Table of Contents
The ideal study material for students to refer to and prepare their notes for their CBSE Term I test is NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 – Tissues. These NCERT Solutions are organized by chapter, and students may find answers to all of the questions in their NCERT textbooks for Class 9 Science. Students may discover extensive explanations for all topics in this study material, which are given in simple language and include examples, diagrams, and flowcharts in a more accessible style.
Tissues are one of the most essential topics in the CBSE Term I test, according to NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6. The solutions have been curated by the faculty in a clear manner to aid students in understanding the ideas. Students can use the study tools offered at INFINITY LEARN to get a better understanding of the chapter.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science – Tissues
1.What is the utility of tissues in multicellular organisms?
A. i) Tissues are specialised to carry out a particular function at a definite place in the body.
ii) For example, the muscle cells form muscular tissues which helps in movement, nerve cells form the nervous tissue which helps in transmission of messages.
2.Name types of simple tissues.
A. Parenchyma, Collenchyma and Sclerenchyma.
3. Where is apical meristem found ?
A. Apical meristem is present at the growing tips of stems and roots.
4.Which tissue makes up the husk of coconut ?
A. The husk of a coconut is made up of sclerenchyma tissue.
5. What are the constituents of phloem ?
A. Constituents of phloem are :
i) Sieve tubes
ii) Companion cells
iii) Phloem parenchyma
iv) Phloem fibres
6. Name the tissue responsible for the movement in our body.
A. Muscular tissue.
7. Give three features of cardiac muscles.
A. i) Cardiac muscles are involuntary muscles.
ii) The cells of cardiac muscles are cylindrical, branched, and uninucleated.
iii) They show rhythmic contraction and relaxation throughout life.

8.What are the functions of areolar tissue?
A. i) It helps in supporting internal organs.
ii) It helps in repairing the tissues of the skin and muscles.
9.What is a tissue ? (or) Define the term “tissue”.
A. A group of cells that are similar in structure and are organised together to perform a specific task is called a tissue.
10. What does a neuron look like?
A. i) A neuron resembles a small tree with fine hair like structures arising from its terminals.
ii) It consists of a cell body with a nucleus and cytoplasm from which elongated hair like structures emerge.
iii) Each of this neuron consists of axon and dendrites.
11. How many types of elements together make up the xylem tissue ? Name them.
A. Xylem is made up of four types of elements. They are :
i) Tracheids
ii) Vessels
iii) Xylem parenchyma
iv) Xylem fibres
12. How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants ?
A.
| SIMPLE TISSUES | COMPLEX TISSUES |
| i) They are made up of only one type of cells. | i) They are made up of more than one type of cells. |
| ii) The cells of these tissues are more or less similar in structure and perform similar functions. | ii) Different types of cells of these tissues perform different functions. For example, in the xylem tissue, trachieds help in water transport, whereas parenchyma stores food. |
| iii) Three types of simple tissues in plants are parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma. | iii) Two types of complex permanent tissues in plants are xylem and phloem. |
Differentiate between parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma on the basis of their cell wall.
A.
| PARENCHYMA | COLLENCHYMA | SCLERENCHYMA |
| i) Cell walls are relatively thin. | i) The cell walls are irregularly thickened at the corners. | i) The cell walls are uniformly thickened. |
| ii) Cells are loosely packed. | ii) There is very little space between the cells. | ii) There are no intercellular spaces. |
| iii) The cell wall in this tissue is made up of cellulose. | iii) Pectin and hemicellulose are the major constituents of the cell. | iii) An additional layer of the cell wall is composed mainly of lignin. |
14. What are the functions of the stomata?
A. i) Stomata helps in exchange of gases (CO2 and O2).
ii) They also help in the process of transpiration (loss of water from the leaf).
15.Diagrammatically show the difference between the three types of muscle fibres.
A.
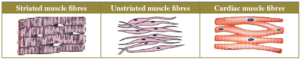
16.What is the specific function of the cardiac muscle?
