Table of Contents
Meristematic tissue is defined as those plant tissues that can divide throughout its life. The term meristem was coined by Carl Wilhelm von Nageli. The meristematic tissues contain undifferentiated cells. They are building blocks of specialized plant structures. The meristematic tissues are responsible for the growth of the plant. The cells in this divide actively, giving rise to new cells constantly.
Meristematic tissue cells divide continuously to generate specialized structures such as leaf and flower buds, root and shoot tips, and so on. These cells help the plant grow in length and width.
Characteristics of Meristematic Tissue
Meristematic tissues are responsible for the growth of the plant. Here are some key characteristics of the meristematic tissues.
- Meristematic tissues are small, undifferentiated, non-specialized cells. They are capable of continuous division of cells forming new ones.
- The primary cell walls of these meristematic tissues are thin, and composed of cellulose.
- Hence, these facilitate cell division and growth.
- Cells have a dense cytoplasm with few vacuoles, or sometimes no vacuoles at all. This leads to active cell division.
- The cells of meristematic tissues have a large, prominent nucleus that controls the rapid division of cells.
- Cells have a dense cytoplasm with few vacuoles, or sometimes no vacuoles at all, allowing for active cell division.
- Each cell has a large, prominent nucleus that controls the rapid division of cells.
- Meristematic cells lack large vacuoles, due to their need for rapid cell division.
- Cells of the meristematic tissues are constantly dividing, leading to mitosis. This helps in girth increase of the plants.
- Since meristematic cells have the property of dividing continuously, they have larger nuclei than cytoplasm.
Do Check: Meristems Activity
What are the types of meristematic tissues?
Meristematic tissues are of different types namely – pro meristem, primary meristem, and secondary meristem. Let us know them in detail going further.
Promeristem
- Known as the youngest and earliest meristematic tissue.
- These tissues originate from the embryo.
- Found in the roots and shoots of the plant.
Primary meristem
- It arises from pro meristem.
- Here cells divide actively forming new cells.
- It is present below the pro meristem.
- After maturing it forms the permanent tissue.
Secondary meristem
- The origin of this tissue is from the primary meristem.
- Permanent tissue forms the secondary meristem further.
Also Check: Apical Meristem
Meristematic Tissue Based on Position
Meristematic tissues differ based on their different position on the plant. Let us check out the different meristematic tissues based on position.
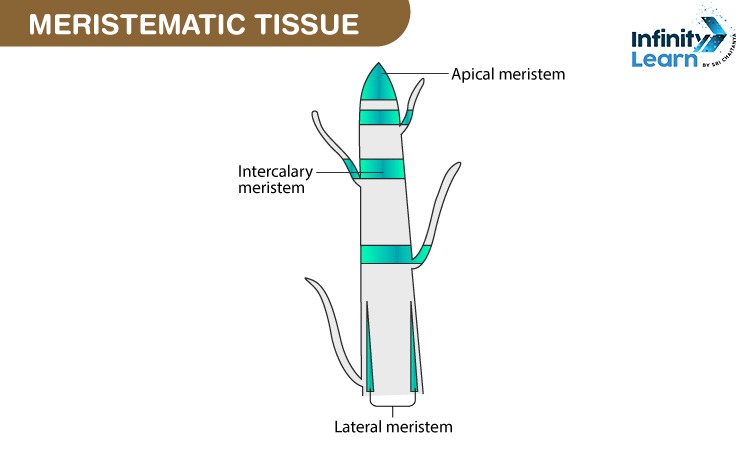
Apical meristem
These meristem tissues are present at the roots and tips of the plant to provide growth to the plants.
Apical meristem is divided into 2 zones.
- They are as follows- Promeristem zone, which contains actively dividing cells.
- The meristematic zone, contains protoderm, procambium and ground meristem.
- Various cells divide and facilitate the growth of the cells in the root and shoot of the plant.
Intercalary meristem
This meristem is located along the sides of stems and roots and helps in increasing the length of the internode.
- They can be found in the grass, monocots, and pines.
- It is a part of the apical meristem and adds to the height of the plant.
- They are usually present at the leaves and internodes at the intercalary position.
Lateral meristem
These meristems divide preclinically or radially and give rise to secondary permanent tissues.
- They are located in the stems and roots on the lateral side.
- Responsible for increasing the width or thickness of the plant.
- Examples include the vascular cambium and cork cambium.
FAQs on Meristematic Tissue
What is meristematic tissue?
Meristematic tissue consists of small and undifferentiated plant cells that continuously divide to produce new cells, hence the growth of the plant.
What are the types of meristematic tissue?
The three types are apical meristem, lateral meristem, and intercalary meristem
What is the main function of meristematic tissue?
Its primary function is to promote plant growth through cell division. It helps in increasing the length and thickness of the plant parts.
Why do meristematic cells have large nuclei?
The large nuclei control the rapid division of cells, which is an important factor for continuous plant growth.
Can meristematic tissue differentiate into other tissues?
Yes, meristematic cells can differentiate into various specialized tissues like xylem, phloem, and epidermis.









