CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 SA2 Science Solved 2016 Set 4
SECTION – A
1. What are cations and anions ?
2. WhatisDNA?
3. Give one example each from your daily life where the domestic waste can be effectively reused and recycled.
4. Why are forest considered “biodiversity hot spots”? List two ways in which an individual can contribute effectively to the management of forests and wildlife ?(HOTS)
5. In a area A, the leaf material available to beetles was very less. What are the two consequencesseen in the beetles ? (HOTS)
6. “A concave mirror of focal length ‘f’ can form a magnified erect as well as an inverted image of an object placed in front of it.” Justify this statement stating the position of the object with respect to the mirror in each case for obtaining these images.
7. What is the difference between the molecules of soaps and detergents, chemically ? Explain the cleansing action of soaps.
8. When we take 1 ml ethanol and 1 ml ethanoic acid along with a few drops of concentrated sulphuric acid in a test tube, a sweet smelling substance is formed. Name the compound and give the balanced chemical equation for the reaction. What do we call the reverse reaction to give back alcohol and carboxylic acid which is used in the preparation of soap ?
9. Based on the group valency of elements, state the formula for the following giving justification for each:
(i) Oxides of 1st group elements,
(ii) Halides of the elements of group 13, and
(iii) Compounds formed when an element of group 2 combines with an element of group16:
10. Ravi read the formation of covalent bonds and came to know the property of carbon. Carbon has four valence electrons. It cannot lose four electrons since very high amount of energy will be required to lose four electrons to form C4+. Carbon cannot gain four electrons to form C4- ion as six protons cannot hold 10 electrons easily and there will be strong interelectronic repulsion.
Questions:
(i) What is the atomic number and electronic configuration of carbon ?
(ii) Explain how covalent bonding is important between carbon compounds. Give any two suggestions.
11. With the help of a cross done with garden pea plants, trace the work done by Mendel with a tall and a short plant to arrive at a 3 :1 ratio in the F2
12. The genotype of green-stemmed tomato plants is denoted by GG and that of purple-stemmed tomato plants as gg. When these two plants are crossed :
(i) What colour of stem would you expect in their F1 progeny ?
(i) Give the percentage of purple-stemmed plant if F1 plants are self pollinated.
(ii) In what ratio would you find the green and purple colour in the F1 progeny ?
13. (a) Give the evidence that the birds have evolved from reptiles.
(b) Insects, octopus, planaria and vertebrates possess eyes. Can we group these animals together on the basis of eyes that they possess ? Justify your answer giving reason.
14. A cross was made between pure breeding pea plants one with round and green seeds and the other with wrinkled and yellow seeds. 3
(a) Write the phenotype of F1progeny. Give reason for your answer.
(b) Write the different types of F2 progeny obtained along with their ratio, when F1progeny was selfed.
15. (a) Define the term magnification. Write the formula for magnification of mirror explaining the symbols used in the formula.
(b) The magnification produced by a convex lens is -2. What is meant by this statement and also write the information regarding image obtained from it.
16. Define the power of lens. The power of lens is + 2.0 D.
(a) Find the focal length of lens in m.
(b) Name the kind of this lens. Explain with the help of figure whether this lens would converge or diverge a beam of lens.
17. (a) ” Stars seem higher than they actually are”. .
(b) “The sky appears dark to passengers flying at very high altitudes”.
Justify these statements with reason.
18. Define angle of deviation. Why do different components of white light split up into spectrum when it passes through a triangular glass prism ? Show the angle of deviation for red colour when white light passes through a prism.
19. (a) Why do we classify elements ?
(b) What are the two criterias used in the development of Modern Periodic Table ?
(c) State the position of (a) metals, (b) non-metals and (c) metalloids in the periodic table.
(d) Would you place two isotopes of chlorine; Cl-35 and Cl-37 in different slots of the periodic table because of their different atomic masses or in the same slot because their chemical properties are same ? Justify your answer.
20. (a) Draw a diagram showing germination of pollen on stigma of a flower.
(b) Label pollen grain, male germ cells, pollen tube and female germ cell in the above diagram.
(c) Define fertilization in plants.
21. (i) How many characters are transmitted in the following cross ? Name them. Identify the dominant and recessive traits.
(ii) What is the information source for making proteins in the cell ?
(iii) Name an organism which can change its sex during its lifetime.
22.(a) State the laws of refraction of light. Explain the term absolute refractive index of a medium and write an expression to relate it with the speed of light in vacuum.
