NCERT Solutions for sophistication 8 science Chapter 7 – Weavers, Iron Smelters and Factory Owners
INFINITY LEARN NCERT Solution Class 8 Science Chapter 7 has all the specified explanations to the exercise questions. the fabric provides all the topics from the category 8 SST History Chapter 7 within the arranged form to form learning easy for all students. Students who find topics complicated to know can use NCERT Solution and understand the concepts easily. NCERT Solutions for sophistication 8 science Chapter 7 provides all the important questions which require to be focused on from the exam point of view. All the details are highlighted which makes learning easy for college kids. the fabric prepares students to try to do their best within the exams.
You can also download NCERT Solutions for sophistication 8 Maths and NCERT Solution for sophistication 8 Science to assist you to revise the complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
What kinds of cloth had a large market in Europe?
Ans: Chintz (chhint), Cossaes (Khassa) and Bandanna.
2. What is Jamdani?
Ans: Jamdani is a fine muslin on which decorative motifs are woven on the looms, typically in grey and white colours.
3. What is bandanna?
Ans: Bandana is a brightly coloured and printed scarf for neck and head.
4. Who are the Agarias?
Ans: Women and men who carried basket loads of iron ore on their heads were called Agarias in Chattisgarh.
5. Fill in the blanks:
(a) The word chintz comes from the word _________.
ANS. chintz
(b) Tipu’s sword was made of_________ steel.
ANS. Wootz
(c) India’s textile exports declined in the _________ century.
ANS. 19th
6. How do the names of different textiles tell us about their histories?
Ans:
i) European traders first saw fine cotton cloth from india in Mosul in present day Iraq. They referred to all finely woven textiles as “Muslin”.
ii) Portuguese first came to India in search and landed in Calicut on the Kerala coast in South- west India. They took back cotton textiles to Europe, along with the spices. They named it “Calico”. Subsequently Calico became the general name for all cotton textiles.
iii) Many other words point to the popularity of Indian textiles in Western markets.
iv) The printed cotton clothes called Chintz, Cossaes and Bandhana.
v) From the 1680s there started a craze for printed Indian cotton textiles in England and Europe mainly for their floral designs, fine texture and relative cheapness. Rich people of England including the Queen herself wore clothes of Indian fabric.
vi) Bandanna is a brightly coloured and printed scarf for the neck or head. This term was derived from the word “Bandhana” (Hindi for tying).
vii) Our clothes were known by their place of origin: Kasimbazar, Patna, Calcutta, Orissa, charpoore.
viii) The widespread use of such words shows how popular Indian textiles had become in different parts of the world.
7. Why did the wool and silk producers in England protest against the import of Indian textiles in the early eighteenth century?
Ans: Indian woolen and silk textiles were very popular in England.
Textile industry had just begun to develop in England in the early 18th century. The wool and silk producers in England found themselves unable to complete with Indian textiles. They wanted to secure market within the country by preventing the entry of Indian textiles. Therefore, they protested against its import.
8. How did the development of cotton industries in Britain affect textile producers in India?
Ans:
Cotton industries in Britain developed and adversely affected textile producers in India in several ways.
i) Indian textiles faced competition with British textiles in the European and American markets.
ii) Export of textiles to England became more and more difficult because the British Government imposed high duties on Indian textiles.
iii) In the beginning of the 19th century, cotton textiles made in Britain successfully ousted Indian goods from their traditional markets in Africa, America and Europe.
iv) Thousands of weavers in India were now thrown out of employment.
v) English and Europeans companies stopped to buy Indian goods. Their agents no longer gave out advances to weavers to secure supplies.
vi) Thousands of rural spinner women were rendered jobless.
9. Why did the Indian iron smelting industry decline in the nineteenth century?
Ans: There are several reasons for the decline of iron smelting industry in India during 19th century.
i) The new forest laws of the colonial government prevented people from entering the reserved forests. it became difficult for the iron smelters to find wood for charcoal. Getting iron ore was a big problem. Hence, many gave up their craft and looked for other jobs.
ii) In some areas the government did grant access to the forests. But the iron smelters had to pay a very high tax to the forest department for every furnace they used. This reduced their income.
iii) By the late 19th century iron and steel was being imported from Britain. Iron smiths in India began using the imported iron to manufacture utensils and implements. This inevitably lowered the demand for iron produced by local smelters.
