Table of Contents
Digestion is crucial as it breaks down complex food into simpler molecules that cells and tissues can absorb easily.
The digestive system is vital for this process. It consists of the alimentary canal and associated glands. The alimentary canal is divided into five main parts: mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine.
The diagram of the human digestive system is helpful for students in Class 10 and 12. It’s a key topic frequently asked in board examinations.
Diagram Of Digestive System
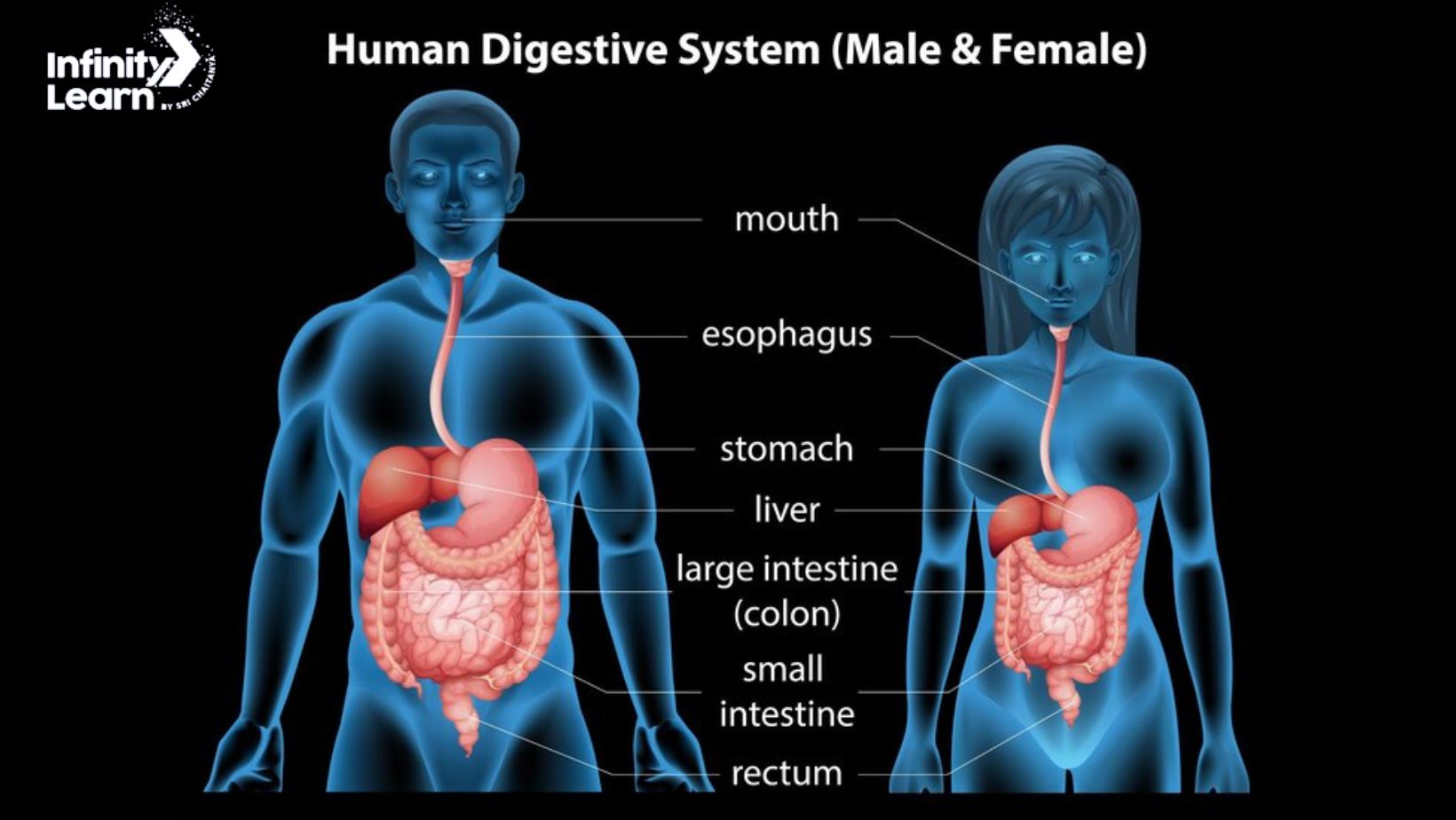
- Mouth: The mouth includes teeth, salivary glands, and the tongue. It’s where digestion begins as teeth break down food and saliva mixes with it.
- Pharynx: This is a tube-like structure connected to the mouth. It helps food move from the mouth to the esophagus.
- Esophagus: A muscular tube about 25 cm long near the trachea. It carries food from the mouth to the stomach.
- Stomach: A hollow, muscular organ on the left side of the abdomen. It stores food, helps digest meals with acids and enzymes, and breaks down food.
- Small Intestine: A long tube behind the stomach, about 9 to 10 feet long. It absorbs nutrients from digested food.
- Large Intestine: A thick tube about 4 to 5 feet long beneath the stomach. It absorbs water and breaks down waste.
- Liver: A large organ on the right side of the stomach. It processes nutrients from the small intestine and produces bile for digesting fats.
Autoclave Diagram | Iron Carbon Diagram
Disorders of the Human Digestive System
- Vomiting: Vomiting means throwing up stomach contents through the mouth.
- Diarrhoea: Diarrhoea is when you have very watery and frequent bowel movements. If it lasts a long time, it can make you dehydrated.
- Constipation: Constipation happens when your bowel movements become irregular, making it hard to pass stool.
- Indigestion: Indigestion causes discomfort or pain in your stomach when food isn’t digested properly. It can make you feel full and is often caused by not enough digestive enzymes, food poisoning, anxiety, overeating, or eating spicy foods.
Human Digestive System Notes
Here are the 6 main steps of digestion:
- Ingestion: Food goes into the alimentary canal and moves through the body.
- Peristalsis: Muscles in the canal walls contract and relax to push the food along.
- Digestion in the Stomach: Food moves to the stomach where it starts to break down.
- Digestion in the Small Intestine: Food is further digested here, and nutrients are absorbed.
- Absorption in the Large Intestine: Water, electrolytes, and vitamins are absorbed here.
- Defecation: Waste is pushed out of the body as stool.
This process helps our body get the energy and nutrients it needs from the food we eat.
Functions of the Human Digestive System
The digestive system has two main jobs: digestion and absorption.
Digestion breaks down food into nutrients. These nutrients give us energy, help repair cells, and make us grow.
Before our bodies can use food and drink, they need to become tiny molecules. These molecules are absorbed into the blood and carried to all parts of the body. The body breaks down nutrients from food and drinks into carbohydrates, vitamins, fats, and proteins.







