Table of Contents
Sodium phosphate refers to a group of chemical compounds that contain sodium (Na) cations and phosphate (PO43-) anions. Sodium phosphate compounds are widely used in various applications, including food and beverages, water treatment, cleaning agents, and as buffering agents in chemical laboratories. They are also used in some medical and pharmaceutical preparations.
It’s important to note that sodium phosphate compounds should be handled and used in accordance with proper safety precautions and guidelines, as they can be hazardous if not used appropriately.
Structural formula of Sodium Phosphate
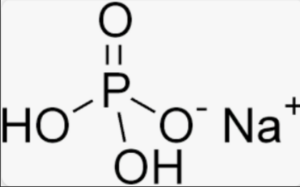
In these structural formulas, the sodium (Na) cations are represented by the Na+ symbol, the phosphate (PO4) anion is represented by the P surrounded by four oxygen (O) atoms, and hydrogen (H) atoms are also shown for disodium phosphate and monosodium phosphate.
Uses of Sodium Phosphate
- Food Industry: Sodium phosphate is used as a food additive and preservative. It can act as a pH buffer, emulsifier, and stabilizer in processed foods, including meat products, cheeses, and baked goods.
- Water Treatment: Sodium phosphate compounds are used in water treatment processes to prevent the formation of scale and corrosion in boilers and cooling systems.
- Cleaning Products: Sodium phosphate is used in some cleaning products, particularly as a builder or water softener to enhance the effectiveness of detergents.
- Medical Applications: Sodium phosphate solutions are used in medical procedures, such as colon cleansing before surgery or medical imaging.
- Laboratory Reagent: Sodium phosphate is used as a reagent in various laboratory applications, including buffer solutions, DNA and RNA isolation, and enzyme assays.
- Fertilizers: Sodium phosphate is sometimes used as a source of phosphorus in fertilizers, promoting plant growth and development.
- Industrial Applications: Sodium phosphate compounds are utilized in several industrial processes, such as metal surface treatment, ceramics production, and textile dyeing.
Physical Properties of Sodium Phosphate Formula
- State: Ozone is a gas at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. It exists as a pale blue gas with a characteristic pungent odor.
- Density: The density of ozone gas is higher than that of oxygen gas (O2). Ozone has a density of about 2.14 kg/m³, which is higher than the density of air.
- Melting Point: Ozone has a low melting point of -192.2°C (-314.0°F). At temperatures below its melting point, ozone solidifies into dark blue crystals.
- Boiling Point: Ozone does not have a distinct boiling point because it decomposes before reaching its boiling point. However, it starts to decompose into oxygen gas at temperatures above -112°C (-170°F).
- Solubility: Ozone is moderately soluble in water. It dissolves in water, forming a weakly acidic solution called ozonated water.
- Stability: Ozone is a relatively unstable molecule and readily decomposes back into oxygen. It is highly reactive and can react with various substances, including organic compounds and pollutants.
- Reactivity: Ozone is a powerful oxidizing agent. It reacts with many substances, including metals, organic compounds, and atmospheric pollutants. This reactivity makes it effective for various applications, such as disinfection, water treatment, and air purification.
- Odour: Ozone has a distinctive odor often described as “fresh” or “sharp.” It is noticeable even at low concentrations and can be detected near electrical equipment or during thunderstorms, where ozone is formed by lightning.
- Toxicity: Ozone is toxic and can be harmful to living organisms. Inhalation of high concentrations of ozone can irritate the respiratory system, cause breathing difficulties, and damage lung tissue. It is important to handle ozone with caution and ensure proper ventilation.
Chemical Properties of Sodium Phosphate Formula
- State: Sodium phosphate compounds are typically white, crystalline solids at room temperature. However, they can also be found as granules or powders.
- Solubility: Sodium phosphate compounds are highly soluble in water. The solubility depends on the specific compound and its hydration state. For example, trisodium phosphate (Na3PO4) is highly soluble in water, while disodium phosphate (Na2HPO4) and monosodium phosphate (NaH2PO4) have lower solubilities but are still readily soluble.
- Hydrates: Sodium phosphate compounds can exist in various hydrate forms, where water molecules are bound to the compound. The hydrates can have different physical properties, including crystal structure and solubility. For example, disodium phosphate dihydrate (Na2HPO4·2H2O) and monosodium phosphate monohydrate (NaH2PO4·H2O) are common hydrate forms.
- Melting and Boiling Points: The melting and boiling points of sodium phosphate compounds depend on the specific compound and its hydration state. Generally, they have relatively high melting points. For example, trisodium phosphate has a melting point around 73.4 °C (164.1 °F), while disodium phosphate dihydrate melts around 35 °C (95 °F).
- pH: Sodium phosphate compounds are commonly used as buffering agents due to their ability to maintain a stable pH in aqueous solutions. The pH of a sodium phosphate solution depends on the specific compound and its concentration.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sodium phosphate, with the chemical formula Na3PO4, is an important compound with various applications. It is commonly used in the food and beverage industry as a food additive and buffering agent. Sodium phosphate is also utilized in medical and pharmaceutical settings as a saline laxative and in some dental products. Additionally, it finds use in water treatment, detergents, and as a component in certain chemical reactions. The versatile nature of sodium phosphate makes it a valuable compound in various industries.
