Table of Contents
Father of Chemistry is Antoine Lavoisier, a French scientist whose work laid the foundation for modern chemistry. Lavoisier’s contributions to the field were groundbreaking, and his discoveries transformed chemistry from a branch of alchemy, filled with theories and guesswork, into a precise, scientific discipline based on experimentation and observation.
Born in 1743, Lavoisier was a brilliant mind who focused on the study of matter and its changes. He is most famous for his work on the law of conservation of mass, which states that matter cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. This idea was revolutionary at the time and challenged earlier beliefs that substances could be transformed or disappear during chemical reactions. Lavoisier’s experiments showed that the total mass of substances before and after a chemical reaction remains the same, which was a fundamental concept in understanding chemical processes.
One of his most significant achievements was the discovery of oxygen’s role in combustion. Prior to Lavoisier’s work, people believed in the phlogiston theory, which stated that a substance called “phlogiston” was released during burning. Lavoisier disproved this theory by showing that oxygen is what supports combustion. This discovery not only changed the way people understood fire but also led to the development of the concept of oxidation, which is still a key idea in chemistry today.
Lavoisier also helped create the modern system of chemical nomenclature, giving scientists a standardized way to name chemicals based on their composition. He identified and named both oxygen and hydrogen, two of the essential elements that make up many compounds. His work in organizing elements and compounds helped chemistry evolve into a more systematic and predictable science.
Because of these contributions, Lavoisier earned the title of Father of Chemistry. His work influenced countless scientists who came after him, and his theories are still taught in schools around the world today. Despite his tragic death in 1794, Lavoisier’s legacy continues to shape the study of chemistry, making him one of the most important figures in the history of science.
Why is Antoine Lavoisier Called the Father of Chemistry?
Antoine Lavoisier is often referred to as the Father of Chemistry because of his many pioneering contributions to the development of chemical science. Some of his most important achievements include:
- The Law of Conservation of Mass: Lavoisier is credited with formulating the law of conservation of mass, which states that matter can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. This fundamental principle was revolutionary, as it established the basis for modern chemical reactions.
- Identification of Oxygen: Lavoisier played a crucial role in the discovery of oxygen and its importance in combustion. Prior to his work, scientists mistakenly believed that fire was caused by a substance called phlogiston. Lavoisier disproved this theory by showing that combustion required oxygen, which was essential for the process.
- The Development of the Metric System: Lavoisier was involved in the development of the metric system, a standardized system of measurements that would later be used worldwide. This system was instrumental in the progress of scientific experiments and precision in chemical research.
- The Concept of Chemical Reactions: Lavoisier was one of the first to describe chemical reactions in terms of the interaction of elements. He showed that in chemical reactions, the reactants combine to form products in a fixed ratio.
These achievements make Lavoisier the figure most commonly associated with the birth of modern chemistry.
Do Check: 10 Interesting Facts about Chemistry
Who is the Father of Modern Chemistry?
The term Father of Modern Chemistry is commonly used to describe Antoine Lavoisier due to his transformative work in the field. Lavoisier’s contributions brought chemistry from a mystical and speculative subject into a rigorous, scientific discipline. His systematic approach to conducting experiments, collecting data, and deriving conclusions laid the groundwork for chemistry as we know it today.
Who is the Father of Chemistry in the World?
As discussed earlier, Antoine Lavoisier is widely considered the Father of Chemistry in the World because of his immense contributions to the scientific field. His theories and discoveries changed the way scientists viewed the chemical processes that take place in nature. He was instrumental in the development of chemical nomenclature, the process of naming chemicals, which is still used in the field today.
Father of Chemistry in India
In India, the title of Father of Chemistry is often attributed to Acharya Prafulla Chandra Ray, a prominent Indian chemist who made significant contributions to the field of chemistry in the early 20th century. Ray is best known for his work on the chemistry of compounds, particularly for his discovery of mercurous nitrate and his contributions to the study of the chemical properties of various elements.
Acharya Ray also established the first Indian chemical company, Bengal Chemicals and Pharmaceuticals, which played a pivotal role in the development of the Indian pharmaceutical industry. His work and vision for science in India earned him the title Father of Indian Chemistry.
