Table of Contents
NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 – Microbes in Human Welfare
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
1. The vitamin whose content increases following the conversion of milk into curd by lactic acid bacteria is a. vitamin C
b. vitamin D
c. vitamin B12
d. vitamin E.
Solution:
Option (c) is the answer
2. Wastewater treatment generates a large quantity of sludge, which can
be treated by:
a. anaerobic digesters
b. floc
c. chemicals
d. oxidation pond.
Solution:
Option (a) is the answer.
3. Methanogenic bacteria are not found in:
a. rumen of cattle
b. gobar gas plant
c. bottom of water-logged paddy fields
d. activated sludge.
Solution:
Option (d) is the answer.
4. Match the following list of bacteria and their commercially important
products:
| Bacterium
A. Aspergillus niger B. Acetobacter acetic C. Clostridium bretylium D. Lactobacillus |
Product
i. Lactic acid ii. Butyric acid iii. Acetic acid iv. Citric acid |
Choose the correct match:
a. A-ii, B-iii, C-iv, D-i
b. A-ii, B-iv, C-iii, D-i
c. A-iv, B-iii, C-ii, D-i
d. A-iv, B-i, C-iii, D-ii
Solution:
Option (c) is the answer.
5. Match the following list of bioactive substances and their roles:
| Bioactive Substance
A. Statin B. Cyclosporin A C. Streptokinase D. Lipase |
Role
i. Removal of oil stains ii. Removal of clots from blood vessels iii. Lowering of blood cholesterol iv. Immuno-suppressive agent |
Choose the correct match:
a. A-ii, B-iii, C-i, D-iv
b. A-iv, B-ii, C-i, D-iii
c. A-iv, B-i, C-ii, D-iii
d. A-iii, B-iv, C-ii, D-i
Solution:
Option (d) is the answer
6. The primary treatment of wastewater involves the removal of:
a. dissolved impurities
b. stable particles
c. toxic substances
d. harmful bacteria.
Solution:
Option (b) is the answer.
7. BOD of wastewater is estimated by measuring the amount of:
a. total organic matter
b. biodegradable organic matter
c. oxygen evolution
d. oxygen consumption.Solution:
Option (d) is the answer.
8. Which one of the following alcoholic drinks are produced without distillation?
a. Wine
b. Whisky
c. Rum
d. Brandy
Solution:
Option (a) is the answer.
9. The technology of biogas production from cow dung was developed in
India largely due to the efforts of:
a. Gas Authority of India
b. Oil and Natural Gas Commission
c. Indian Agricultural Research Institute and Khadi & Village
Industries Commission
d. Indian Oil Corporation
Solution:
Option (c) is the answer.
10. The free-living fungus Trichoderma can be used for:
a. killing insects
b. biological control of plant diseases
c. controlling butterfly caterpillars
d. producing antibiotics
Solution:
Option (b) is the answer.
11. What would happen if oxygen availability to activated sludge flocs is
reduced?
a. It will slow down the rate of degradation of organic matter
b. The center of flocs will become anoxic, which would cause the death
of bacteria and eventually breakage of flocs.
c. Flocs would increase in size as anaerobic bacteria would grow
around flocs.
d. Protozoa would grow in large numbers
Solution:
Option (b) is the answer.
12. Mycorrhiza does not help the host plant in:
a. Enhancing its phosphorus uptake capacity
b. Increasing its tolerance to drought
c. Enhancing its resistance to root pathogens
d. Increasing its resistance to insects.Solution:
Option (d) is the answer.
13. Which one of the following is not a nitrogen-fixing organism?
a. Anabaena
b. Nostoc
c. Azotobacter
d. Pseudomonas
Solution:
Option (d) is the answer.
14. Big holes in Swiss cheese are made by a:
a. a machine
b. a bacterium that produces methane gas
c. a bacterium producing a large amount of carbon dioxide
d. a fungus that releases a lot of gases during its metabolic activities.Solution:
Option (c) is the answer.
15. The residue left after methane production from cattle dung is:
a. burnt
b. buried in landfills
c. used as manure
d. used in civil construction.
Solution:
Option (c) is the answer
16. Methanogens do not produce:
a. oxygen
b. methane
c. hydrogen sulfide
d. carbon dioxide.
Solution:
Option (a) is the answer.
17. Activated sludge should have the ability to settle quickly so that it can:
a. be rapidly pumped back from the sedimentation tank to the aeration tank
b. absorb pathogenic bacteria present in wastewater while sinking
to the bottom of the settling tank
c. be discarded and anaerobically digested
d. absorb colloidal organic matter.
Solution:
Option (a) is the answer.
18. Match the items in Column ‘A’ and Column ‘B’ and choose the correct answer.
| Column I
A. Ladybird B. Mycorrhiza C. Biological control D. Biogas |
Column II
i. Methane bacterium ii. Trichoderma iii. Aphids iv. Glomus |
The correct answer is:
a. A-ii, B-iv, C-iii, D-i
b. A-iii, B-iv, C-ii, D-i
c. A-iv, B-i, C-ii, D-iii
d. A-iii, B-ii, C-i, D-iv
Solution:
Option (b) is the answer.
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Why does ‘Swiss cheese’ have big holes? Solution:
The big holes in ‘swiss cheese’ are made by a bacterium known as Penicillium Sherman which consumes the lactose protein in the cheese to form lactic acid
2. What are fermentors?
Solution:
Fermentors are large vessels which are used for the commercial production of fermented products. It is used for the fermentation by growing microorganisms.
3. Name a microbe used for statin production. How do statins lower blood cholesterol level?
Solution:
A microbe which is used in the production of statin is Monascuspurpureus.
4. Why do we prefer to call secondary wastewater treatment as a biological treatment?
Solution:
It is preferred to call secondary wastewater treatment as biological treatment as it involves the use of micro-organisms for the treatment of wastewater.
5. Which Nucleopolyhydro viruses are being used nowadays?
Solution:
Nucleopolyhydro viruses (NPVs) are being used nowadays as a biological pesticide to kill insects such as caterpillars and butterflies which damages plants and crops.
6. How has the discovery of antibiotics helped mankind in the field of medicine?
Solution:
The discovery of antibiotics has helped mankind in the field of medicine by providing resistance against bacterial infections.
7. Why is distillation required for producing certain alcoholic drinks?
Solution:
Distillation is required for producing certain alcoholic drinks because it increases the overall alcohol content in alcoholic drinks.
8. Write the most important characteristic that Aspergillus niger, Clostridium bretylium, and Lactobacillus share.
Solution:
The most important characteristic that Aspergillus niger, Clostridium butylicum, and Lactobacillus share are that they all are micro-organisms which are involved in the production of various acids. Aspergillus niger is used for the production of citric acid, Clostridium butylicum is used for the production of butyric acid and Lactobacillus is used for the production of lactic acid.
9. What would happen if our intestine harbours microbial flora exactly similar to that found in the rumen of cattle?
Solution:
If our intestine harbours microbial flora exactly similar to that found in the rumen of cattle then our digestive system would be able to digest cellulose and methane can be produced in our digestive system.
10. Give any two microbes that are useful in biotechnology.
Solution:
E. Coli and agrobacterium are the two microbes which are useful in the biotechnology.
11. What is the source organism for ECORI, restriction endonuclease?
Solution:
The source organism for ECORI, restriction endonucleases Escherichia coli (e.g., E.Coli). It is a gram-negative, rod-shaped bacteria which is found in the intestines of warm-blooded animals.
12. Name any genetically modified crop.
Solution:
Bt cotton is a genetically modified (GM) crop which produces an insecticide which makes the plant resistant to bollworm.
13. Why are blue-green algae not popular as bio fertilizers?
Solution:
Blue-green algae are not popular as biofertilizers as they produce slippery mucus and also cause algal bloom.
14. Which species of Penicillium produces Roquefort cheese?
Solution:
The species of Penicillium which produces Roquefort cheese is Penicillium roqueforti.
15. Name the states involved in the Ganga action plan.
Solution:
The states which are involved in Ganga action plan are Jharkhand, UP, Bihar, West Bengal.
16. Name any two industrially important enzymes.
Solution:
i) Lipase: It is used for the removal of oily stains from clothes and it is used widely in detergents.
ii) Amylase: It is used in the food and fermentation industry.
17. Name an immune immunosuppressive agent?
Solution:
Cyclosporin A is an immune-suppressive agent produced by the Trichodermapolysporum fungus.
18. Give an example of a rod-shaped virus.
Solution:
An example of the rod-shaped virus is Tobacco Mosaic virus which causes a disease known as a mosaic disease in tobacco leaves
19. What is the group of bacteria found in both the rumen of cattle and stage of sewage treatment?
Solution:
Methanogens are the group of bacteria found in both the rumen of cattle and sludge of sewage treatment. Methanogens release methane gas.
20. Name a microbe used for the production of Swiss cheese.
Solution:
A microbe which is used for the production of Swiss cheese is Penicillium Sherman which consumes the lactose protein in the cheese to form lactic acid
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Why are flocs important in biological treatment of wastewater?
