Table of Contents
Force and Pressure Class 8 Notes Extra Questions Science Chapter 11
Force and Pressure Class 8 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is the name of the instrument used to measure atmospheric pressure?
Answer:
Barometer
Question 2.
Give two examples of contact force.
Answer:
- Muscular force
- Force of friction
Question 3.
Name the force exerted on a ball of dough to make a flat chapati.
Answer:
Muscular force
Question 4.
What kind of force is an electrostatic force?
Answer:
Non-contact force
Question 5.
Is the gravity a property of earth only?
Answer: No

Class 8 HOTS Course
The Class 8 HOTS Course enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills through engaging activities and advanced learning techniques, ensuring academic excellence.
Question 6.
Name the force due to which every object falls on earth.
Answer:
Gravitational force
Question 7.
What do you mean by pressure?
Answer:
Force per unit area (Force/Area)
Question 8.
Do liquids and gases also exert pressure?
Answer:
Yes
Question 9.
What are the two states of motion?
Answer:
- The state of rest.
- The state of motion.
Question 10.
What kind of force is friction?
Answer:
Contact force
Question 11.
What type of force is gravitational force?
Answer:
Non-contact force
Question 12.
Is it true that force acting on an object can also change its shape?
Answer:
Yes, it is true.
Question 13.
While sieving grains, small pieces fall down. Which force pulls them down?
Answer:
Gravitational force
Question 14.
How can we change the speed and the direction of a moving body?
Answer:
By applying force.
Question 15.
What is the distance moved by an object in unit time called?
Answer:
Speed
Question 16.
Does force of gravity act on dust particles?
Answer:
Yes
Question 17.
Does the force of gravitation exist between two astronauts in space?
Answer:
Yes
Question 18.
What is a force?
Answer:
A push or pull on an object is called force.
Question 19.
What is the SI unit of pressure?
Answer:
Pascal (Pa)
Question 20.
At least how many objects are needed to apply a force?
Answer:
At least two objects are needed to apply a force.
Question 21.
Give one example of gravitational force.
Answer:
An apple falling from the tree to ground.
Question 22.
What is meant by atmospheric pressure?
Answer:
The weight of air acting per unit area is known as atmospheric pressure.
Question 23.
What do you mean by magnitude?
Answer:
The strength of a force is usually expressed by its magnitude.
Question 24.
What is muscular force?
Answer:
The force resulting due to the action of muscles is known as muscular force.
Question 25.
What is contact force?
Answer:
Force that can be applied only when it is in contact with an object is called contact force.
Question 26.
What do you mean by the term atmosphere?
Answer:
The envelop of air all around us is known as atmosphere.
Force and Pressure Class 8 Extra Questions Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define pressure.
Answer:
The force acting per unit surface area is called pressure. SI unit of pressure is measured in Newton/ Metre2, which is equal to 1 Pascal (Pa).
Question 2.
How do fluids exert pressure?
Answer:
Fluids exert pressure in all directions. Fluids also exert pressure on the walls of the container that hold them.
Question 3.
A force of 100 N is applied on an area of 4 m2. Compute pressure being applied on the area.
Answer:
Given: Force = 100 N, Area = 4 m2
∴ Pressure = \(\frac{\text { Force }}{\text { Area }}=\frac{100}{4}\) = 25pa.
Question 4.
Which force is responsible for downward movement of a parachutes? Will he come down with the same speed without the parachute?
Answer:
Force of gravity is responsible for this downward movement. No, without parachute he will come down with a higher speed.
Question 5.
Two thermocol balls held close to each other move away from each other. When they are released, name the force which might be responsible for this phenomenon. Explain.
Answer:
Electrostatic force is responsible for this phenomenon. The two balls have similar charges, that’s why they move away due to repulsion between them.
Question 6.
How does an applied force changes the speed of an object?
Answer:
If the applied force is in the direction of motion, the speed of the object increases. But if the force applied in the direction opposite to the motion, then it decreases the speed of the object.
Question 7.
Name the forces acting on the car sticking to an electromagnet in a Junkyard. Which one of them is larger?