Father of Organic Chemistry
While Antoine Lavoisier made crucial contributions to the birth of chemistry as a scientific discipline, the Father of Organic Chemistry title is often given to Friedrich Wöhler. In 1828, Wöhler synthesized urea, an organic compound, from ammonium cyanate, which disproved the theory that organic compounds could only be produced by living organisms. This was a pivotal moment in chemistry that helped define the field of organic chemistry.
Father of Inorganic Chemistry
The title of the Father of Inorganic Chemistry is frequently attributed to Jöns Jakob Berzelius, a Swedish chemist. Berzelius was instrumental in developing the modern system of chemical notation and identifying elements like silicon and thorium. His contributions were foundational in distinguishing between organic and inorganic chemistry, and his work on atomic weights paved the way for future chemical theories.
Who is Called the Father of Chemistry?
When someone asks Who is called the Father of Chemistry? the answer is Antoine Lavoisier. His systematic approach to scientific experimentation, his identification of oxygen, and his work on the law of conservation of mass all solidified his place in history as the Father of Chemistry.
Who is Known as the Father of Chemistry?
Antoine Lavoisier is known globally as the Father of Chemistry. His rigorous methods of research and his discoveries about the nature of chemical reactions and elements established him as one of the most influential figures in the history of science.
Father of Physics and Chemistry
Lavoisier is also known for his contributions to physics in addition to chemistry. He collaborated with scientists of his time, including Pierre-Simon Laplace, to explore the relationship between heat, energy, and chemical reactions. Though his work on physics was overshadowed by his chemical studies, his holistic approach to science helped to bridge the gap between different scientific fields.
Who is Known as the Father of Modern Chemistry?
As we discussed earlier, Antoine Lavoisier is universally recognized as the Father of Modern Chemistry. His contributions were pivotal in transitioning chemistry from the alchemical practices of earlier centuries to the scientific discipline it is today. By advocating for systematic methods of experimentation and data collection, he set the stage for later chemists to build on his work.
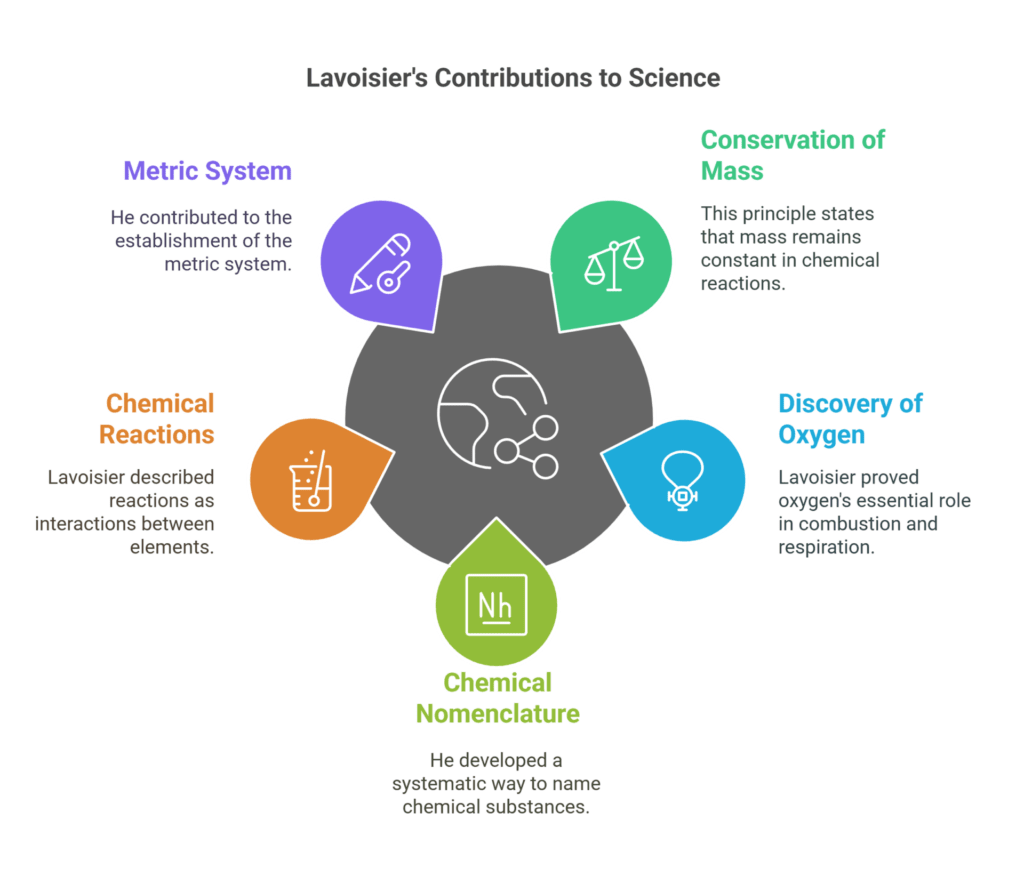
The Impact of Lavoisier’s Work
Lavoisier’s work impacted not just chemistry but also influenced other branches of science. His insistence on precision and experimentation became a model for future generations of scientists. Here is a table summarizing his major contributions:
| Contribution | Explanation |
| Law of Conservation of Mass | Matter cannot be created or destroyed in chemical reactions. |
| Discovery of Oxygen | Proved that oxygen was essential for combustion and respiration. |