(b) The absolute refractive indices of two media ‘A’ and ‘B’ are 2.0 and 1.5 respectively. If the speed of light in medium ‘B’ is 2xl08 m/s, calculate the speed of light in :
(i) vacuum,
(ii) medium ‘A’.
23. (a) Describe an activity along with a labeled diagram the phenomenon of dispersion through a prism.
(b) Explain in brief the formation of rainbow with the help of a figure. 5
24. An estimated 50 million tons of E-waste are produced each year. The USA discards 30 million computers each year and 100 million phones are disposed off in Europe each year. The Environmental Protection Agency estimates that only 15-20% of e-waste is recycled, the rest of these electronics go directly into landfills and incinerators.
(a) Mention any two possible reasons for generation of E-waste in large amount.
(b) Suggest any two ways by which you can help in reducing the e-waste in the environment ? (HOTS)
SECTION-B
25. Student adds a few drops of ethanoic acid to test tubes X, Y and Z containing aqueous solutions of sodium chloride, sodium hydroxide and sodium carbonate, respectively. If he now brings a burning splinter near the mouth of the test tubes immediately after adding ethanoic acid in each one of them, in which of the test tube or test tubes the flame will be extinguished ?
(a) X and Y
(B) Y and Z
(C) X and Z
(D) only Z
26. About 2 ml of acetic acid was taken in each of the three test-tubes B Q and R and 5 ml, 10 ml and 15 ml of distilled water were added to them, respectively. Instantaneously a clear solution is observed in the test-tubes:
(A) P and Q only (B) Q and R only
(C) R and P only (D) P, Q and R.
27. When ethanoic acid is added to a solution of substance X, colourless and odourless gas Y is liberated. The gas Y turns lime water milky. The substance X is :
(A) Sodium hydrogen carbonate (B) Sodium hydroxide
(C) Sodium acetate (D) Sodium chloride.
28. Identify the figures showing the process of budding in yeast.
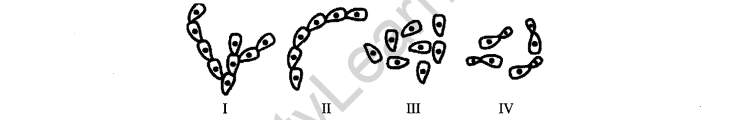
(A) I, II and III (B) II, III and IV
(C) I, II and IV (D) III, IV and I
29. You are asked by your teacher to study the different parts of an embryo of a gram seed. Given below are the steps to be followed for the experiment: 1
I. Soak the gram seeds in plain water and keep them overnight.
II. Cut a soaked seed and observe its different parts.
III. Take some dry gram seeds in a petri dish.
IV. Drain the excess water.
V. Cover the soaked seeds with a wet cotton cloth and leave them for a day.
The correct sequence of these steps is :
(A) III, I, V, IV, II (B) III, I, II, IV, V
(C) III, IV, V, I, II (D) III, I, IV, V, II
30. Four students P Q, R and S differently reported the following set of organs to be analogous : 1
P. Forelimb of a frog and forelimb of a lizard.
Q. Forelimb of a bird and forelimb of a human.
R. Wings of a parrot and wings of a butterfly.
S. Wings of a bird and wings of a bat.
The two students who have reported correctly are :
(A) P and Q
(B) Q and R
(c) R andS
(D) PandS
(D) Size of the parent cell to undergo fission is not appropriate.
31. A student wants to find the focal length of a concave mirror given to him. He focuses a distant object with this mirror, to obtain a sharp image. The chosen object should not be :
(A) A building
(B) A tree
(C) A window
(D) The sun
32. The focal length of the concave mirror in the experimental set up shown below, equals
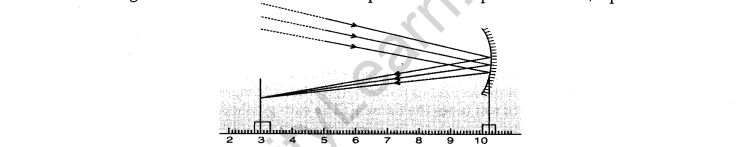
(A) 10.4 cm (B) 3. 4 cm
(C) 7.0 cm (D) 7.1cm
33. A student has obtained the image of a distant object with a concave mirror to determine its focal length. If he has selected a well-illuminated red building as object, which of the following correctly describes the features of the image formed ?
