Table of Contents
- Reason for Sky being Blue
- Summary
- What’s Next?
In the previous segment, we understood why stars twinkle at night. In this segment, we will learn about the physics behind the blue sky.
Why is the sky blue?
- The colour of the sky is blue due to the atmosphere of the earth and the sunlight.
- The white light coming from the sun is a mixture of seven primary colours. Each coloured light has a corresponding frequency and wavelength associated with it. The violet coloured light has the shortest wavelength of all, while the red one has the largest wavelength.
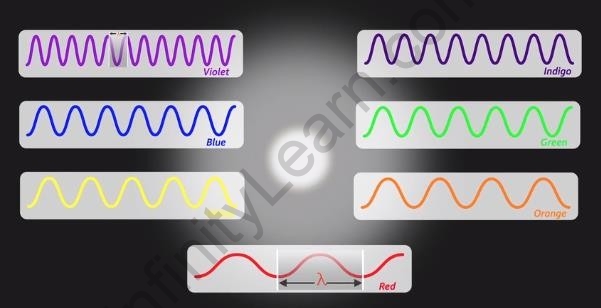
Different wavelengths of light
- The earth’s atmosphere is mainly composed of gases, dust particles, water droplets and
water vapour.
- Among these gases, nitrogen is present in abundant quantities, at around 78%, followed by oxygen which is approximately 21%, and the remaining is filled with the likes of argon, carbon dioxide, and other gases.




