Table of Contents
BODMAS Rule Questions for Class 7
The BODMAS rule, crucial in math, helps solve arithmetic expressions correctly. It means Brackets, Order (powers and roots), Division, Multiplication, Addition, and Subtraction. It guides the order of operations in an expression, ensuring consistent and correct solutions.
Understanding BODMAS is vital for Class 7 students to tackle complex math problems efficiently. First, solve expressions inside brackets, then handle powers or roots. Next, do division and multiplication from left to right. Finally, do addition and subtraction, also from left to right.
What is BODMAS?
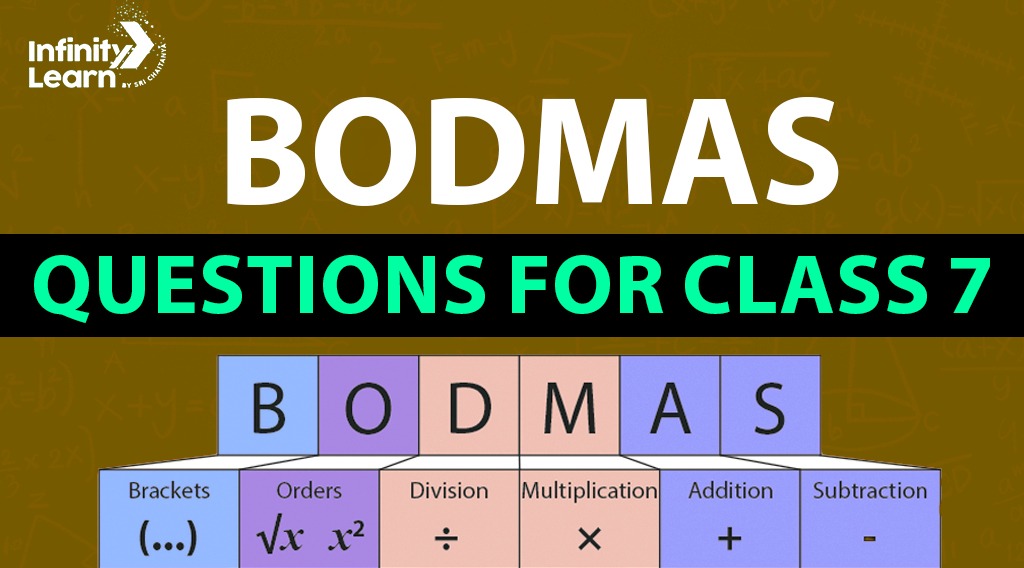
BODMAS is an acronym used in mathematics to remind students of the correct order to perform operations in complex calculations. BODMAS full form is:
- B: Brackets (solve expressions inside parentheses, square brackets, curly braces, etc.)
- O: Order (solve powers and roots)
- D: Division
- M: Multiplication
- A: Addition
- S: Subtraction
The BODMAS rule is crucial because it defines the sequence in which these mathematical operations should be carried out to ensure that everyone arrives at the same answer when solving the same arithmetic expression. It helps prevent confusion and errors in calculations, providing a clear, systematic approach to handling multiple operations.
BODMAS Questions for Class 7 with Solutions
Here are BODMAS questions for class 7 with solutions and topics of BODMAS
Topic 1: Basic Brackets
Understanding how to simplify expressions within brackets first.
- Calculate: 7 + (6 × 3)
- Step 1: Solve inside the brackets first: 6 × 3 = 18.
- Step 2: Add the result to 7: 7 + 18 = 25.
- Solution: 25
- Evaluate: (4 + 3) × 5
- Step 1: Solve inside the brackets first: 4 + 3 = 7.
- Step 2: Multiply the result by 5: 7 × 5 = 35.
- Solution: 35
- Solve: 42 ÷ (7 + 7)
- Step 1: Solve inside the brackets first: 7 + 7 = 14.
- Step 2: Divide 42 by the result: 42 ÷ 14 = 3.
- Solution: 3
Topic 2: Orders and Powers
Handling powers and roots as part of the operations sequence.
- Find the value of: (23) + 6
- Step 1: Calculate the power: 23 = 8.
- Step 2: Add 6 to the result: 8 + 6 = 14.
- Solution: 14
- Determine: (32 + 42)
- Step 1: Calculate each power: 32 = 9 and 42 = 16.
- Step 2: Add the results: 9 + 16 = 25.
- Solution: 25
- Calculate: (6 × (10 – 8)2) ÷ 2
- Step 1: Solve inside the brackets: 10 – 8 = 2.
- Step 2: Calculate the power: 22 = 4.
- Step 3: Multiply 6 by the result of the power: 6 × 4 = 24.
- Step 4: Divide by 2: 24 ÷ 2 = 12.
- Solution: 12
Topic 3: Mixed Operations
Combining multiple operations, emphasizing the correct sequence of BODMAS.
- Compute: 50 – (2 × 15)
- Step 1: Solve inside the brackets: 2 × 15 = 30.
- Step 2: Subtract the result from 50: 50 – 30 = 20.
- Solution: 20
- Evaluate: 100 ÷ (10 × (5 – 3))
- Step 1: Solve inside the inner brackets: 5 – 3 = 2.
- Step 2: Multiply the result by 10: 10 × 2 = 20.
- Step 3: Divide 100 by 20: 100 ÷ 20 = 5.