10. What problems did the Indian textile industry face in the early years of its development?
Ans: In the early years of its development the Indian textile industry faced several problems.
i) It found it difficult to compete with the cheap textiles imported from
ii) In most countries, governments supported industrialization by imposing heavy duties on imports. the colonial government in India refused such protection to local industries.
iii) However, during the First World War when textile imports from Britain declined Indian factories were called upon to produce cloth for military supplies. This boosted up cotton factory production in India.
11. What helped TISCO expand steel production during the First World War?
i) Before the First World War India imported British Steel for rails.
ii) When in 1914 the war broke out, steel produced in Britain now had to meet the demands of war in Europe.
iii) Imports of British steel into India declined and the Indian Railways turned to TISCO for supply of rails.
iv) As the war dragged on for several years, TISCO had to produce shells and carriage wheels for the war.
v) By 1919 the colonial governments was buying 90% of the steel manufactured by TISCO.
vi) Over time TISCO became the biggest steel industry within the British empire.
12. Find out about the history of any craft around the area you live. You may wish to know about the community of craftsmen, the changes in the techniques they use and the markets they supply. How have these changed in the past 50 years?
History of Handloom weaving:
- Spinning of thread
- Weaving by Julahas in village
- Sale of the fabric in the local market
- Looms were set up
- Fabric woven for local, national and international markets
- Power looms
- International markets.
Changes in the Past 50 years
- Constitution of All India Handloom board in 1952.
- Government support for the supply of yam, dyes chemicals, etc.
- Encouragement by giving awards.
- Insurance cover against calamities etc.
- On a map of India, locate the centers of different crafts today. Find out when these centers came up.
Ans: 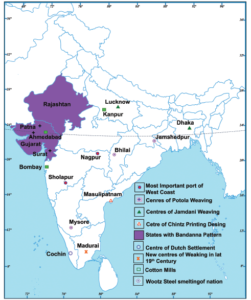
NCERT Solutions for sophistication 8 science History Our Pasts-3 Chapter 7 Weavers, Iron Smelters and Factory Owners
NCERT Solutions for sophistication 8 science Chapter 7 – Free PDF Download
PDF for NCERT Solutions for sophistication 8 science Chapter 7 is out there on INFINITY LEARN website and app. The PDFs are liberal to download from the websites. the category 8 SST Chapter 7 Weavers, Iron Smelters, And Factory Owners provide all the knowledge regarding the chapter and every one the important questions for exam preparations. the fabric is ready in such how that student can ask it for his or her last-minute preparation. All the questions are given in a proper and arranged manner which makes understanding concepts easier.
Chapter 7 – Our Pasts III – Weavers, Iron Smelters, And Factory Owners
NCERT Solutions for sophistication 9 science Chapter 7 – Our Pasts III belongs to the chapter named “Weavers, Iron Smelters and Factory Owners”. The chapter is all about Indian textile and markets. It explains the history of the Indian market and therefore the history of Indian textile history. NCERT Solutions for sophistication 8 science Chapter 7 highlights all the details of the chapter and explains all the topics intimately. the fabric explains the chapter in its simplest form in order that students can learn it easily.
Class 8 science Chapter-wise Marks Weightage
Chapter 7 of Our Pasts III Class 8 is that the most vital and has the very best weightage among all chapters. Since it’s the very best marks weightage, this chapter must be prepared well and for that NCERT Solutions for sophistication 8 Our Pasts III Chapter 7 is that the best. Here are some more details about the NCERT Class 8 History Chapter 7
7.1 Short answer questions. 4 Questions
7.2 Fill in the blanks. 3 Questions
7.3 Long answer questions. 7 Questions
7.4 Locating the centres of different crafts on a map.
7.5 Exercise questions.
7.5.1 Multiple choice questions. 5 Questions
7.5.2 Fill in the blanks. 7 Questions
7.5.3 True or False. 6 Questions
7.5.4 Match the column.
7.5.5 Very short answer-type questions. 17 Questions
7.5.6 Short answer type questions. 8 Questions
7.5.7 Long answer type questions. 2 Questions
Why are NCERT Solutions for sophistication 8 science Chapter 7 important?
NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 7 is that the best material for exam preparations.
- This material contains all the important questions alongside their answers and therefore the best explanations.
- The material provides all the topics of the chapter which are most vital and explains each topic and event intimately.
- All the questions provided within the material are suggested by the simplest subject experts.
- The material is formed in such how that student can give their best within the exam using this material.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q1. In England, the producers of wood and silk began to protest against the import of Indian textiles. What was the reason?
Ans: The Indian market was rising and had begun to send the fabric to England. The Indian textile materials were the simplest and unique which is why they started developing within the early 18th century. The Indian textiles were very strong competitors for wool and silk producers in England. England wool and silk producers weren’t ready to compete with Indian textiles in order that they needed to secure the market. Hence, they started protesting against the import of Indian textiles.
Q2. What were the explanations for the Indian iron smelting industry that wasn’t accepted within the nineteenth century?
Ans: The Indian iron smelting industries were packed up within the nineteenth century due to several reasons. a number of them are as follows:
- The colonial government declared several forests because of the reserved forest. They made a rule of preventing people from entering the reserved forests.
- Even if they got access to enter some forests, they needed to pay very high taxes for using every furnace.
- Later, within the 19th century, iron was imported from Britain. due to this, nobody was curious about buying iron from local smelters.
Q3. What are the advantages of studying from the NCERT Solutions for sophistication 8 History Chapter 7?
Ans: NCERT Solutions for sophistication 8 History Chapter 7 can help students score high marks in school 8 History. NCERT Solutions can help students understand the chapter properly. All answers are available in PDF format and are given in easy and straightforward language in order that students can steel themselves against their exams and obtain high marks. All NCERT Solutions are prepared by expert subject teachers.
Q4. What are the important concepts discussed in Chapter 7 of NCERT Solutions for sophistication 8 History?
Ans: Class 8 History Chapter 7 deals with a spread of topics like the changes brought by the British within the education system of India. British wanted to civilize the people of India by making cultural changes. They wanted to vary the customs and values of individuals in India. NCERT Solutions for sophistication 8 History can help students clear their doubts about the chapter and steel themselves against their exams. The solutions provided by INFINITY LEARN are freed from cost. they’re also available on the INFINITY LEARN Mobile app.
Q5. Who are factory owners?
Ans: In NCERT Class 8 History Chapter 7, India was popular for textiles, iron, and steel industries during British time. British companies gained control over the assembly of textiles and other industries. The factory owners didn’t get their rights. All NCERT Solutions Class 8 science are available on INFINITY LEARN for a straightforward understanding of the concepts.
Q6. Who were the weavers in Class 8?
Ans: Weavers were a category of artisans in India who want to weave beautiful handicrafts using their skills. All information about weavers and craftsmen is out there on INFINITY LEARN. it’s the simplest source for clearing doubts and preparing for the exams. The notes and solutions given on INFINITY LEARN can help students understand the concepts. they will understand all concepts about Class 8 history easily. All solutions are prepared by expert subject teachers.
Q7. Why are the explanations that the Indian iron smelting industry declined within the nineteenth century?
Ans: The Indian iron smelting industry declined thanks to the subsequent reasons:
- High taxes were imposed on the iron smelters by the forest companies.
- Forest authorities also imposed forest laws on Indian smelters thanks to which they weren’t ready to get charcoal which is a crucial component required for iron smelting.
- The British company began to import iron from England. This put an adverse effect on iron smelters to continue with their profession.
Q8. Who was Charles Weld Class 8 history?
Ans: Charles Weld may be a popular personality known within the history of India. He alongside Jamshedji Tata is liable for the establishment of Tata Steel Industries. you’ll get full details about Charles Weld’s history online. Students can NCERT Class 8 History Chapter 7 to urge information about Charles Weld. NCERT Solutions for sophistication 8 History can help students to know the concepts about Class 8 history. Students can download the answers from the INFINITY LEARN website.