A. Virtual, inverted and diminished image in red shade.
B. Real, erect and diminished image in pink shade.
C. Real, inverted and diminished image in red shade.
D. Virtual, erect and enlarged image in red shade.
34. Is a sample containing dil. HC1 hard ? Why ?
35. Write two precautions to be taken while identifying different parts of an embryo of a dicot seed.
36. A student performed an experiment with convex lens and found the virtual image of an object. Find
(a) Position of the object
(b) Draw ray diagram for the above situation.
Answers
SECTION- A
1. What are cations and anions ?
Ans. Positively charged ions are called cations and negatively charged ions are called anions. [C.B.S.E. Marking Scheme, 2012] 1
2. WhatisDNA?
Ans. DNA is the carrier of hereditary information from parents to the next generation / Hereditary material present in all living cells. [CBSE Marking Scheme, 2015] 1
3. Give one example each from your daily life where the domestic waste can be effectively reused and recycled.
Ans. Reuse : We can reuse the empty bottles of jam, pickles etc. for the storage purposes.
Recycle : We can recycle old newspapers, aluminium cans etc.
4. Why are forest considered “biodiversity hot spots”? List two ways in which an individual can contribute effectively to the management of forests and wildlife ?(HOTS)
Ans. Biodiversity is measured by the number of different life forms found in an area. In a forest, various species are available which include bacteria, fungi, ferns, plants, nematodes, insects, birds, reptiles and mammals. Forests are therefore, called biodiversity hot spots.
An individual can contribute in management of forest and wildlife by
(a) Avoiding cutting of forest and killing of wildlife.
(b) Educating people about the importance of forest and wildlife in our life.
[CBSE Marking Scheme, 2015] 1 + 1
5. In a area A, the leaf material available to beetles was very less. What are the two consequencesseen in the beetles ? (HOTS)
Ans. The consequences are as follows :
They switched to new type of food and entered new niches.
This lead to arise of diverse variety of beetles as some changes in beetles will take place to make them adaptable to new niches. [CBSE Marking Scheme, 2014,8XSVHLC] 1 + 1
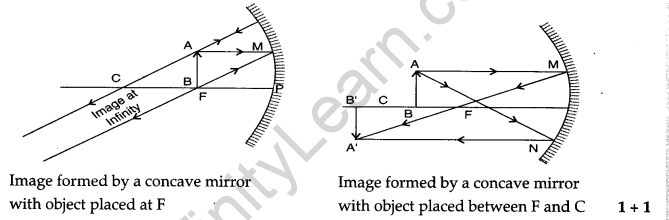
6. “A concave mirror of focal length ‘f’ can form a magnified erect as well as an inverted image of an object placed in front of it.” Justify this statement stating the position of the object with respect to the mirror in each case for obtaining these images.
Ans.
7. What is the difference between the molecules of soaps and detergents, chemically ? Explain the cleansing action of soaps.
Ans. Detergents are sodium salt of long chain benzene sulphonic acids.
Soaps are sodium or potassium salt of long chain fatty acids that have cleaning action in water, e.g., Sodium stearate.
Cleansing Action of Soap : A soap molecule consists of two dissimilar parts :
(i) A short ionic part comprising the carboxylate salt— COO-Na+ which is water soluble.
(ii) A long hydrocarbon chain which is hydrophobic.
When soap is dissolved in water, it form a colloidal suspension. In this colloidal suspension, the soap molecules cluster together to form micelles and remain radially suspended in water with the hydrocarbon end towards the centre and the ionic end directed outward. The dirt particles always adhere to the oily or greasy layer present on the skin or clothes. When a dirty cloth is dipped into a soap solution, its non-polar hydrocarbon end of micelles attached to the grease or oil present in dirt and polar end remains in water layer.
The mechanical action of rubbing subsequently, dislodges the oily layer from the dirty surface shaping it into small globules. A stable emulsion of oil in water is formed. The emulsified oil or grease globules bearing the dirt can now be readily washed with water. [CBSE Marking Scheme 2015] 3
8. When we take 1 ml ethanol and 1 ml ethanoic acid along with a few drops of concentrated sulphuric acid in a test tube, a sweet smellingsubstance is formed. Name the compound and give the balanced chemical equation for the reaction. What do we call the reverse reaction to give back alcohol and carboxylic acid which is used in the preparation of soap ?