Answer:
Magnetic force (in the upward direction) and force of gravity or the weight of the car (downward). Magnetic force is larger than the force of gravity.
Question 8.
What is the similarity between electrostatic and magnetic forces?
Answer:
- Both are non-contact forces.
- Both are attractive as well as repulsive forces.
Question 9.
What are the effects of force on an object?
Answer:
- Force can change the state of motion of an object.
- Force changes the speed of a moving object.
- Force can cause an object to turn or change direction.
- Force can change the shape of an object.
Force and Pressure Class 8 Extra Questions Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is force? State the difference between contact force and non-contact force.
Answer:
| Contact force | Non-contact force |
| Force that can be applied only when it is in contact with an object is called a contact force, e.g., muscular force, frictional force | The force exerted on an object without touching it is known as non-contact force, e.g., gravitational force, magnetic force |
Question 2.
Define the different types of forces.
Answer:
Force can act on a body from a distance or by being in contact with it. Depending on this, forces can be classified as contact and non-contact forces.
- Contact forces: When force is applied on an object by direct or indirect physical contact the applied force is called contact force. Muscular and frictional force are example of contact force.
- Muscular force: The force resulting due to the action of muscles is known as the muscular force.
- Frictional force: The force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other.
- Non-contact forces: When a force is applied to an object by another body that is not in direct contact with it is called non-contact force. Gravitational, magnetic and electrostatic force are example of non-contact force.
- Gravitational force: The attractive force of the earth which acts upon all the objects is known as the force of gravity or just gravity.
- Electrostatic force: The force exerted by a charged body on another charged or uncharged 1 body is known as electrostatic force.
- Magnetic force: The force exerted between a magnet and other magnet or magnetic material is known as magnetic force.
Question 3.
Why it is easier to walk on soft sand if we have flat shoes rather than shoes with sharp heels (or pencil heels)?
Answer:
A flat shoe has a greater area in contact with the soft sand and exerts less pressure on the soft ground. Due to this the ‘flat’ shoes do not sink much in soft sand and it is easy to walk on it. On the other hand, a sharp heel has a small area in contact with the soft sand and exerts a greater pressure on the sand. Due to this, the sharp heels sink deep into soft sand making it difficult for the wearer to walk on it.
Question 4.
What is pressure? What is the relation of pressure with area on which it is applied?
Answer:
Force exerted on per unit area is called pressure. Pressure is related with area on which it is applied. When the area is increased the pressure exerted is less. But when the area on which pressure is exerted is decrease the pressure increases. So we can conclude that pressure increases with decrease in area. List the characteristics of pressure exerted by a liquid.
- Liquid exerts pressure in all directions.
- Pressure in liquid does not depends on shape, size and surface area of the container.
- Pressure increases with depth.
- All points at the same level in a liquid are at the same pressure.
- Pressure does not depend on the surface of the immersed object.
Also Read: NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Force and Pressure
Force and Pressure Class 8 Extra Questions Higher Order Thinking Skills
Question 1.
We know that there is a huge amount of atmospheric pressure on us. But we do not experience its effect why?
Answer:
The pressure of air inside our body is same as that of the atmosphere. Therefore, we do not experience its effect.
Question 2.
Why do sea divers wear specially designed suits?
Answer:
Since the pressure of liquid increases with the increasing depth of sea. Specially designed suits protect scuba divers from the huge pressure of the water underneath.
Question 3.
Two persons are applying forces on two opposite sides of a moving cart. The cart still moves with the same speed in the same direction. What do you infer about the magnitudes and direction of the forces applied?
Answer:
Both the persons are applying forces from opposite direction with equal magnitudes.
Question 4.
An archer shoots an arrow in the air horizontally. However, after moving some distance, the arrow falls to the ground. Name the initial force that sets the arrow in motion. Explain why the arrow ultimately falls down.
Answer:
The initial force is muscular force which sets the arrow in motion. The force of gravity that acts on the arrow in the downward direction brings it to the ground.
Question 5.
Two rods: A and B, having same weight and equal length have different thickness. Rod A is thinner while Rod B is thicker. They are held vertically on the surface of sand. Which one of them will sink more? Why?
Answer:
Rod A will go deeper as it has a smaller area of contact, therefore the same force produces more pres¬sure. In case of rod B the same force produces less pressure.
Question 6.
It is difficult to cut cloth using a pair of scissors with blunt blades. Explain.
Answer:
Blunt blades have larger area compared to the sharp-edged blades. Thus, the applied force produces a lower pressure in case of blunt blades, which makes it difficult to cut the cloth.
Question 7.
Observe the figures given below carefully.
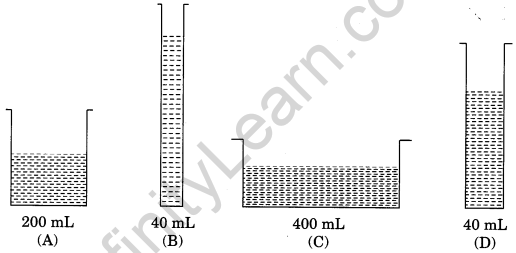
Volume of water in each vessel is shown above. Arrange them in order of decreasing pressure at the base of each vessel. Explain the reason.
Answer:
Pressure of a liquid column depends upon the height of the liquid column and not on volume of the liquid. Decreasing order of pressure at the base of each vessel is B > D > A > C.
Force and Pressure Class 8 Extra Questions Value-Based Questions
Question 1.
On Lokesh’s birthday Shreya was given charge to amuse children with some little tricks. Shreya sticked balloons to the wall by just rubbing them in her clothes. She bent the water stream from a tap without touching it. She did so by bringing big balloon near to the flowing water. All children were very happy on seeing this little magic. Everybody praised Shreya.
- How do balloons stick to walls?
- How Shreya bent the water stream by bringing a big balloon near it and without touching it?
- What values of Shreya is shown here?
Answer:
- On rubbing the balloon with hair or clothes, it acquire negative charges. The negative charges are attracted to the positive charges on the wall and balloon sticks to the wall.
- Negative charge on the balloon attracts positive charge on water molecules. Thus, bent the water molecules.
- Shreya is dutiful, friendly with scientific aptitude.
Activities and Projects
Question 1.
Make a 50 cm × 50 cm bed of dry sand about 10 cm in thickness. Make sure that its top surface is levelled. Take a wooden or a plastic stool. Cut two strips of graph paper each with a width of 1 cm. Paste them vertically on any leg of the stool—one at the bottom and the other from the top. Now gently put the stool on the sand bed with its legs resting on the sand. Increase the size of sand bed if required. Now put a load, say a school bag full of books, on the seat of the stool. Mark the level of sand on the graph strip. This would give you the depth, if any, to which the legs of stool sink in sand. Next, turn the stool upside down so that now it rests on its seat on the sand bed. Note the depth to which the stool sinks now. Next, put the same load on the stool and note the depth to which it sinks in the sand. Compare the pressure exerted by the stool in the two situations.
Answer:
Pressure exerted by the stool is greatest in first situation.
Question 2.
Take a tumbler and fill it with water. Cover the mouth of the tumbler with a thick card simi¬lar to that of a postcard. Hold the tumbler with one hand while keeping the card pressed to its mouth with your other hand. Turn the tumbler upside down while keeping the card pressed to its mouth. Make sure that the tumbler is held vertical. Gently remove the hand pressing the card. What do you observe? Does the card get detached allowing the water to spill? With a little practice you will find that the card continues to hold water in the tumbler even after it is not supported by your hand. Also try this activity by using a piece of cloth to hold the tumbler in an upside down position (Fig. 11.10).
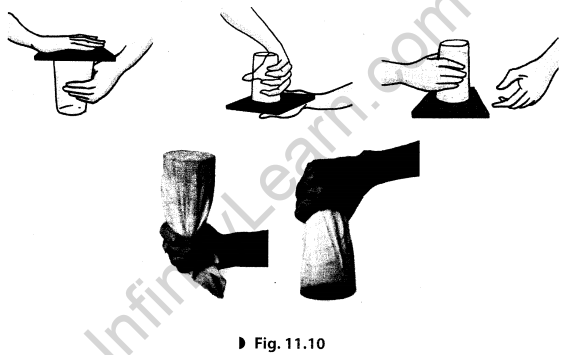
Answer:
Do it yourself.