| Chemical Nomenclature | Created a system for naming chemicals that is still used today. |
| Understanding of Chemical Reactions | Described chemical reactions as interactions between elements. |
| Metric System Development | Contributed to the establishment of the metric system for scientific measurement. |
Legacy of Lavoisier
Lavoisier’s legacy is immense, and his work paved the way for later discoveries in chemistry, biology, and physics. His approach to science — using experiments, measurements, and observation — became the standard method for scientific inquiry. His groundbreaking research continues to influence chemistry education and practice around the world today.
Conclusion
Antoine Lavoisier’s work is foundational to the development of modern chemistry. His discoveries revolutionized the way we understand the natural world, particularly with the identification of oxygen, the law of conservation of mass, and the creation of a chemical nomenclature system.
Whether you are asking Who is the father of chemistry? or Who is the father of modern chemistry? the answer remains the same: Antoine Lavoisier. His contributions laid the groundwork for all the subsequent advancements in chemical science, from organic chemistry to inorganic chemistry.
In India, the contributions of scientists like Acharya Prafulla Chandra Ray are equally important, as they established a unique legacy in Indian chemistry. From the father of chemistry to the father of modern chemistry and organic chemistry, the legacy of these scientific pioneers lives on.
FAQs on Father of Chemistry
Who is the father of chemistry?
Antoine Lavoisier is considered the father of modern chemistry. He discovered the law of conservation of mass and helped develop the theory of combustion.
Who is the father of human chemistry?
John Dalton is often called the father of atomic theory, which is an important part of human chemistry, as it helped explain how matter interacts at the molecular level.
Who is the father of history in chemistry?
Jons Jacob Berzelius is considered the father of the history of chemistry because of his work in developing modern chemical symbols and atomic weights.
रसायन शास्त्र के जनक कौन है?
रसायन शास्त्र के जनक आंट्वाइन लवोज़ीयर (Antoine Lavoisier) को माना जाता है।
मानव रसायन का जनक कौन है?
जॉन डाल्टन (John Dalton) को मानव रसायन का जनक कहा जाता है।
Who is king of chemistry?
Dmitri Mendeleev, the creator of the periodic table, is often referred to as the 'king of chemistry' due to his significant contributions.
Who is father of Indian chemistry?
Prafulla Chandra Ray is known as the father of Indian chemistry for his work in the field of chemistry and his contributions to science in India.
Who is called God of chemistry?
Marie Curie is often referred to as the 'God of Chemistry' because of her groundbreaking research in radioactivity.
Who is the father of science?
Galileo Galilei is often considered the father of modern science for his contributions to physics, astronomy, and the scientific method.