Table of Contents
Wattless Current: Considering the wattless current and the definition of inductor or capacitor is connected, the total power consumption will be zero. The wattles current is the current flowing in an electrical circuit where the power consumption is zero.
This type of current is also known as Idle Current. This only happens in an inductive or capacitive circuit. This is due to the fact that in both inductive and capacitive circuits, the voltage and current vary by a factor of 90.
The normal power is based on the cos part, which becomes zero when the distance between them reaches ninety. Hypothetically, we can say that this peculiarity occurs as it streams along the voltage bearing or, every now and then, completely against it, rendering the network zero. Because the network done methodologies is zero, the power also relates to zero, resulting in a Current that is also cradled.
This only occurs in an inductive or capacitive circuit. Voltage and current vary by 90 in both inductive and capacitive circuits. The normal power is based on the cos part, which becomes zero when the distance between them reaches ninety.
Hypothetically, we can say that this peculiarity occurs as it flows along the voltage bearing or, every now and then, completely against it, forming a network. Because the network methodology is zero, the power is also zero, resulting in a Wattless current. This type of electrical current will not drain any energy from the circuit. Wattles’s current is formed in theory when it flows in the opposite direction of voltage or, in rare situations, completely against it, causing it to zero. As networkers approach zero, power will also begin to approach zero, eventually resulting in a Wattless current.
Overview
When there is only a capacitor or inductor in a circuit, power dissipation is zero even though the current is flowing through it. This current is referred to as a wattless current. In a purely inductive or capacitive circuit, this wattless current occurs.
In an alternating current circuit, wattless current occurs when the average power consumed is equal to zero. This type of current is also known as Idle Current. If the average power consumed in the circuit is zero, the current in the alternating current circuit is said to be wattled.
There is no specific formula for wattless current. Wattles’ current is a condition or special case of an alternating current circuit that contains only a capacitor or inductor. However, we can confirm the presence of wattless current by satisfying the condition that total power consumption must equal zero.
This edition is verifiable, but you must know the phase difference between the two sinusoidal waves. When the average power consumed in an alternating current circuit is zero, the current is said to be Wattles Current. This type of current is also known as Idle Current.
If the average power consumed by an AC circuit containing either capacitor or inductor current is zero, the circuit is said to be wattless.
Wattless Current is defined as follows: if the average power used in such a circuit equals zero, the current in an alternating current circuit is said to be Wattless Current. In the case of an alternating current circuit, the average power can be given by
Pav=ErmsIrmscosΦ
It occurs primarily in completely inductive or capacitive circuits. Because the voltage and current in both inductive and capacitive systems vary by a 90-degree angle. In theory, this phenomenon occurs as it moves along or even entirely against the path of voltage, allowing the network to be completed at zero. As a result, as the network nears zero, the energy falls to zero, resulting in a Wattless current. Furthermore, the average one-cycle wattless component is null or zero.
The amplitude of wattless current can be expressed as follows: =iQsin
The transmitted power would be in both directions if the current was displaced by a quarter of a cycle in time from the voltage. As a result, there is no net power transfer, and the current is referred to as wattless. The graph below depicts the flow of power, but the average is zero.
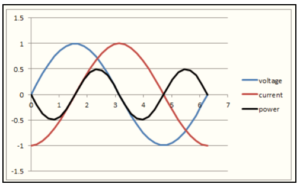
This effect is said to exist because it flows along or even entirely against the path of voltage, allowing the network to operate at zero. As a result, when the network approaches zero, the energy falls to zero, resulting in a Wattless current.
Wattless current formula
A wattless current is an AC current component that consumes no power in a circuit. The equation gives the average power dissipated in an AC circuit.
P=VIcosΦ
The current in an electrical AC circuit is referred to as Wattless Current when it is present in any electrical circuit, more specifically when the circuit consists of only an inductor or capacitor, and the total power consumption is zero. Idle current is another name for wattless current.
Wattles’ current is the current flowing in any electrical AC circuit that contains either a capacitor or an inductor. It is said to be wattless if the average power consumed by the circuit is zero.
The formula for calculating wattless current is as follows:
P=VIcosΦ
The voltage applied to the circuit is denoted by the letter V.
When an electrical circuit consists only of a capacitor or an inductor, the phase difference between voltage and current is π/2.
P=VI cosπ/2
P=VI(0)
=P
=0
The power consumed in an alternating current circuit with only an inductor or a capacitor is zero. This condition is met when the phase difference between voltage and current is ninety. The current flowing through such a circuit is referred to as wattless current. One important point to note here is that an AC circuit consisting only of a capacitor will lead by π/2. phase angle, whereas an AC circuit consisting only of an inductor will lag by π/2 phase angle.
Define wattless current,
In an alternating current circuit, wattless current occurs when the average power consumed is equal to zero. This type of current is also known as Idle Current. If the average power consumed in the circuit is zero, the current in the alternating current circuit is said to be wattled.
Current in a circuit is wattless if,
The current in an alternating current circuit is said to be wattless current if the average power consumed in such a circuit is zero, and such current is also known as idle current. The average power of an alternating current circuit is given by
Pav=ErmsIrmscosΦ
The current in a circuit is wattless if Resistance in the circuit is zero.
Wattles’ current is also known as inactive current. If you don’t put the concepts into practice on a daily basis, you’ll end up like Wattles’s current. Recognize the importance of comprehensive reasoning and cumulative understanding. As a result, the material is designed for easy comprehension and quick learning. The study materials are available for free download in the form of PDFs.
Also, read Power Factor in AC Circuit.
FAQs
What does the Wattless part of the current mean?
Wattless current is also known as inactive current. As we are all aware, the power in a circuit is measured in watts, which is zero in this case; as a result, it is referred to as wattless current. This only happens in simple inductive or capacitive circuits. By circuiting 90, the voltage and current contrast in both inductive and capacitive circuits. Because the average power depends on the cos part, the point between them is ninety.
Where is Wattles's current used, and how is it achieved in an alternating current circuit?
The wattless current is also known as the inactive current. As it stands, the age of wattless flow occurs in simple inductive or capacitive electrical circuits. The wattless flow is produced clearly in an electrical circuit using a single capacitor or inductor.
What is the difference between power factor and wattless current?
Real power in a wattless current is zero, and thus power factor is zero.



