Table of Contents
What is benzene?
Benzene is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H6. It is a colorless, flammable liquid with a sweet smell. Benzene is mainly used as a precursor to polymers and other chemicals.

Benzene
Benzene is a hydrocarbon that is composed of six carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms. It is a colorless, flammable liquid that has a sweet odor. Benzene is a major component of gasoline and is used to make plastics, resins, and other synthetic materials.
Structure of Benzene:
Benzene is a cyclic organic compound with the chemical formula C₆H₆. It is one of the most important aromatic hydrocarbons and has a unique structure that consists of a ring of six carbon atoms, with alternating single and double bonds. The structure of benzene is often represented using a hexagon with a circle inside, as shown below:
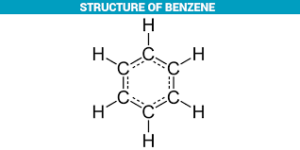
Each corner of the hexagon represents a carbon atom, and the lines inside the hexagon represent the bonds between the carbon atoms. In the case of benzene, the bonds are alternating single and double bonds. The circle inside the hexagon represents a delocalized π (pi) electron system, which is responsible for the unique stability and reactivity of benzene.
The actual structure of benzene can be visualized using a resonance hybrid model, where the π electrons are delocalized over all six carbon atoms. This delocalization gives benzene its characteristic stability and reactivity.
It’s important to note that the structure of benzene is planar, meaning all carbon atoms and hydrogen atoms are in the same plane. The bond angles within the benzene ring are approximately 120 degrees, giving it a regular hexagonal shape.
The structure of benzene has been extensively studied and is widely accepted in organic chemistry. Its unique properties and reactivity make it a fundamental building block for a wide range of organic compounds and industrial processes.
Properties of Benzene
- Benzene is a hydrocarbon that is composed of six carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms. The carbon atoms are all bonded together in a hexagonal ring. The hydrogen atoms are attached to the carbon atoms in a alternating pattern. This makes benzene a unique hydrocarbon because it is not a typical alkane. Benzene is a liquid at room temperature and has a sweet smell. It is a colorless liquid that is slightly soluble in water.
- Benzene is a flammable liquid and will ignite easily. It is also toxic to humans. Exposure to benzene can cause cancer and other health problems.
- Benzene is a relatively stable molecule and does not react with most other chemicals. However, it can react with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water. It can also react with other hydrocarbons to form compounds called polymers. Benzene is also flammable and can be ignited with a spark.
- Benzene is a carcinogen, meaning that it can cause cancer. It is most harmful to the liver and can cause a type of cancer called leukemia. Benzene can also cause other health problems, such as birth defects and low blood pressure.
Resonance in benzene –
- Benzene is a hydrocarbon molecule with a ring-shaped structure. The six carbon atoms in the ring are all sp2-hybridized and the carbon-carbon bonds are all single bonds. The electron-deficient carbon atoms in the ring are each surrounded by three hydrogen atoms, giving the molecule a planar, “flat” shape.
- The carbon-carbon bonds in benzene are all equal in length and strength, and the electrons in the ring are evenly distributed. This makes the benzene molecule very stable and non-reactive.
- However, if a molecule of benzene is hit by a very strong force, such as a lightning bolt, the carbon-carbon bonds can break and the molecule can split into two pieces. When the bonds break, the electrons in the ring are no longer evenly distributed and the molecule becomes unstable.
- The two pieces of the molecule will then try to re-form the ring, and this can cause the molecule to vibrate. The vibrations will cause the two pieces of the molecule to move back and forth, and this is called resonance.
- Resonance is responsible for the characteristic “sweet” smell of benzene.
Uses of Benzene
Benzene is a colorless and highly flammable liquid with a sweet odor. It is mainly used as an intermediate in the production of other chemicals and products. Some of its other uses include:
• As a solvent for extracting oils from plants, dyeing fabrics, and making plastics
• In the production of phenol, nylon, and other synthetic fibers
• As an additive in gasoline to increase octane ratings
About Benzene
Benzene is an important organic compound with the chemical formula C6H6. It is a colorless liquid with a sweet odor. Benzene is mainly used as an industrial solvent and is also used in the manufacture of plastics, pesticides, and other chemicals. Benzene is a carcinogen and can cause leukemia.
Characteristics of Benzene
- Benzene is a colorless, flammable liquid with a sweet odor. It is a hydrocarbon and has the chemical formula C6H6. Benzene is typically used as a solvent and is also found in gasoline.
- Benzene is a hydrocarbon, meaning it is made up of hydrogen and carbon atoms. It has a chemical formula of C6H6, meaning it has six hydrogen atoms and six carbon atoms. Benzene is a colorless, flammable liquid with a sweet odor. It is typically used as a solvent, meaning it is used to dissolve other substances. Benzene is also found in gasoline.









