Table of Contents
The human heart plays a vital role in our bodies, pumping blood to every part and then back again. Signs of a heart attack, like chest pain, trouble breathing, feeling sick, and sweating, are crucial to recognize.
In classes 10 and 12, understanding the heart’s diagram is important and often tested. You can find a detailed explanation alongside a labeled diagram for studying
For Class 10 students, mastering the structure and function of the heart—including the atria, ventricles, valves, arteries, and veins—is crucial. A well-labelled human heart diagram not only helps visualize these components but also strengthens conceptual clarity for both board exams and practical applications.
Since questions based on the human heart diagram for Class 10 frequently appear in exams, having a clear and easy-to-understand illustration with detailed annotations makes learning more effective and exam-oriented. This topic bridges textbook theory with real-life biological functions, making it one of the most important chapters in Class 10 science.
Also Check: Animal Cell Diagram
What is the Human Heart Diagram?
The human heart diagram is a visual representation of the heart’s structure, showing its different parts, chambers, and the flow of blood through it. It is commonly used in biology textbooks and classrooms, especially in Class 10 and 12, to help students understand how the heart functions as the central part of the circulatory system.
The diagram usually includes:
- Four chambers – two atria (upper) and two ventricles (lower)
- Major blood vessels – such as the aorta, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein, and vena cava
- Valves – that control blood flow (like the mitral valve, tricuspid valve, etc.)
A well-labelled heart diagram makes it easier to understand the direction of blood flow, the oxygenation process, and the role each part plays in maintaining circulation.
How Does the Human Heart Work?
The heart works like a powerful pump that keeps blood moving throughout the body in a continuous loop. Here’s how it works in a simple step-by-step process:
- Oxygen-poor blood from the body enters the right atrium through the superior and inferior vena cava.
- This blood flows into the right ventricle, which pumps it to the lungs via the pulmonary artery.
- In the lungs, the blood receives fresh oxygen and releases carbon dioxide.
- Oxygen-rich blood returns to the heart through the pulmonary veins into the left atrium.
- It then moves into the left ventricle, which is the strongest chamber.
- The left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to the rest of the body through the aorta.
This entire process is called the circulatory cycle, and it happens continuously, keeping every cell in the body alive and functioning.
Labelled Diagram of Heart
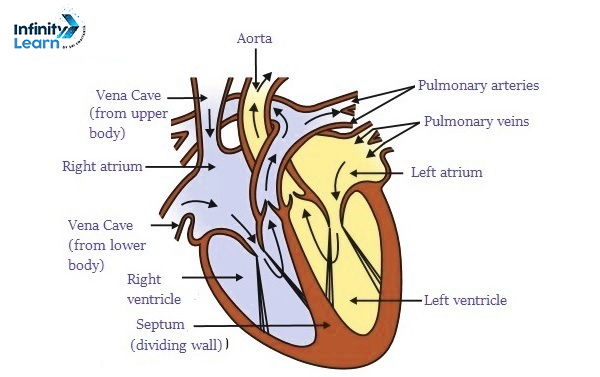
The heart has four parts:
- The top two parts are called auricles.
- The bottom two parts are called ventricles.
- The heart wall has three layers:
- The outside layer is called epicardium.
- The middle layer is called myocardium.
- The inner layer is called endocardium.
- There are four valves in the heart:
- The aortic valve stops blood from flowing back when it moves from the left ventricle to the aorta.
- The mitral valve stops blood from flowing back when it moves from the left atrium to the left ventricle.
- The pulmonary valve stops blood from flowing back when it moves from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery.
- The tricuspid valve stops blood from flowing back when it moves from the right atrium to the right ventricle.
- Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to different body parts. But the pulmonary artery is different; it carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs for cleaning.
- Veins carry impure blood from different body parts back to the heart for oxygenation. But the pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood to the heart.
Why is the Human Heart Diagram Important?
- Helps students visualize internal anatomy
- Useful for understanding the blood circulation process
- Often included in Class 10 and 12 exams
- Builds a strong base for careers in medicine, biology, and health sciences
Human Heart Diagram Class 10 FAQs
What is a human heart with a diagram?
A human heart is a vital organ in the body that pumps blood through the circulatory system.
Which figure is connected to heart?
The figure connected to the heart is the circulatory system, which includes blood vessels like arteries and veins.
Which part is important in heart?
The important part of the heart is the left ventricle, responsible for pumping oxygen-rich blood to the body.
How many chambers does a heart diagram have?
A heart diagram typically has four chambers: two atria and two ventricles.
What does the heart diagram depict?
The heart diagram depicts the structure of the heart and its chambers, showing how blood flows through it.
What is the main function of the heart for kids?
The main function of the heart for kids is to pump blood to all parts of the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients and removing waste.
Why do we need a heart for kids?
We need a heart to stay alive because it pumps blood, delivering oxygen and nutrients to our organs and tissues.
What shape is the human heart for kids?
The human heart for kids is usually depicted as a simple, symmetrical shape, like a rounded triangle or an oval.