A. The specific function of the cardiac muscle is the rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the heart.
17. Differentiate between striated, unstriated and cardiac muscles on the basis of their structure and site/location in the body.
A.
| On the Basis of Structure | ||
| Striated muscle | Unstriated muscle | Cardiac muscle |
| Cell are cylindrical | Cells are long | Cells are cylindrical |
| Cells are not branched | Cells are not branched | Cells are branched |
| Cells are multinucleated | Cells are uninucleated | Cells are uninucleated |
| Alternate light and dark bands are present | There are no bands | Faint bands are present |
| Its ends are blunt | Its ends are tapering | Its ends are flat and wavy |
| On the basis of location | ||
| These muscles are present in body parts such as hands, legs, tongue, etc. | These muscles are present in the alimentary canal, blood vessels, etc. | These muscles are present in the heart. |
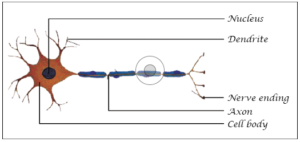
18. Draw a labelled diagram of a neuron.
A.
19. Name the following :
a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth.
b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans.
c) Tissue that transports food in plants.
d) Tissue that stores fat in our body.
e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix.
f) Tissue present in the brain.
A. a) Squamous epithelium b) Tendon c) Phloem
d) Adipose tissue e) Blood f) Nervous tissue
20.Identify the type of tissue in the following :
Skin, bark of tree, bone, lining of kidney tubule, vascular bundle.
A. Skin : Stratified squamous epithelial tissue
Bark of tree : Simple permanent tissue
Bone : Connective tissue
Lining of kidney tubule : Cuboidal epithelial tissue
Vascular bundle : Complex permanent tissue
21. Name the regions in which parenchyma tissue is present.
A. Leaves, fruits and flowers.
22. What is the role of epidermis in plants ?
A. i) It protects all the parts of the plant.
ii) It protects the plant against mechanical injuries.
iii) It allows exchange of gases through the stomata.
iv) This aids in protection against the loss of water.
23. How does the cork act as a protective tissue?
A. i) The outer protective layer or bark of a tree is known as the cork.
ii) It is made up of dead cells. Therefore, it protects the plant against mechanical injury, temperature extremes, etc.
iii) It also prevents the loss of water by evaporation.
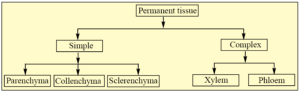
Complete the table :
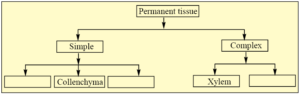
A.
Class 9, Science Chapter 6: Tissue is a fascinating topic that covers everything there is to know about tissue, including varieties of tissue and their functions. The anatomy and physiology of the human body are covered in this topic, which serves as a foundation for the following level. Other topics covered in this chapter include the different types of tissues found in multicellular creatures, their structure, location, and functions. Students can discover some fun activities or experiments on tissues to go along with this lesson.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6: Tissues: Significant Features
- NCERT Solutions are the greatest study materials for students who are having difficulty locating answers to various queries linked to the various disciplines.
- Students can find crucial questions, keynotes, and other information on the topic in addition to the textbook solutions.
- These NCERT Solutions were created by a group of qualified teachers and include all of the chapter’s essential ideas as well as other relevant problems from the perspective of the term test.
- The solutions included in these study materials are well-organized and organized in a methodical manner to allow for comprehensive learning and greater understanding by all pupils.
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6, Tissues, gives comprehensive information on the topic, including definitions and examples that are presented in a clear and understandable manner for students.
What are some of the benefits of using INFINITY LEARN NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6?
- Students who are having trouble obtaining answers to their topics can use INFINITY LEARN NCERT Solutions.
- Students can readily access crucial questions, shortcut approaches, and other information.
- The solutions are created by qualified professors and include all of the fundamental concepts and problems that are crucial for the CBSE Term I exam.
- These solutions are organized in a systematic way that encourages students to learn in-depth.
- Important definitions and examples are presented in an interactive format to make learning enjoyable for pupils.