Ans. 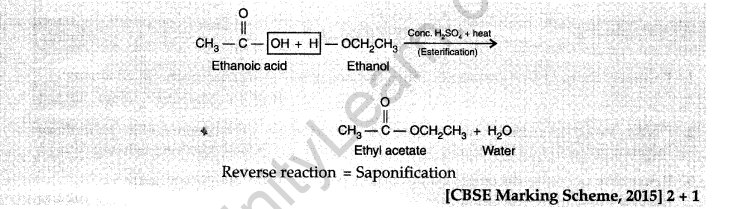
9. Based on the group valency of elements, state the formula for the following giving justification for each:
(i) Oxides of 1st group elements,
(ii) Halides of the elements of group 13, and
(iii) Compounds formed when an element of group 2 combines with an element of group16:
Ans. (i) Valency of group 1 elements : 1 Valency of oxygen : 2 Oxides of group 1 elements :
Formula of the oxides of group 1 is M20, where M is the group 1 element and O is oxygen.
(ii) Valency of group 13 elements : 3 Valency of halogens : 1 Halides of group 13 elements :
Formula of the halides of group 13 is MX, where M is the group 13 element and X is halogen.
(iii) Valency of group 2 elements : 2 Valency of group 16 elements : 2 Compounds of group 2 and group 16 elements :
Formula of the compounds of group 2 and 16 is MN, where M is the group 2 element and N is the group 16 element. 1 + 1 + 1
10. Ravi read the formation of covalent bonds and came to know the property of carbon. Carbon has four valence electrons. It cannot lose four electrons since very high amount of energy will be required to lose four electrons to form C4+. Carbon cannot gain four electrons to form C4- ion as six protons cannot hold 10 electrons easily and there will be strong interelectronic repulsion.
Questions:
(i) What is the atomic number and electronic configuration of carbon ?
(ii) Explain how covalent bonding is important between carbon compounds. Give any two suggestions.
Ans. (i) Atomic number of carbon = 6.
Electronic configuration of carbon = 2, 4. 1 + 1 + 1
(ii) (a) Carbon forms maximum number of compounds due to covalent bonding.
(b) Carbon compounds have covalent bonds due to which they are poor conductors of electricity. They do not contain ions or free electrons to conduct electricity.
11. With the help of a cross done with garden pea plants, trace the work done by Mendel with a tall and a short plant to arrive at a 3 :1 ratio in the F2
Ans. 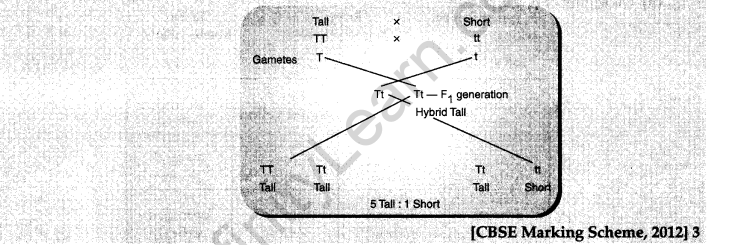
12. The genotype of green-stemmed tomato plants is denoted by GG and that of purple-stemmed tomato plants as gg. When these two plants are crossed :
(i) What colour of stem would you expect in their F1 progeny ?
(i) Give the percentage of purple-stemmed plant if F1 plants are self pollinated.
(ii) In what ratio would you find the green and purple colour in the F1 progeny ?
Ans. (i) Green colour
(ii) 25%
(iii)3:1 [CBSE Marking Scheme, 2012]
13. (a) Give the evidence that the birds have evolved from reptiles.
(b) Insects, octopus, planaria and vertebrates possess eyes. Can we group these animals together on the basis of eyes that they possess ? Justify your answer giving reason.
Ans. (a) Fossils provide evidence of evolution. A fossil bird called Archaeopteryx, which lived in the Late Jurassic Period around 148-150 million years ago, had feathered wings like that of birds and a long bony tail, jaws with sharp teeth and various skeletal features like that of reptiles. Thus, Archaeopteryx is considered a connecting link between reptiles and birds. Some dinosaurs had feathers that provide them insulation in cold weather; however, they could not fly using those feathers. Birds seem to have later used feathers to fly. This, of course, means that birds are very closely .related to reptiles because dinosaurs were reptiles. Hence, it suggests that birds have evolved from reptiles.
(b) While making groups, we need to decide the characteristics that are responsible for the more fundamental differences among organisms. The characteristics that account for the broadest divisions among living organisms should be independent of any other characteristics in their effects on the forms and structural functions of organisms like cellularity, mode of nutrition and nature of cell. Insects, octopus and planaria are invertebrates. They cannot be grouped together with vertebrates, as they lack an internal skeleton with a backbone. Also, all of them belong to different phyla on the basis of different characteristics they possess. Just on the basis of one characteristic, i.e., presence of eyes, these organisms cannot be grouped together.
