Table of Contents
Table of Contents
- Image Characteristics of a Convex Mirror
– Different Types of Reflection in a Convex Mirror
- Summary
- What’s Next?
In the previous segment, we learnt about the position of Images for a concave mirror using ray diagrams. In this segment, let us understand the image characteristics of a convex mirror.
What are the image characteristics of a convex mirror?
- A spherical mirror whose reflective surface is curved outwards is known as a convex mirror.
- Consider a convex mirror whose pole, the centre of curvature, and focal point are represented by the points P, C, and F respectively as shown below.
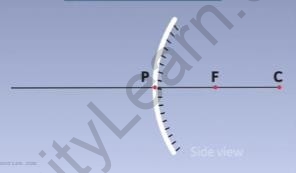
Side view of a convex mirror
- For a convex mirror, the focal point lies behind the reflective surface, and hence no ray of light can be incident at the focal point.
- When rays of light are directed towards the focal point of a convex mirror when extended, then the reflected rays travel parallel to the principal axis.
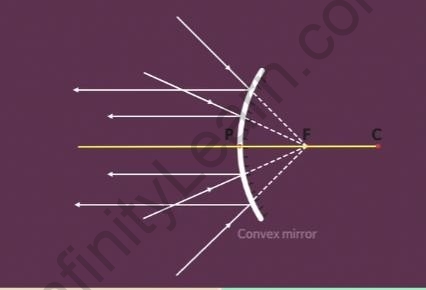
Rays of light directed towards the focal point of a convex mirror
- When rays of light are incident on the convex mirror parallel to the principal axis, then the reflected rays appear to be originating from the focal point.
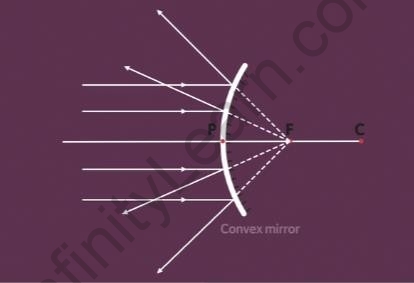
Rays of light parallel to the principal axis incident on a convex mirror
What are the different types of reflection in a convex mirror?
(i) Object is at infinity
The ray diagram of an object at infinity for a convex mirror is as follows:






