Table of Contents
Electrolysis of sodium chloride is a crucial system to fabricate many bulk chemical substances of business application, like chlorine, sodium hydroxide, and so forth. Sodium chloride is electrolyzed either in a molten kingdom or in aqueous solutions. Electrolysis is, additionally done in the presence of additional salts to resource the redox reactions.
Join Our Courses: JEE Class 11 Students | JEE Class 12 Students | JEE Dropper
Electrolysis of Molten Sodium Chloride
Electrolysis includes the motion of ions to the electrode. Solid-kingdom does no longer allows the motion of ions and is incorrect for electrolysis. When melted at excessive temperature, sodium chloride separates into sodium and chloride ions, so that, electrolysis can take location to shape sodium atoms and chlorine gasoline.
NaCl → Na +(l) + Cl–(l)
At cathode: decrease of 2Na+(l) + e-→ Na(l)
At anode: oxidation of 2Cl–(l) → Cl2(g) + 2e–
Net Reaction is composed as: 2Na +(l) + 2Cl-(l) → 2Na(l) + Cl2(g)
Down’s Process:
Sodium chloride melts at a completely high temperature of 801°C. Addition of anhydride calcium chloride within the ratio of CaCl2: NaCl = three:2 reduces the melting factor to 580°C. Electrolysis is achieved with an iron cathode and graphite anode and iron gauze preventing the integration of merchandise chlorine and sodium. The merchandise of molten sodium chloride is sodium steel and chlorine gas.
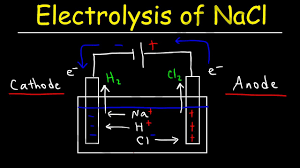
Electrolysis of Aqueous Sodium Chloride
Sodium chloride is dissociated and exists as sodium and chloride ions in an aqueous solution. Electrolysis of sodium chloride is less complicated in an aqueous answer. But, water itself can go through discount and oxidation reactions at distinctive potentials. So, the substance this is oxidized or decreased isn’t sodium and chloride ions on my own however it could involve the water molecule also.
Two competing reactions are viable at each cathode and anode. At Cathode: reduction response: at pH =7
Water may be reduced to hydrogen gas or Sodium ions reduced to sodium metallic.
2H2O(l) + 2e– → H2(g) + 2OH– E° = -1.0 V
Na+(l) + e– → Na(l) E° = -2.71V
At anode: Oxidation reaction: at pH =7. Water may be oxidized to oxygen or chloride ion oxidized to chlorine molecule.
2H2O → O2(g) + 4H+ + 4e– E° =-1.42 V
2Cl– → Cl2 + 2e– E =- 1.36V
Hence, the fabricated from the electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride may be whatever among,
i) sodium metal or hydrogen gasoline at the cathode and
ii) chlorine or oxygen gasoline on the anode,
With a side made from sodium hydroxide on account of the response of sodium and water. The made of electrolysis depends on the awareness of sodium chloride aqueous answer.
A) Very Dilute Aqueous Sodium Chloride Solution
Water has very low conductivity and the small quantity of ionic sodium chloride helps the ionic conductivity of the solution. In small concentrations, the electrolysis of water will become more important yielding hydrogen at the cathode and oxygen at the anode.
At cathode: 2H2O + 2e– → H2(g) + 2OH– E° = -1.Zero V
At anode: 2H2O → O2(g) + 4H+ + 4e– E° = +1.4 V
Net response of electrolysis of exceptionally weakened watery sodium chloride is given as;
2H2O → H2(g) + 2OH– + O2(g) E° = – 2.4 V
b) High Concentration of Sodium Chloride
At Cathode: discount reaction: at pH =7
2H2O(l) + 2e– → H2(g) + 2OH– E° = -1.Zero V
Na+(l) + e– → Na(l) E° = -2.71V
Reduction (over) ability of water being more tremendous than the discount of sodium ions, water is decomposed to free up hydrogen at the cathode.
