Table of Contents
Do you understand the significance of punctuation? It is not just letters and symbols on a page – it is the glue that holds our sentences together. Consider the following example: “Iliketeddybear” versus “I like Teddy Bear.” Just a few marks can completely transform the meaning. That’s how crucial punctuation is in writing.
Writing without any punctuation is like sailing without a compass – you may end up lost and confused. Without proper punctuation, all your grammar knowledge and sentence structure will be in vain. It’s like having a beautiful painting without the right frame to showcase its beauty. Without punctuation, your writing lacks clarity and flow. Effective use of punctuation enhances the clarity and flow of your writing, while a rich English vocabulary adds depth and precision to your expression, creating compelling and engaging content.
Learning how to use punctuation correctly will enhance your writing and make it more engaging for your readers. It’s like adding a splash of color to a black and white photo or using the perfect seasoning to elevate a dish to new heights. So, let’s explore what it is, the different punctuation marks in the English language, and how to use them effectively.
What Is Punctuation? – Meaning and Definition with Examples
Punctuation refers to a set of symbols or marks that we use in writing to separate sentences and phrases, indicate pauses, and clarify the intended meaning of a text. Imagine reading a never-ending sentence without any breaks – it would be like trying to run a marathon without taking a single breath. Punctuation serves as a visual guide for readers, helping them interpret the writer’s ideas accurately.
To illustrate the importance of punctuation, consider the following example:
“Let’s eat Grandma!” versus “Let’s eat, Grandma!”
In this case, a simple comma completely changes the meaning of the sentence. Without proper punctuation, misunderstandings can arise and alter the intended message.
Throughout this section, we will delve into each type of punctuation mark individually, explaining their functions and providing practical examples to help you understand their usage better.
The Punctuation Marks in English Grammar with Examples
Understanding the proper usage of all punctuation marks is important for effective writing. A misplaced or misused mark can alter the intended meaning of a sentence or lead to confusion for readers. Therefore, mastering these punctuation marks is vital for anyone seeking to communicate clearly and professionally in written English.
When we get to know these important writing tools, we improve how we write. It helps us make our messages clear and exact.
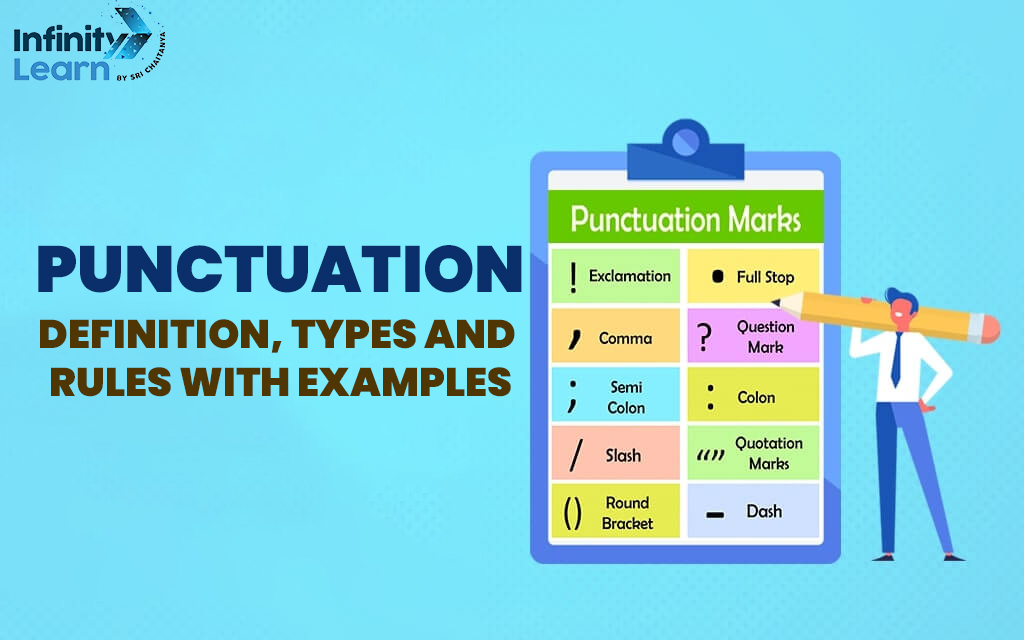
Punctuation marks play a crucial role in conveying meaning and clarity in written English. There are a total of 14 commonly used punctuation marks in the English language.
1. Period (.)
2. Comma (,)
3. Question mark (?)
4. Exclamation mark (!)
5. Colon (:)
6. Semicolon (;)
7. Quotation marks (” “)
8. Apostrophe (‘)
9. Hyphen (-)
10. Dash (— or –)
11. Parentheses (())
12. Brackets ([] or {})
13. Ellipsis (…)
14. Slash (/)
Each of these punctuation marks have their own specific purpose, whether it be indicating the end of a sentence, separating items in a list, denoting quotations, or adding emphasis to a statement.