14. A cross was made between pure breeding pea plants one with round and green seeds and the other with wrinkled and yellow seeds. 3
(a) Write the phenotype of F1progeny. Give reason for your answer.
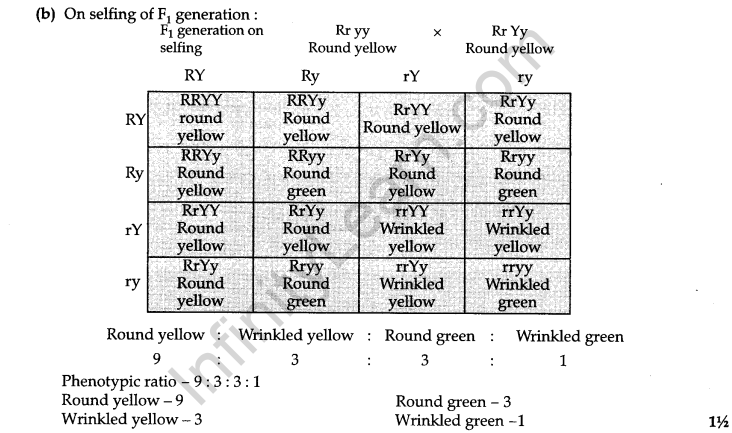
(b) Write the different types of F2 progeny obtained along with their ratio, when F1progeny was selfed.
Ans. (a) The cross was made between round, green seeds and wrinkled, yellow seeds. In the given cross, two traits were taken into account, which is a dihybrid cross. Yellow colour and round shape is dominant over green colour and wrinkled shape.
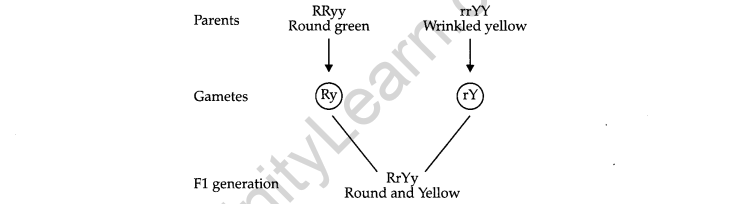
The above cross shows round and yellow seeds in the F1 generation. It occurs because dominant traits (round and yellow) express itself, whereas recessive traits (wrinkled and green) get suppressed.
15. (a) Define the term magnification. Write the formula for magnification of mirror explaining the symbols used in the formula.
(b) The magnification produced by a convex lens is -2. What is meant by this statement and also write the information regarding image obtained from it.
Ans. (a) Ratio of height of the image to height of the object is magnification.
M (mirror) =h1/h = -v/u
M = Magnification
h = height of object
h1 = height of image
v = image distance
u = object distance.
(b) It means image formed is two times the size of object and the image formed is inverted formed in front of the lens. [CBSE Marking Scheme, 2014] 2 + 1
16. Define the power of lens. The power of lens is + 2.0 D.
(a) Find the focal length of lens in m.
(b) Name the kind of this lens. Explain with the help of figure whether this lens would converge or diverge a beam of lens.
Ans. (a) The ability of a lens to converge/diverge a beam of light rays is expressed in terms of its power
(P). It is the inverse of focal length,/(in meters).
Hence, power of a lens is given by the relation
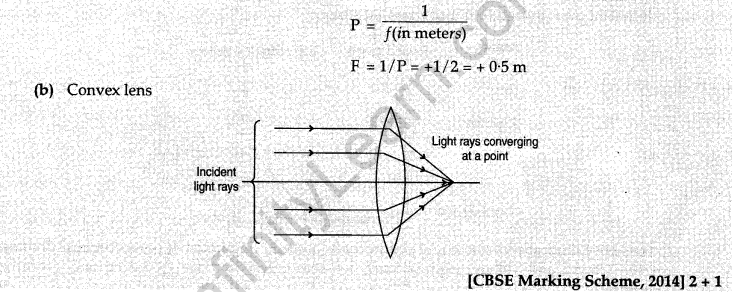
17. (a) ” Stars seem higher than they actually are”. .
(b) “The sky appears dark to passengers flying at very high altitudes”.
Justify these statements with reason.
Ans. (a) Light coming from the stars is supposed to travel in a straight line. But the refractive index of air is not same throughout. It changes as hot air is rarer than cold air. So refraction takes place. In this case, starlight continuously travels from a rarer medium to a denser medium. Hence, it continuously bends towards the normal. The continuous bending of starlight towards the normal results in a rise of the apparent position of the star.