At anode: Oxidation reaction: at pH =7
2H2O → O2(g) + 4H+ + 4e– E° =-1.4 V
2Cl– → Cl2 + 2e– E =- 1.36V
The thermo-dynamical discount ability of water and chloride is +zero.82V and 0.1.36V respectively. Oxidation of water being greater superb is greater possible and so, the evolution of oxygen gas must show up on the anode. Be that as it may, the development of oxygen from water has an overvoltage of – 0.6V making the voltage for the oxidation of water – 1.4V. Chloride oxidation is greater fantastic than the internet voltage of water oxidation. So, chloride is, oxidized to chlorine on the anode. The internet response taking location is given as;
At cathode – 2H2O(l) + 2e– → H2(g) + 2OH–
At anode – 2Cl– → Cl2 + 2e–
The standard response is as follows;
2H2O(l) + 2Cl– → H2(g) + Cl2 + 2OH–
Or
2H2O(l) + 2NaCl → H2(g) + Cl2 + 2NaOH
At excessive salt concentration, hydrogen and chlorine are made of electrolysis with sodium hydroxide as a via product.
In the Castner-Kellner system, brine (aqueous sodium chloride) is, electrolyzed in a mobile having cubicles. Graphite anode is within the side cubicles and iron cathode is in the vital compartment. Mercury is at the bottom and separates, the two booths and acts as a conduit for wearing sodium shaped at the stop cubicles to the relevant compartment.
Brine, added to the stop compartment is, electrolyzed to sodium and chlorine. While chlorine escapes on the top of the mobile, sodium forms sodium amalgam with mercury at the lowest. Sodium transferred to the critical compartment reacts with water to shape sodium hydroxide and hydrogen.
The fabricated from the electrolysis of concentrated aqueous sodium chloride are sodium hydroxide, hydrogen gasoline and chlorine gas.
Mercury used inside the Caster-Kellner technique contaminates the products and is an environmental chance because of sublimation. Mercury being cancer-causing is backed out for the electrolysis of watery sodium chloride.
Presently all of the Chlor-alkali industries generating chlorine and sodium hydroxide uses a semipermeable membrane ‘Nafion’ to separate the anode and cathode compartments.
Nafion is a sulfonated ionic tetra fluoro-ethylene copolymer. The membrane lets in the sodium ion to waft throughout the membrane into the cathode cell. Additional reinforcing with different semipermeable membranes prevents any returned mixing of incoming chloride and hydroxide ions throughout, Nafion.
C) Electrolysis of Aqueous Sodium Chloride in Intermediate Concentration
At cathode: decrease of water to hydrogen is more plausible than sodium hydrogen. In all aqueous answers discount of water to hydrogen takes location at the cathode as compared to the discount of sodium ion. At anode: The oxidation ability of water and chloride ions are nearly identical (-1.4V and 1.36V respectively).
At better awareness of sodium chloride, chloride oxidation is favoured kinetically, at the same time as at low concentrations oxidation of water to hydrogen is favoured kinetically. At the middle of the road focuses, both water and chloride particles are oxidized. So, both oxygen and chlorine gases evolve at the anode, concurrently.
At Cathode: discount response: at pH =7, 2H2O(l) + 2e– → H2(g) + 2OH–
At Anode: Oxidation response: at pH =7, 2H2O → O2(g) + 4H+ + 4e–
2Cl– → Cl2 + 2e–
Reduction response x three 6H2O(l) + 6e– → 3H2(g) + 6OH–
So, the internet response is;
4H2O(l) + 2Cl– → 3H2(g) + 2OH– + Cl2 + O2
Or
4H2O(l) + 2NaCl → 3H2(g) + 2NaOH + Cl2 + O2
Sodium chloride electrolysis in an aqueous solution yields extraordinary products, relying on the relative awareness of sodium chloride and water. The electrolysis is thermodynamically controlled at very low and excessive concentrations of sodium chloride and kinetically managed at inter-mediatory concentrations.
Do you want to be an IITian? Well, here is the good news. Infinity Learn has a track record of producing 20% IITians every year. Join our specially curated JEE 2024 course to make your IIT dream come true.

JEE Foundation Class for 10
JEE Foundation Class for 10 enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills through engaging activities and advanced learning techniques, ensuring academic excellence.
FAQs
What are the products from the electrolysis of NaCl?
The product of electrolysis of concentrated aqueous sodium chloride are sodium hydroxide, hydrogen gas and chlorine gas.
What is the electrolysis of saltwater?
Electrolysis of Salt Water. In chemistry, electrolysis is a method of separating bonded elements and compounds by passing an electric current through them. An ionic compound, in this case, salt, is dissolved with an appropriate solvent, such as water, so that its ions are available in the liquid.






