Table of Contents
The Father of Botany: Botany, the scientific study of plants, has been shaped over centuries by the contributions of many scholars, scientists, and naturalists. However, when it comes to the title “Father of Botany,” one name stands out—Theophrastus.
While many figures have made significant contributions to the field of botany, Theophrastus’s works have had the longest-lasting impact, earning him this prestigious title. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the life, contributions, and lasting legacy of Theophrastus, along with the figures who also played essential roles in shaping the field of botany.
Who is the Father of Botany?
The title “Father of Botany” is often attributed to Theophrastus, a Greek philosopher who lived during the 4th and 3rd centuries BCE. He is recognized for his groundbreaking work in the systematic study of plants. Theophrastus was a student of Aristotle, and after Aristotle’s death, Theophrastus became the head of the Lyceum, a philosophical school in Athens.
His contributions to botany are so significant that even today, centuries later, many consider his works foundational to the field. Although botany has evolved considerably over the years, Theophrastus’s classification methods and observations laid the groundwork for many subsequent developments in plant science.
Early Life of Theophrastus
Theophrastus was born in Eresos, a city on the island of Lesbos in Greece, around 371 BCE. His early education under the tutelage of Aristotle had a significant influence on his intellectual development. While Aristotle made contributions to various branches of philosophy and science, it was Theophrastus’s interest in plants that led him to explore botany in depth.
Theophrastus’s studies were influenced by Aristotle’s work on the natural world, particularly the classification of animals. However, Theophrastus expanded upon this foundation by focusing on plants. His work marked a shift from mythological and philosophical explanations of plants to a more empirical and systematic approach.
Theophrastus’s Contributions to Botany
Theophrastus made a series of groundbreaking observations and contributions that would shape the future of botany. His two most famous works—“Enquiry into Plants” (Historia Plantarum) and “On the Causes of Plants”—offered detailed descriptions of plant anatomy, classification, and their role in the natural world.
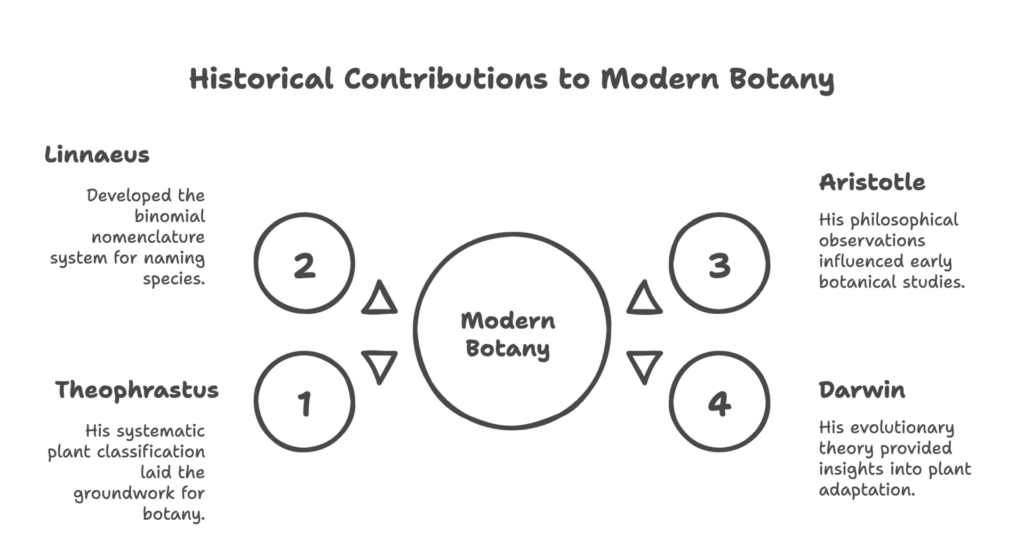
- Plant Classification: Theophrastus is credited with establishing one of the earliest systems of plant classification. He categorized plants based on their structure, uses, and habitats. While his classification system was rudimentary by today’s standards, it laid the foundation for later botanists, such as Linnaeus, to refine and formalize plant classification systems.
- Plant Physiology and Growth: Theophrastus studied plant growth and reproduction. He was among the first to describe the process of germination and the role of the soil in plant health. His observations on plant behavior under various environmental conditions were groundbreaking.
Theophrastus’s Legacy in Botany
The Foundations of Modern Botany
Theophrastus’s systematic approach to plants marked the beginning of botany as a scientific discipline. By organizing and categorizing plants based on observable characteristics, he created a framework that future botanists could build upon. His work provided the first comprehensive text on plant biology, influencing generations of scholars in Europe and beyond.
Theophrastus’s Impact on Plant Classification
One of Theophrastus’s most important contributions was his attempt to classify plants into different groups based on their morphology (structure) and uses. For instance, he categorized plants into trees, shrubs, and herbs, laying the groundwork for modern plant taxonomy. While the modern classification system, based on the binomial nomenclature system developed by Linnaeus, is more refined, Theophrastus’s early efforts were a vital step toward organizing the plant kingdom.