Question 3.
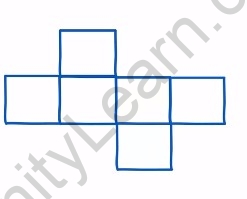
Take 4-5 plastic bottles of different shapes and sizes. Join them together with small pieces of glass or rubber tube as shown in Fig. 11.11. Keep this arrangement on a level surface. Now pour water in any one of the bottles. Note whether the bottle in which water is poured gets filled first or all the bottles get filled up simultaneously. Note the level of water in all the bottles from time to time. Try to explain your observations.
For more information on force and pressure visit:
kids.earth.nasa.gov/archive/air_pressure/
Answer:
Water level in all the bottles will be same because pressure will be same at same height.
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct option.
Question 1.
The pressure which is exerted by air around us is known as
(a) force
(b) atmospheric pressure
(c) muscular force
(d) friction
Question 2.
Force acting on per unit area is called
(a) non-contact forces
(b) contact forces
(c) force
(d) pressure
Question 3.
A ___________ exerted by an object on another is a force.
(a) Push or pull
(b) Contact or non-contact force
(c) Pressure
(d) Magnitude
Question 4.
The force exerted by the earth to pull the object towards itself is called
(a) electrostatic force
(b) gravitational force
(c) muscular force
(d) contact force
Question 5.
Muscular force is also called ___________ force.
(a) non-contact
(b) contact
(c) gravitational
(d) magnetic
Question 6.
The force exerted by a charged body on another char
(a) gravitational force
(b) electrostatic force
(c) non-contact force
(d) contact force
Question 7.
Force changes the
(a) motion of body
(b) speed of body
(c) shape of body
(d) all of these
Question 8.
The force exerted by our muscle is called
(a) electrostatic force
(b) muscular force
(c) gravitational force
(d) non-contact force
Question 9.
1 kilogram weight is equal to
(a) 98 N
(b) 9.8 N
(c) 0.98 N
(d) 0.098 N
Question 10.
A spring balance is used for measuring
(a) mass
(b) weight
(c) pressure
(d) speed
Question 11.
Two boys A and B are applying force on a block. If the block moves towards the boy A, which one of the following statements is correct?
(a) Magnitude of force applied by A is greater than that of B.
(b) Magnitude of force applied by A is smaller than that of B.
(c) Net force on the block is towards B.
(d) Magnitude of force applied by A is equal to that of B.
Question 12.
When two forces act in opposite directions, then net force acting is the
(a) sum of two forces
(b) difference between two forces
(c) both of these
(d) none of these
Question 13.
The strength of force is expressed by its
(a) weight
(b) mass
(c) magnitude
(d) longitudinal force
Question 14.
Leaves fall down on the ground due to
(a) electrostatic force
(b) magnetic force
(c) gravitational force
(d) muscular force
Question 15.
State of motion is described by
(a) Position of rest
(b) Position of motion
(c) Both by the state of rest or motion
(d) None of these
Question 16.
When the hammer strikes the gong of an electric bell, which of the following force is responsible for the movement of hammer?
(a) Gravitational force alone
(b) Magnetic force alone
(c) Electrostatic force alone
(d) Frictional force alone
Question 17.
During dry weather, while combing hair, sometimes we experience hair flying apart. The force respon¬sible for this is
(a) force of gravity
(b) force of friction
(c) electrostatic force
(d) magnetic force
Question 18.
A container is filled with water as shown in the given figure. Which of the following statements is correct about pressure of water?
(a) Pressure at A > Pressure at B > Pressure at C
(b) Pressure at A = Pressure at B = Pressure at C
(c) Pressure at A < Pressure at B > Pressure at C
(d) Pressure at A < Pressure at B < Pressure at C
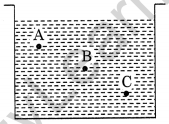
Question 19.
Two objects repel each other. This repulsion could be due to
(a) frictional force only
(b) electrostatic force only
(c) magnetic force only
(d) either a magnetic or an electrostatic force
Question 20.
Which one of the following forces is a contact force?
(a) Force of gravity
(b) Magnetic force
(c) Force of friction
(d) Electrostatic force
Question 21.
A brick is kept in three different ways on a table as shown in given figure. The pressure exerted by the brick on the table will be
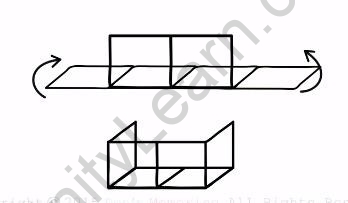
(a) maximum in position A
(b) maximum in position C
(c) maximum in position B
(d) equal in all cases
Answer:
1. (b)
2. (d)
3. (a)
4. (b)
5. (b)
6. (b)
7. (d)
8. (b)
9. (b)
10. (b)
11. (b)
12. (b)
13. (c)
14. (c)
15. (c)
16. (c)
17. (c)
18. (d)
19. (d)
20. (c)
21. (a)
III. Fill in the Blanks
Fill in the blanks with suitable word/s.
1. We ___________ the bucket to take out water from well.
2. The strength of a force is usually expressed by its ___________.
3. ___________ force is the force resulting due to the action of muscles.
4. The envelop of air all around us is called ___________.
5. To open a door we or ___________ the door.
6. Force of friction is an example of ___________ force.
7. Force ___________ is called pressure.
8. Force has ___________ as well as direction.
9. Fruits fall ___________ due to the force of gravity.
10. The body at rest is called ___________ body.
11. ___________ and ___________ forces are the two kinds of forces.
12. Force exerted by magnet is called ___________ force.
13. We apply force on ___________ while walking.
14. Force is ___________ to pressure.
15. The ___________ is measured by an instrument called barometer.
Answer:
1. pull
2. magnitude
3. Muscular
4. atmosphere
5. push, pull
6. contact
7. per unit area
8. magnitude
9. downward
10. stationary
11. Contact, non-contact
12. magnetic
13. ground
14. directly proportional
15. atmospheric pressure
III. Match the following
Match the items given in column I suitably with those given in column II.
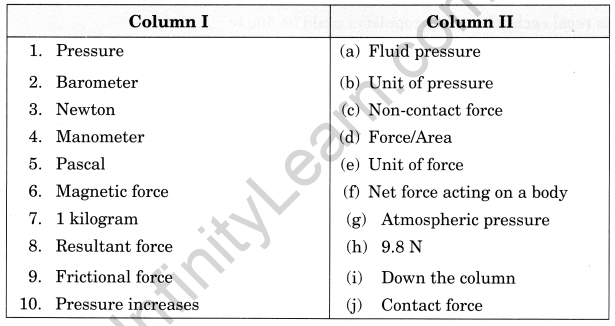
Answer:
1. (d)
2. (g)
3. (e)
4. (a)
5. (b)
6. (c)
7. (h)
8. (f)
9. (j)
10. (i)
IV. True or False
State whether the given statements are true or false.
1. Force applied on an object in opposite directions add to one another.
2. Pressure does not depend on area of contact.
3. A force can change the state of motion of an object.
4. Force cannot change the speed of an object.
5. Atmospheric pressure is less at higher altitudes.
6. Force of gravity is a contact force.
7. Muscular force is also known as contact force.
8. Pascal is the unit of force.
9. To move an object faster it has to be pushed or pulled repeatedly.
10. Magnitude is the strength of force.
11. Force can change the shape of an object.
12. At least two objects must interact for a force to come into play.
13. Magnetic force is a non-contact force.
14. An apple from a tree falls on the ground due to the force of gravity.
15. Newton is the unit of force.
Answer:
1. False
2. False
3. True
4. False
5. True
6. False
7. True
8. False
9. True
10. True
11. True
12. True
13. True
14. True
15. True