(b) Scattering of light takes place because of the particles present in the at mosphere. At high altitude due to absence of atmosphere, scattering of light do not take place and hence sky appears dark to passengers flying at high altitude. [CBSE Marking Scheme, 2014,8XSVHLC]
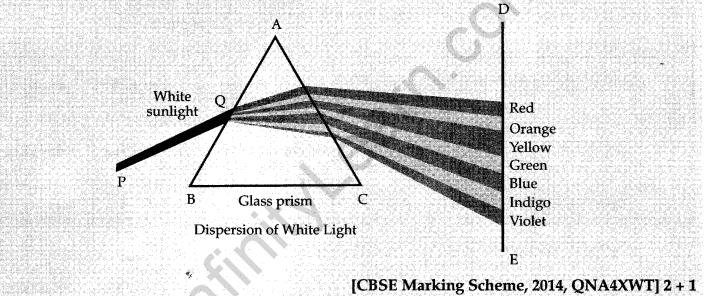
18. Define angle of deviation. Why do different components of white light split up into spectrum when it passes through a triangular glass prism ? Show the angle of deviation for red colour when white light passes through a prism.
Ans. The angle between the extended incident ray and the emergent ray is called the angle of deviation. This is because the different colours travel through a glass prism at different speeds.
19. (a) Why do we classify elements ?
(b) What are the two criterias used in the development of Modern Periodic Table ?
(c) State the position of (a) metals, (b) non-metals and (c) metalloids in the periodic table.
Ans. (a) To study the properties of elements and to keep the elements with similar properties together.
(b) Chemical properties of elements and atomic number.
(c) Metals lies on extreme left, metalloids lie in the middle and non-metals lie on the right side.
(d) They should be placed in the same slot, Since they have same numbers of electrons. [CBSE Marking Scheme, 2011] 1 + 1 + 2 + 1
20. (a) Draw a diagram showing germination of pollen on stigma of a flower.
(b) Label pollen grain, male germ cells, pollen tube and female germ cell in the above diagram.
(c) Define fertilization in plants.
Ans. 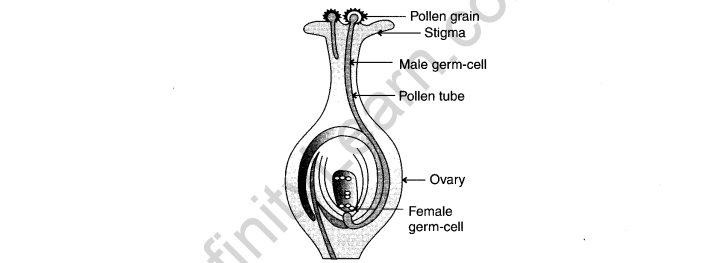
The fusion of male and female gametes of all sexually-reproducing organisms is called fertilization. 2 + 2 + 1
21. (i) How many characters are transmitted in the following cross ? Name them. Identify the dominant and recessive traits.
(ii) What is the information source for making proteins in the cell ?
(iii) Name an organism which can change its sex during its lifetime.
Ans.(i)Two characters. They are shape of seed and colour of seed.round shape and yellow colour of seed are the dominant characteristics . wrinkled shape and green colour of seed are the recessive characteristics
(ii)Cellular DNA is the information source for making proteins in the cell.
(iii)Snails can change their sex during their lifetime.
22.(a) State the laws of refraction of light. Explain the term absolute refractive index of a medium and write an expression to relate it with the speed of light in vacuum.
(b) The absolute refractive indices of two media ‘A’ and ‘B’ are 2.0 and 1.5 respectively. If the speed of light in medium ‘B’ is 2xl08 m/s, calculate the speed of light in :
(i) vacuum,
(ii) medium ‘A’.
Ans. (a) Laws of refraction of light:
(b) The incident ray, the normal and the refracted ray at the point of incidence all lies in the same plane for the two given transparent medium.
(c) The ratio of size of angle of incidence (i.e., sin z) to the sine of angle of refraction (i.e., sin r) is always constant for the light of given colour and for the given pair of media.