Using Punctuation in Sentences with Examples
Punctuation marks are super important in English. They help to make sentences clear and convey their meanings better. Here are examples of the 14 punctuation marks commonly used:
| Punctuation Mark | Usage | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Period (.) | Indicates the end of a declarative sentence. | “She walked to the store.” |
| Comma (,) | Separates items in a list or clauses within a sentence. | “He enjoys reading, writing, and painting.” |
| Question Mark (?) | Shows the end of an interrogative sentence (asking a question). | “Where is the nearest café?” |
| Exclamation Mark (!) | Adds emphasis or shows strong emotion. | “Stop!” or “What a beautiful sunset!” |
| Quotation Marks (” “) | Encloses direct speech or quotes. | She said, “I’ll be there at 5 PM.” |
| Colon (:) | Introduces a list or elaborates on a preceding statement. | “There are three things I love: music, art, and books.” |
| Semicolon (;) | Links related independent clauses in a sentence. | “She sings beautifully; her voice mesmerizes everyone.” |
| Dash (—) | Indicates a break or interruption in a sentence. | “The concert—though delayed—was worth the wait.” |
| Ellipsis (…) | Indicates omission or a pause in speech or thought. | “I wonder where… Oh, there it is!” |
| Parentheses (()) | Adds extra information or aside within a sentence. | “The conference (scheduled for tomorrow) has been postponed.” |
| Brackets ([]) | Contains added information within a quote or text. | “He said, ‘I am [really] looking forward to it.'” |
| Apostrophe (‘) | Indicates possession or omission of letters. | “That’s Tom’s book.” or “Can’t you see?” |
| Hyphen (-) | Joins words or parts of words; shows compound words. | “Well-being” or “six-year-old child” |
| Slash (/) | Indicates alternatives or separates words or phrases. | “He/She” or “and/or” |
These examples illustrate how each punctuation mark functions within sentences to add clarity, emphasize, or separate different elements.
Basic Punctuation Rules Everyone Needs to Know
Now that we have explored the different punctuation marks, let’s dive into some fundamental rules that everyone needs to know. These rules will help you navigate the realm of punctuation and enhance your writing clarity.
- Use a period to end a sentence that makes a statement or provides information.
- Employ commas to separate items in a list, connect clauses, and indicate pauses within a sentence.
- End interrogative sentences with a question mark to denote questions.
- Use an exclamation mark to convey strong emotions or exclamations.
- The colon introduces a list or an explanation, while the semicolon connects closely related independent clauses.
- Use an apostrophe to indicate possession or in contractions.
- Employ quotation marks to denote speech or quoted text.
- By adhering to these basic punctuation rules, you will ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and easy to understand.
Conclusion
Punctuation serve as the silent heroes that give structure and clarity to our written communication. From the common period and comma to the slightly more complex semicolon and dash, each punctuation mark has its own unique purpose.
It’s important for Students to realize that although these marks might seem small, they hold immense power in how our writing comes across. If we don’t use them properly, our message might get mixed up or misunderstood.
Therefore, let’s embrace these small yet powerful tools. When we use these marks correctly, we can greatly enhance how we communicate. They help us express our thoughts clearly and ensure that our ideas are easily understood.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the definition of punctuation?
Punctuation refers to the set of symbols used in writing to clarify the meaning and structure of sentences. It includes various marks and symbols, such as commas, periods, question marks, and more, which aid in organizing and conveying the intended message in written communication.
What is punctuation in English grammar with examples?
Punctuation in English grammar involves using symbols and marks to organize sentences, clarify meaning, and indicate pauses or emphasis. For instance, using commas to separate clauses, periods to end sentences, question marks for inquiries, and exclamation marks for strong emotions or exclamations are all examples of punctuation in English grammar.
What are the 10 rules of punctuation?
The 10 fundamental rules of punctuation include: Use a comma to separate items in a list. Place a period at the end of a declarative sentence. Use a question mark at the end of an interrogative sentence. Employ an exclamation mark for strong emotions or exclamatory sentences. Use a colon to introduce a list or explanation. Employ a semicolon to connect closely related independent clauses. Use an apostrophe to indicate possession or contraction. Employ quotation marks to indicate speech or quoted text. Use a hyphen to join words or indicate a range. Employ parentheses to provide additional information or clarification.
What are the 14 punctuation marks?
The 14 punctuation marks are: comma, period, question mark, exclamation mark, colon, semicolon, apostrophe, quotation marks, hyphen, dash, parentheses, brackets, braces, and ellipsis.
How do you Punctuate a sentence?
Punctuating a sentence involves using specific marks and symbols to clarify its structure and meaning. Here are some key punctuation rules for sentences in English: End with a Period: Use a period to end a declarative sentence that makes a statement or gives information. Example: She enjoys reading books. Question Mark: End an interrogative sentence with a question mark to indicate a question. Example: Are you going to the party? Exclamation Mark: Use an exclamation mark to express strong emotions or exclamations. Example: What a wonderful surprise! Comma: Use commas to separate items in a list, connect independent clauses with a coordinating conjunction (like and, but, or), or to indicate pauses. Examples: I need eggs, milk, and bread from the store. She went to the store, and then she visited her friend. Colon : Use a colon to introduce a list or an explanation. Example: There are three things I love: reading, writing, and painting. Semicolon: Use a semicolon to connect closely related independent clauses. Example: She finished her work; then, she went for a walk. Apostrophe: Use an apostrophe to indicate possession or contraction. Examples: John's car is in the garage. That's the book I was looking for. Remember, proper punctuation helps to convey meaning clearly and helps in effective communication.








