger Reserve. |
| Andhra Pradesh | 18 | Includes ESZs near Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam Tiger Reserve and Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary. |
| Maharashtra | 42 | ESZs around Tadoba-Andhari Tiger Reserve and Sanjay Gandhi National Park. |
| Karnataka | 32 | Covers ESZs around Bandipur Tiger Reserve and Nagarhole National Park. |
| Tamil Nadu | 25 | Includes ESZs around Mudumalai Tiger Reserve and Kalakad Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve. |
| Kerala | 15 | ESZs around Periyar Tiger Reserve and Silent Valley National Park. |
| Rajasthan | 30 | Covers Sariska Tiger Reserve and Ranthambore National Park. |
| Madhya Pradesh | 38 | ESZs around Kanha Tiger Reserve and Panna National Park. |
Also Read: Wildlife Sanctuaries in India
Features of Eco Sensitive Zones
Ecologically Sensitive Zones (ESZs) are designated areas protected under specific regulations to safeguard natural resources from potential risks and hazards. These zones permit activities that promote environmental sustainability and agricultural productivity while prohibiting or regulating activities that could harm the ecosystem.
- In Eco-Sensitive Zones (ESZs), allowed activities include farming, rainwater harvesting, organic farming, and renewable energy use.
- Prohibited activities in ESZs include mining, sawmills, polluting industries, hydroelectric projects, commercial wood use, hot-air balloon tourism, and waste dumping.
- Activities such as constructing hotels, utilizing natural water bodies, installing cables, implementing heavy technologies, and expanding roads are regulated in Ecologically Sensitive Zones (ESZs) to reduce environmental impact.
These guidelines ensure that ESZs strike a balance between conservation efforts and the livelihoods of local communities. By regulating harmful activities and promoting sustainable practices, ESZs aim to enhance the environmental quality and preserve biodiversity in sensitive areas.
Why Eco Sensitive Zones in News?
Recently, the Union Minister of Environment, Forest and Climate Change announced plans to file a review petition in the Supreme Court. The petition aims to reconsider the court’s directive on eco-sensitive zones (ESZs).
In June 2022, the Supreme Court ruled that every protected forest, national park, and wildlife sanctuary in India must have a mandatory ESZ of at least one kilometer from their boundaries. This decision stemmed from a petition focused on safeguarding forest lands in Tamil Nadu’s Nilgiris district.
The Ministry’s move seeks to address concerns and potentially revise the implementation of ESZs nationwide, reflecting ongoing debates over conservation measures and sustainable development practices.
Also Read: Climate Map of India
Activities Allowed in ESZs
The activities permitted within ESZs are strictly regulated to ensure minimal ecological impact. Here’s a brief overview:
| Allowed Activities | Restricted Activities |
| – Non-destructive recreational activities | – Commercial mining |
| – Eco-friendly tourism | – Major construction projects |
| – Sustainable agriculture | – Large-scale industrial activities |
| – Research and education activities | – Polluting industries |
Significance of ESZs
ESZs play a crucial role in:
- Conservation: Protecting endangered species and habitats.
- Biodiversity: Maintaining genetic diversity and ecosystem services.
- Climate Resilience: Enhancing resilience against climate change impacts.
Also Read: Earthquake Zoning Map of India
Challenges and Threats to Eco-Sensitive Zones
Despite their importance, ESZs face several challenges:
- Enforcement: Inconsistent enforcement of regulations.
- Conflict: Conflicts between conservationists and local communities.
- Development Pressure: Pressure for economic development conflicting with conservation goals.
Eco Sensitive Zones FAQs
What is an example of an eco-sensitive area?
An example of an eco-sensitive area could be the buffer zone around a national park, set up to protect wildlife and their habitats from human activities.
What are the environmentally sensitive areas?
Environmentally sensitive areas are regions where the ecosystem is fragile and can be easily damaged by human activities such as construction, agriculture, or pollution.
Where are environmentally sensitive areas exist?
Environmentally sensitive areas exist globally, from coastlines and wetlands to mountains and unique habitats rich in plants and animals.
What is allowed in an eco-sensitive zone?
In eco-sensitive zones, activities such as organic farming, low-impact tourism, rainwater harvesting, and renewable energy projects are permitted. However, activities like mining, logging, and industrial pollution are either restricted or prohibited to protect the natural environment and wildlife.