Other Important Figures in the History of Botany
Linnaeus: The Father of Modern Taxonomy
Carl Linnaeus, a Swedish botanist from the 18th century, is often called the Father of Modern Taxonomy. Linnaeus is best known for developing the binomial nomenclature system, which assigns each species a two-part Latin name (genus and species). This system has become the universal standard for naming plants and animals.
Aristotle: The Philosopher Botanist
Aristotle, the Greek philosopher, made important early contributions to biology and botany. Though he was not primarily a botanist, his works laid the intellectual foundation for the study of plants. Aristotle’s observations on plant life in his book “History of Animals” were pivotal in shaping the later development of botany.
Darwin: The Theory of Evolution and Botany
Charles Darwin, the British naturalist, revolutionized biology with his theory of evolution by natural selection. While Darwin’s primary focus was on animal life, his ideas had a profound impact on plant biology. Darwin’s work provided insight into how plants evolved in response to environmental pressures, expanding our understanding of plant growth, reproduction, and adaptation.
Theophrastus’s Works and Their Influence
“Enquiry into Plants”
Theophrastus’s most important work, “Enquiry into Plants”, was a comprehensive study of plant life, covering over 500 species. This work provided detailed descriptions of plant structure, classification, and medicinal uses. It also included observations on plant growth and the impact of environmental factors, such as soil type and climate, on plant health.
“On the Causes of Plants”
In “On the Causes of Plants”, Theophrastus explored the reasons behind plant growth and reproduction. He attempted to explain the mechanisms of plant life, including the role of water, soil, and sunlight in fostering healthy plants. Though his theories were rudimentary, they laid the groundwork for future investigations into plant physiology.
Theophrastus’s pioneering work in botany has had a lasting impact on the study of plants. His early contributions to plant classification, growth, and reproduction continue to influence modern botany. However, botany is a field that has evolved significantly over the centuries, with key figures like Linnaeus, Darwin, and Aristotle making critical contributions. Together, these scholars have shaped our understanding of the plant world, and their collective work forms the foundation of modern plant science.
Understanding the history of botany, from Theophrastus to contemporary scientists, helps us appreciate the scientific method and the importance of systematic observation. Whether you are a student of botany or simply curious about the natural world, these historical figures have given us the tools to explore and appreciate the fascinating world of plants.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) “Father of Botany”
Who is known as the Father of Botany?
Theophrastus is widely recognized as the Father of Botany for his foundational contributions to the systematic study of plants. His works on plant classification and physiology paved the way for future botanists
Why is Theophrastus considered the Father of Botany?
Theophrastus is considered the Father of Botany because he was the first to approach the study of plants in a scientific, systematic manner. His classifications of plants and detailed observations on plant growth laid the foundation for modern botany.
What was Linnaeus's contribution to botany?
Carl Linnaeus, known as the Father of Modern Taxonomy, developed the binomial nomenclature system, which standardized the naming of plant and animal species. His work built upon Theophrastus’s ideas but created a more structured and universally accepted system.
How did Darwin influence the study of botany?
Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection had a significant impact on plant biology. His work showed how plants adapt to their environment over time, influencing the study of plant evolution and ecology.
What is the difference between Theophrastus’s work and Linnaeus’s work in botany?
Theophrastus laid the foundational groundwork for plant classification, while Linnaeus refined and formalized these ideas into a standardized system. Linnaeus’s binomial nomenclature system made plant identification and classification much easier and more consistent globally.
Who is the father of botany?
The father of botany is Theophrastus, a Greek philosopher and student of Aristotle, who lived around 371–287 BC. He is credited with founding botany as a scientific discipline due to his extensive studies on plants, their structure, growth, and classification. His works, such as Enquiry into Plants and On the Causes of Plants, laid the foundation for the study of plant biology, providing valuable insights into plant species and their functions.
Who is the father of botany, and what is the history behind him?
Theophrastus, often referred to as the father of botany, was a Greek philosopher and botanist from ancient Greece. He succeeded Aristotle in leading the Lyceum, a school in Athens. Theophrastus made significant contributions to the study of plants, systematically documenting their properties, growth patterns, and medicinal uses. His pioneering work in cataloging plant species and classifying them according to their medicinal and morphological properties marked the beginning of modern botany.
Who is the father of botany in India?
In India, Sir Jagdish Chandra Bose is often recognized as a prominent figure in the field of botany. While Theophrastus is considered the father of botany globally, Bose made significant advancements in the study of plant physiology, particularly plant response to stimuli. His experiments in the early 20th century, which demonstrated that plants have life and respond to external factors, greatly influenced modern plant science.
What did Theophrastus contribute to botany?
