Table of Contents
Table of Contents
- China Rose as an Indicator
- Litmus Paper
- Types of Litmus Paper
- Summary
- Did You Know?
- What’s Next?
In the previous segment, we learned how turmeric acts as a natural indicator. In this video, we will learn about another natural indicator.
How can China Rose be used as an indicator?
China Rose, also known as Hibiscus rosa-sinensis, can be used as a natural indicator due to its pigment content. The flowers of China Rose contain a water-soluble pigment called anthocyanin, which exhibits different colors at varying pH levels. This property makes China Rose a suitable indicator for acid-base titrations or pH determination.

China Rose solution as indicator:
Here’s how China Rose can be used as an indicator:
- Preparation of China Rose Indicator Solution:
- Collect fresh China Rose flowers and separate the petals from the rest of the flower.
- Rinse the petals with distilled water to remove any impurities.
- Place the petals in a container and add boiling water.
- Allow the petals to steep in the water for several minutes, extracting the pigments.
- Filter the liquid to obtain the China Rose indicator solution.
- pH Range and Color Changes:
- China Rose indicator solution exhibits different colors at different pH levels:
- Acidic pH (pH 1-6): The indicator solution appears red.
- Neutral pH (pH 7): The indicator solution may appear purple.
- Alkaline pH (pH 8-14): The indicator solution turns green or yellow.
- China Rose indicator solution exhibits different colors at different pH levels:
What is Litmus paper?
Litmus paper is a type of pH indicator paper that is commonly used in laboratories and other settings to determine the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. It is made from a mixture of natural dyes extracted from lichens, particularly Roccella tinctoria and Dactylopus coccus.
Litmus paper comes in two main forms: blue litmus paper and red litmus paper. Blue litmus paper is usually blue in color, while red litmus paper is red. These papers change color in the presence of an acidic or basic solution, allowing for a quick and convenient assessment of the pH of a substance.
When blue litmus paper comes into contact with an acidic solution, it turns red. This is because the acidic solution donates hydrogen ions (H+) to the litmus dye, resulting in a color change. On the other hand, when red litmus paper comes into contact with a basic solution, it turns blue. This is because the basic solution accepts hydrogen ions, causing the litmus dye to change its color.

Litmus Extraction
Types of litmus paper
Litmus paper is a commonly used pH indicator in the form of strips or small squares of paper infused with litmus dye. Litmus paper is available in two main types:
- Blue Litmus Paper:
- Blue litmus paper is prepared by impregnating the paper with a water-soluble blue dye extracted from lichens.
- Blue litmus paper is used as an acid-base indicator.
- It remains blue in neutral or basic solutions (pH 7-14).
- When exposed to acidic solutions (pH 0-6), it turns red.
- Red Litmus Paper:
- Red litmus paper is also made by impregnating the paper with a water-soluble dye, but this dye is extracted from different lichens than the one used for blue litmus paper.
- Red litmus paper is primarily used to detect the presence of bases.
- It remains red in neutral or acidic solutions (pH 0-6).
- When exposed to alkaline solutions (pH 8-14), it turns blue.
Note:
Litmus paper can provide a quick and approximate indication of pH values, but it does not give precise pH measurements like a pH meter or pH indicator solutions. It is most commonly used for simple qualitative tests to determine whether a solution is acidic or basic.
It’s important to handle litmus paper with clean, dry hands to avoid contamination and preserve its effectiveness. Additionally, storing litmus paper in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight helps maintain its shelf life and accuracy.
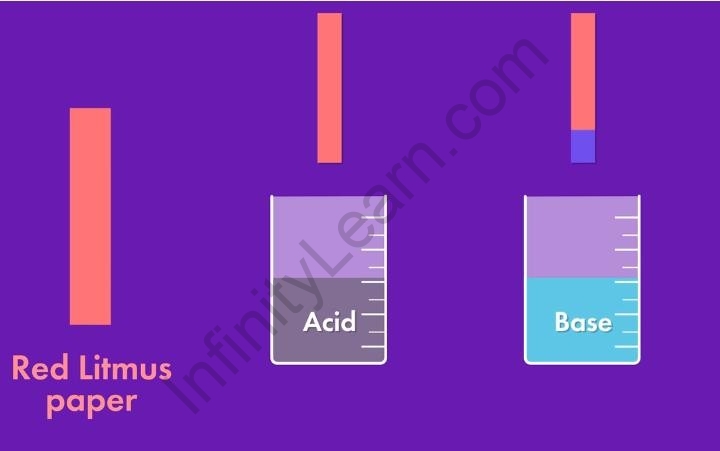
Effect of acid and base on red litmus paper
Red litmus paper is typically used to test for the presence of a base or to determine if a substance is basic in nature. When red litmus paper comes into contact with a basic solution, it undergoes a color change.
Effects of Acid on Red Litmus Paper:
- No Change: When red litmus paper is exposed to an acidic solution, it remains red. Acidic solutions do not cause any noticeable color change in red litmus paper.
Effects of Base on Red Litmus Paper:
- Color Change to Blue: When red litmus paper is exposed to a basic solution, it turns blue. This color change is due to the reaction between the base and the litmus dye. The basic solution accepts hydrogen ions (H+) from the litmus dye, causing the red litmus paper to change its color.
It’s important to note that red litmus paper is not sensitive to weak bases or mildly alkaline solutions. It mainly detects strong bases that can significantly alter the pH of a solution.
In summary, red litmus paper is used as an indicator to test for the presence of a base. If red litmus paper turns blue when in contact with a substance, it indicates that the substance is basic. If there is no color change, it suggests that the substance is either neutral or acidic.