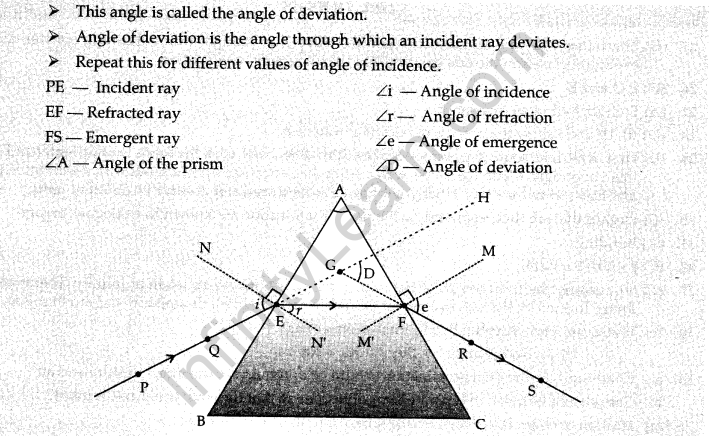
23. (a) Describe an activity along with a labeled diagram the phenomenon of dispersion through a prism.
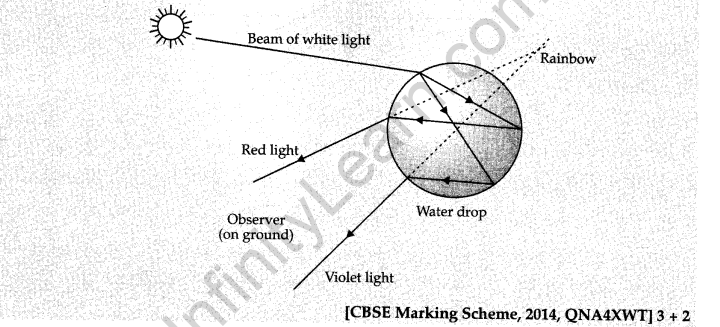
(b) Explain in brief the formation of rainbow with the help of a figure. 5
Ans. (a) Place a prism on a white sheet of paper with the triangular face on the sheet and trace its boundary ABC.
- Fix two pins T and S on one side.
- Place the prism on the boundary ABC.
- Looking through the other side fix two more pins Q and R in such a way that all the four pins appear to be in the same line.
- Remove the pins and mark their positions.
- Join TS and RQ and extend them to meet the faces of the prism at P and O respectively.
- Join PO.
- TP represents the incident ray.
- PO represents the refracted ray.
- OR represents the emergent ray which is bent towards the base.
- Let PN and ON be the normal at the points P and O respectively.
- Let 7 be the angle of incidence and V be the angle of refraction.
- If the incident ray TP is extended forward and the emergent ray RO backwards, they meet at M forming the angle OML.
- Measure the angle OML.
(b) Rainbow forms when sunlight hits the water droplets suspended in the atmosphere and undergoes total internal reflection. When the sunlight comes out of the drop it disperses, where the drop acts like a small prism. This dispersion or breaking up of light into several colors is what forms the rainbow.
24. An estimated 50 million tons of E-waste are produced each year. The USA discards 30 million computers each year and 100 million phones are disposed off in Europe each year. The Environmental Protection Agency estimates that only 15-20% of e-waste is recycled, the rest of these electronics go directly into landfills and incinerators.
(a) Mention any two possible reasons for generation of E-waste in large amount.
(b) Suggest any two ways by which you can help in reducing the e-waste in the environment ? (HOTS)
Ans. (a) Improvement in our life style has led to use of more of electronic gadgets like computers, laptops, mobile phones etc. The companies in order to increase their sales keep on launching new upgraded versions which attract the buyers and increase the waste.
(b) Think about the utility and then only buy the upgraded models not just because friends are having so I should also buy it.
Try to reuse the old TV, computers, mobile phones or other electronic gadgets if it is in working condition by selling/giving it to the needy. [CBSE Marking Scheme, 2015] 2 1/2 + 2 1/2
SECTION-B
25. Student adds a few drops of ethanoic acid to test tubes X, Y and Z containing aqueous solutions of sodium chloride, sodium hydroxide and sodium carbonate, respectively. If he now brings a burning splinter near the mouth of the test tubes immediately after adding ethanoic acid in each one of them, in which of the test tube or test tubes the flame will be extinguished ?
(a) X and Y
(B) Y and Z
(C) X and Z
(D) only Z
Ans. (D) The flame will be extinguished when test tube Z is brought near a burning splinter due to evolution of carbon dioxide gas, which does not support combustion.
26. About 2 ml of acetic acid was taken in each of the three test-tubes B Q and R and 5 ml, 10 ml and 15 ml of distilled water were added to them, respectively. Instantaneously a clear solution is observed in the test-tubes:
(A) P and Q only (B) Q and R only
(C) R and P only (D) P, Q and R.