Theophrastus made groundbreaking contributions to botany, such as: Classification of Plants: He classified plants based on their medicinal and morphological features. Plant Anatomy: His studies led to the identification of plant structures like leaves, roots, and stems. Ecology: Theophrastus wrote about the ecological conditions needed for various plants to thrive. His two major works, Enquiry into Plants and On the Causes of Plants, laid the groundwork for plant biology and were influential for centuries.
How did Theophrastus contribute to botany?
Theophrastus contributed to botany by: Providing Detailed Descriptions of Plants: His writings detailed over 500 plant species, including trees, shrubs, and herbs. Developing Plant Classification: He categorized plants by their uses and forms, which influenced future botanical classifications. Introducing Plant Studies into Scientific Inquiry: His work bridged the gap between philosophy and science, making botany a more systematic field of study.
What were the main achievements of Theophrastus in botany?
The main achievements of Theophrastus in botany include: Development of Plant Classification Systems: He was one of the first to classify plants systematically based on their physical features and uses. Study of Plant Growth: He studied how plants grow and reproduce, laying the foundation for plant physiology. Work on Medicinal Plants: He documented the medicinal uses of various plants, a vital contribution to ancient medicine and modern pharmacology.
Why is Theophrastus called the father of botany?
Theophrastus is called the father of botany because his systematic studies of plants and their classification laid the foundation for modern botany. His works, particularly Enquiry into Plants, were the first to document plant life in such detail and serve as a guide for future plant scientists.
What is Theophrastus's legacy in botany?
Theophrastus's legacy in botany is immense. His writings were the primary source of botanical knowledge for over a thousand years, influencing scholars in ancient and medieval times. His system of classification influenced later naturalists and botanists, and his approach to plant study paved the way for the modern field of plant biology.
How did Theophrastus’s work shape modern botany?
Theophrastus’s work shaped modern botany by introducing the concept of classifying plants based on their observable features. His detailed observations on plant growth, reproduction, and ecology laid the groundwork for botanical taxonomy and plant physiology. His studies inspired generations of botanists to adopt a more scientific approach to understanding plant life.
Is Aristotle the father of botany?
No, Aristotle is not considered the father of botany. Although Aristotle made significant contributions to many fields, including biology, his studies were more focused on animals and general philosophy. Theophrastus, his student, is recognized as the father of botany due to his specific focus on plants and their classification.
Who is known as the father of modern botany?
Carl Linnaeus, a Swedish botanist, is often considered the father of modern botany. Linnaeus developed the binomial nomenclature system, which is still used today for naming species. His work revolutionized the classification of plants and animals, providing a more structured and universally accepted system.
What is the difference between Aristotle and Theophrastus in botany?
Aristotle and Theophrastus had different focuses within the realm of natural history: Aristotle: Focused primarily on animal biology and general philosophy. He laid the foundation for biological classification but did not specialize in plants. Theophrastus: As Aristotle’s student, Theophrastus specialized in the study of plants. His detailed classifications and studies of plant growth, reproduction, and anatomy made him the father of botany.
What is the significance of Theophrastus in the context of botany?
Theophrastus is significant in the context of botany because he was the first to systematically study and categorize plants. His contributions to plant classification, plant physiology, and ecological studies formed the basis of future botanical research. His work influenced generations of scholars and laid the foundation for modern botany.
Why is Theophrastus important to the history of botany?
Theophrastus is important to the history of botany because his work marked the beginning of botany as a scientific discipline. His classifications and studies on the structure and function of plants helped transform botany from a collection of folklore into a more systematic and scientific study of plant life.
How did Theophrastus impact the study of plants and nature?
Theophrastus had a lasting impact on the study of plants and nature by: Establishing early principles of plant classification and taxonomy. Encouraging the study of plant life from a scientific perspective rather than purely medicinal or philosophical. Influencing the development of plant biology and ecology through his observations on plant growth, reproduction, and environment.
What are the five branches of botany?
Botany is the scientific study of plants, and it has several specialized branches, each focusing on different aspects of plant life. The five primary branches of botany are: Plant Physiology: This branch studies how plants function, including processes such as photosynthesis, respiration, and nutrient uptake. It focuses on understanding the internal mechanisms of plant growth and development. Plant Ecology: This branch examines the relationship between plants and their environment. It studies plant distribution, abundance, and how plants interact with other organisms and environmental factors like soil, climate, and water. Plant Taxonomy: Plant taxonomy is the classification and naming of plants. It organizes plant species into hierarchical categories based on shared characteristics, helping scientists identify, describe, and study plant diversity. Plant Genetics: This branch investigates the genetic makeup of plants, including inheritance patterns and how traits are passed down through generations. It plays a significant role in plant breeding and genetic modification. Plant Pathology: Plant pathology focuses on the study of plant diseases caused by pathogens such as fungi, bacteria, viruses, and nematodes. It helps in understanding the spread of diseases and developing methods for disease management.