- Solution: 5
- Solve: 5 + 32 × 2
- Step 1: Calculate the power: 32 = 9.
- Step 2: Multiply the result by 2: 9 × 2 = 18.
- Step 3: Add 5 to the result: 5 + 18 = 23.
- Solution: 23
- Find the value of: 9 × (5 – (3 – 1))
- Step 1: Solve inside the inner brackets: 3 – 1 = 2.
- Step 2: Subtract the result from 5: 5 – 2 = 3.
- Step 3: Multiply 9 by 3: 9 × 3 = 27.
- Solution: 27
- Compute: 2 + 6 × (5 ÷ (2 + 1))
- Step 1: Solve inside the brackets: 2 + 1 = 3.
- Step 2: Divide 5 by 3: 5 ÷ 3 ≈ 1.67.
- Step 3: Multiply 6 by 1.67: 6 × 1.67 ≈ 10.
- Step 4: Add 2 to 10: 2 + 10 ≈ 12.
- Solution: Approximately 12
- Determine: 5 + 32 × 2
- Step 1: Calculate the power: 32 = 9.
- Step 2: Multiply 9 by 2: 9 × 2 = 18.
- Step 3: Add 5 to the result: 5 + 18 = 23.
- Solution: 23
- Calculate: (42) ÷ (8 ÷ 4)
- Step 1: Calculate the power: 42 = 16.
- Step 2: Divide 8 by 4: 8 ÷ 4 = 2.
- Step 3: Divide the result of the power by 2: 16 ÷ 2 = 8.
- Solution: 8
- Evaluate: 2 + 6 × (5 ÷ (2 + 1))
- Step 1: Solve inside the brackets: 2 + 1 = 3.
- Step 2: Divide 5 by 3: 5 ÷ 3 ≈ 1.67.
- Step 3: Multiply 6 by 1.67: 6 × 1.67 ≈ 10.
- Step 4: Add 2 to 10: 2 + 10 ≈ 12.
- Solution: Approximately 12
- Solve: (3 + 5) × 22
- Step 1: Solve inside the brackets: 3 + 5 = 8.
- Step 2: Calculate the power: 22 = 4.
- Step 3: Multiply 8 by 4: 8 × 4 = 32.
- Solution: 32
Tips to Remember BODMAS Rule for Class 7
Here are some tips to help remember and effectively apply the BODMAS rule:
- Understand the Acronym: Memorize what BODMAS stands for—Brackets, Orders (powers and roots), Division and Multiplication, Addition and Subtraction. Remembering this order is crucial as it dictates the sequence in which parts of a mathematical expression should be solved.
- Practice with Brackets: Start by practicing problems that involve different types of brackets like parentheses ( ), square brackets [ ], and curly braces { }. This helps in understanding how to prioritize operations within various types of brackets.
- Master Orders: Ensure you’re comfortable with calculating powers and roots, as these are often where mistakes happen. Use flashcards or apps to drill powers and roots to gain fluency.
- Division and Multiplication: Recognize that division and multiplication have the same priority and are solved from left to right. Practice exercises with mixed division and multiplication to build confidence.
- Sequential Processing: Always work operations from left to right, especially within the same priority level. For example, in expressions involving both addition and subtraction, solve them in the order they appear from left to right.
- Use Mnemonics: Create a catchy phrase or story using the BODMAS acronym to make it more memorable. For instance, “Big Elephants Destroy Mice And Snails” can be used to represent Brackets, Exponents (Orders), Division, Multiplication, Addition, and Subtraction.
- Apply Real-World Problems: Solve real-world problems that require the use of the BODMAS rule. This application helps solidify understanding and shows the practical importance of the rule.
- Error Checking: After solving an expression, revisit each step to ensure that the BODMAS rule was correctly applied. This habit can prevent and correct mistakes.
- Interactive Learning Tools: Utilize online quizzes, games, and interactive tools designed to teach the BODMAS rule. These tools make learning fun and engaging, which can enhance memory and understanding.
- Group Study Sessions: Collaborate with peers in study groups to solve BODMAS problems together. Explaining steps to others and hearing how peers solve problems can reinforce learning and uncover common mistakes.
By following these tips, Class 7 students can gain a strong grasp of the BODMAS rule, leading to greater confidence and accuracy in solving mathematical expressions.
FAQs on BODMAS Questions for Class 7
What is the BODMAS rule for Class 7?
The BODMAS rule for Class 7 helps students solve mathematical expressions accurately by setting the order of operations: Brackets, Order, Division, Multiplication, Addition, and Subtraction.
Who is the father of BODMAS?
BODMAS isn't attributed to a specific 'father' as it is a rule developed over time in mathematics to help ensure consistency in solving arithmetic expressions.
What is the key stage of BODMAS?
The key stage of BODMAS is understanding and applying the correct order of operations when solving mathematical problems, ensuring accuracy in calculations.
What comes first in BODMAS?
In BODMAS, Brackets come first. This means you solve or simplify anything inside brackets before handling other operations.
Which bracket is solved first?
In BODMAS, parentheses or round brackets ( ) are solved first. If there are nested brackets, solve the innermost bracket first and work outward.
What does the O in BODMAS stand for?
The 'O' in BODMAS stands for 'Order'. This refers to powers and roots in expressions, which are handled after solving anything inside brackets.