Ans. (D) Q and R.
27. When ethanoic acid is added to a solution of substance X, colourless and odourless gas Y is liberated. The gas Y turns lime water milky. The substance X is :
(A) Sodium hydrogen carbonate (B) Sodium hydroxide
(C) Sodium acetate (D) Sodium chloride.
Ans. (A) Sodium hydrogen carbonate.
28. Identify the figures showing the process of budding in yeast.

(A) I, II and III (B) II, III and IV
(C) I, II and IV (D) III, IV and I
Ans. (D) III, IV and I show the process of budding in a yeast.
29. You are asked by your teacher to study the different parts of an embryo of a gram seed. Given below are the steps to be followed for the experiment: 1
I. Soak the gram seeds in plain water and keep them overnight.
II. Cut a soaked seed and observe its different parts.
III. Take some dry gram seeds in a petri dish.
IV. Drain the excess water.
V. Cover the soaked seeds with a wet cotton cloth and leave them for a day.
The correct sequence of these steps is :
(A) III, I, V, IV, II (B) III, I, II, IV, V
(C) III, IV, V, I, II (D) III, I, IV, V, II
Ans. (D) First of all, take some dry gram seeds in a Petri dish. Now, soak the seeds in plain water and keep them overnight. Drain the excess water. After that, cover the soaked seeds with a wet cotton cloth and leave them for a day. Finally, cut open a soaked seed and observe its different parts
30. Four students P Q, R and S differently reported the following set of organs to be analogous : 1
P. Forelimb of a frog and forelimb of a lizard.
Q. Forelimb of a bird and forelimb of a human.
R. Wings of a parrot and wings of a butterfly.
S. Wings of a bird and wings of a bat.
The two students who have reported correctly are :
(A) P and Q
(B) Q and R
(c) R andS
(D) PandS
(D) Size of the parent cell to undergo fission is not appropriate.
Ans. (C) Organs that are different in origin but similar in function are known as analogous organs. 1
31. A student wants to find the focal length of a concave mirror given to him. He focuses a distant object with this mirror, to obtain a sharp image. The chosen object should not be :
(A) A building
(B) A tree
(C) A window
(D) The sun
Ans. (A) Building.
32. The focal length of the concave mirror in the experimental set up shown below, equals

(A) 10.4 cm (B) 3. 4 cm
(C) 7.0 cm (D) 7.1cm
Ans. (C) f= 10-3 = 7cm.
33. A student has obtained the image of a distant object with a concave mirror to determine its focal length. If he has selected a well-illuminated red building as object, which of the following correctly describes the features of the image formed ?
A. Virtual, inverted and diminished image in red shade.
B. Real, erect and diminished image in pink shade.
C. Real, inverted and diminished image in red shade.
D. Virtual, erect and enlarged image in red shade.
Ans. (C) To measure the focal length of the mirror, the object should be taken at infinity. Therefore, the image formed by the concave mirror would be real, inverted, diminished and red in shade. 1
34. Is a sample containing dil. HC1 hard ? Why ?
Ans. Yes. Hydrogen ions provided by HC1 makes water hard
H+ + Na+ stearate” —> Steric acid + Na+
35. Write two precautions to be taken while identifying different parts of an embryo of a dicot seed.
Ans. a. Conditions for the seed germination should be optimum i.e. warmth, moisture and air
b. Care should be taken to separate two cotyledons so that the embryonal axis is intact
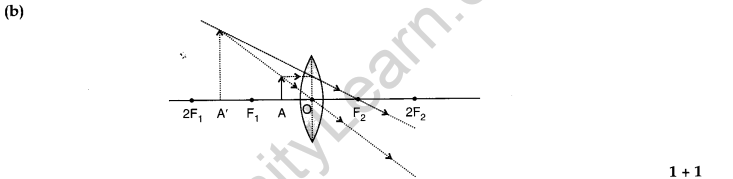
36. A student performed an experiment with convex lens and found the virtual image of an object. Find
(a) Position of the object
(b) Draw ray diagram for the above situation.
Ans.(a ) Position of object is between lens and local length of a convex lens.
(Download Questions PDF)
[gview file=”https://resultscareer.files.wordpress.com/2016/02/cbse-sample-papers-for-class-10-sa2-science-solved-2016-set-4-questions.pdf”]
(Download Solutions PDF)
[gview file=”https://resultscareer.files.wordpress.com/2016/02/cbse-sample-papers-for-class-10-sa2-science-solved-2016-set-4-solutions.pdf”]