Solved Examples on Sodium Phosphate Formula
Example 1: Calculating the molarity of a sodium phosphate solution
Problem: Calculate the molarity of a solution prepared by dissolving 10 grams of trisodium phosphate (Na3PO4) in enough water to make a final volume of 500 mL.
Solution:
Step 1: Convert the mass of trisodium phosphate to moles.
10 grams of Na3PO4 * (1 mole Na3PO4/ molar mass Na3PO4) = x moles
Step 2: Calculate the molarity of the solution.
Molarity (M) = moles / volume (in liters)
Molarity = x moles / 0.5 L
Final Answer: The molarity of the sodium phosphate solution is M moles/L.
Example 2: Precipitation reaction of sodium phosphate with calcium chloride Problem: Write a balanced chemical equation for the precipitation reaction between sodium phosphate (Na3PO4) and calcium chloride (CaCl2).
Solution: The balanced chemical equation for the precipitation reaction is:
3Na3PO4 + 2CaCl2 → Ca3(PO4)2 + 6NaCl
In this reaction, sodium phosphate reacts with calcium chloride to form calcium phosphate (Ca3(PO4)2) as a precipitate and sodium chloride (NaCl) as a soluble product.
Frequently Asked Questions on Sodium Phosphate Formula
1: What is sodium phosphate used for?
Answer: Some common uses of sodium phosphate compounds include:
- Food and Beverage Industry: Sodium phosphate compounds are used as food additives for various purposes, including pH regulation, emulsification, and texture improvement. They are commonly used in processed meats, baked goods, dairy products, and beverages.
- Water Treatment: Sodium phosphate compounds are utilized in water treatment processes, such as boiler water conditioning and water softening. They help prevent the formation of scale and reduce the potential for corrosion.
- Cleaning Agents: Trisodium phosphate (TSP) is a popular cleaning agent used in household cleaners, detergents, and degreasers. It effectively removes grease, grime, and stains from surfaces.
- Industrial Applications: Sodium phosphate compounds find application in various industrial processes, including metal treatment, textile processing, and as catalysts in chemical reactions.
- Laboratory and Research: Sodium phosphate compounds are used in laboratories as buffering agents to maintain pH levels in chemical and biological experiments. They help stabilize the pH of solutions, making them suitable for specific experimental conditions.
- Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Preparations: Some sodium phosphate compounds have pharmaceutical applications, particularly in the formulation of oral rehydration solutions and laxatives.
2: Is sodium phosphate formula acid or base?
Answer: Trisodium phosphate which is also known as sodium phosphate, is a chemical compound with the formula Na3PO4. It is basic accepting protons (H+) and forming the PO43- anion.
3: Why is sodium phosphate used in food?
Answer: Sodium phosphate is used in food for various purposes. It helps regulate pH levels, acting as a buffering agent, and stabilizes the acidity or alkalinity of food products. It also functions as an emulsifier, improving the texture and stability of emulsions. Sodium phosphate enhances moisture retention, extends the shelf life of foods, and contributes to improved texture and mouthfeel. Its use is regulated to ensure safety and adherence to guidelines.
4: What is the pH of sodium phosphate?
Answer: Here are the approximate pH ranges for commonly used sodium phosphate compounds at typical concentrations:
- Trisodium Phosphate (Na3PO4): The pH of a 0.1 M solution of trisodium phosphate is around 11-12, making it alkaline.
- Disodium Phosphate (Na2HPO4): The pH of a 0.1 M solution of disodium phosphate is around 8-9, making it slightly alkaline.
- Monosodium Phosphate (NaH2PO4): The pH of a 0.1 M solution of monosodium phosphate is around 4-5, making it acidic.
5: Is sodium phosphate a weak acid or base?
Answer: Here are the general classifications for the commonly used sodium phosphate compounds:
- Trisodium Phosphate (Na3PO4): Trisodium phosphate is not considered an acid or a base. It is a salt formed by the reaction of a strong base (sodium hydroxide) with a strong acid (phosphoric acid).
- Disodium Phosphate (Na2HPO4): Disodium phosphate is a weak base. It can accept protons (H+) from water to form hydroxide ions (OH–) and sodium dihydrogen phosphate (NaH2PO4).
- Monosodium Phosphate (NaH2PO4): Monosodium phosphate is a weak acid. It can donate protons (H+) to water, forming hydronium ions (H3O+) and hydrogen phosphate ions (HPO42-).
6: What is sodium phosphate?
Answer: Sodium phosphate is a compound composed of sodium cations (Na+) and phosphate anions (PO43-). It exists in several forms, including monosodium phosphate (NaH2PO4), disodium phosphate (Na2HPO4), and trisodium phosphate (Na3PO4).
7: What is a sodium phosphate enema?
Answer: A sodium phosphate enema is a medical procedure that involves the introduction of a solution containing sodium phosphate into the rectum and colon. It is used for various purposes, such as bowel cleansing, constipation relief, or as a preparation for certain medical procedures. The solution works by increasing water content in the bowel, stimulating bowel movement, and softening stool.
8: Is sodium phosphate a salt?
Answer: Yes, sodium phosphate is a salt. It is composed of sodium cations (Na+) and phosphate anions (PO43-). Salts are formed when an acid reacts with a base, and in the case of sodium phosphate, it is formed by the reaction between phosphoric acid and sodium hydroxide. Sodium phosphate is available in various forms, such as monosodium phosphate (NaH2PO4), disodium phosphate (Na2HPO4), and trisodium phosphate (Na3PO4), each having different applications and properties.