Solution:
Flocs are important in the biological treatment of wastewater as they help in reducing the biological Oxygen Demand (i.e., B.O.D) in the water to make it less polluted and habitable for aquatic animals, reduce the pathogens and digest the organic waste.
2. How has the bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis helped us in controlling caterpillars of insect pests?
Solution:
The bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis helps us in controlling caterpillars of insects’ pests by producing a type of endotoxin in the midgut of the caterpillar after it gets ingested by the pest. The released endotoxin will destroy the midgut lining of the insects.
3. How do mycorrhizal fungi help the plants harbouring them?
Solution:
Mycorrhiza is a fungus which helps the plants harbouring them in drawing more nutrients like phosphorous from the soil and transferring it to the host plant. This also helps ion drawing more water from the soil which increases the ability of plants to withstand the environmental conditions like drought.
4. Why are cyanobacteria considered useful in paddy fields?
Solution:
Cyanobacteria are considered to be useful in the paddy fields because it fixes the nitrogen from the atmosphere and provides organic matter which increases the fertility of the soil.
5. How was penicillin discovered?
Solution:
In 1921, Alexander Fleming discovered penicillin accidentally. Once returned from a vacation to find that one of his staphylococcus culture plates had accidentally gotten contaminated with mould. The mould inhibited the growth of staphylococcus culture. This made him conclude that the antibiotic was isolated from the fungus which was called Penicillium notatum.
6. Name the scientists who were credited for showing the role of Penicillin as an antibiotic?
Solution:
Alexander Fleming discovered penicillin in 1921 but he was not credited for showing its role as an antibiotic.
7. How do bioactive molecules of fungal origin help in restoring good health of humans?
Solution:
Bioactive molecules of fungal origin help in restoring the good health of humans as a number of bioactive molecules are significant in the medical treatment of humans.
a) Statin which helps in lowering the blood cholesterol level
b) Cyclosporin A which is an immunosuppressive agent.
c) Lipase is an enzyme which can remove oil stains and also digests the fats in our digestive system.
8. What roles do enzymes play in detergents that we use for washing clothes? Are these enzymes produced from some unique microorganisms?
Solution:
Enzymes like lipase and proteases are enzymes which play an important role in detergents. They are added in detergent formulations to clean and remove oily stains from the clothes.
9. What is the chemical nature of biogas? Name an organism which is involved in biogas production?
Solution:
Biogas consists of three major constituent gases. Methane (CH3) is present in about 60-70 % of the total volume, Carbon dioxide (CO2) is present in about 30-40% of the total volume and Hydrogen sulphide is present in about 0.1% of the total volume. Methanogens are the organisms which are involved in biogas production.
10. How do microbes reduce the environmental degradation caused by chemicals?
Solution:
Microbes help in reducing the environmental degradation caused by chemicals. The bioremediation can be observed in agriculture. Bio fertilizers consist of microbes which enrich the soil by fixing the nitrogen from the atmosphere. Bio pesticides are also used to kill pests by producing an endotoxin which is ingested by the pest and causes the midgut lining to get destroyed.
11. What is a broad-spectrum antibiotic? Name one such antibiotic.
Solution:
Broad-spectrum antibiotics are a class of antibiotics which can be used for treating multiple bacterial infections. An example of such an antibiotic is Ampicillin.
12. What are viruses parasitising bacteria called? Draw a well-labelled diagram of the same.
Solution:
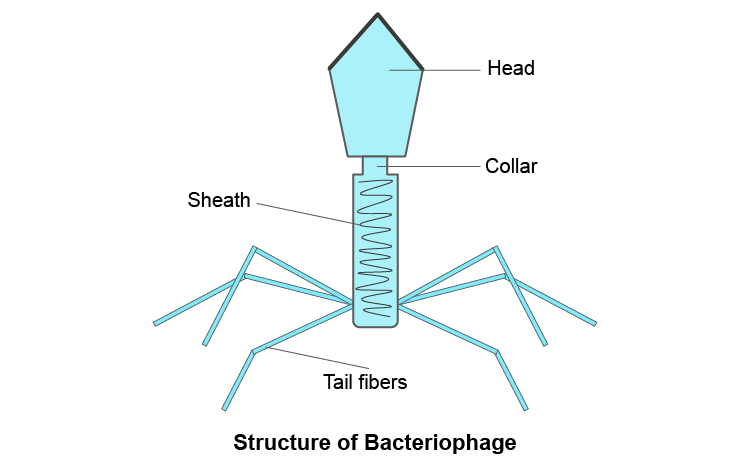
The viruses’ parasitising are known as bacteriophage.
13. Which bacterium has been used as a clot-buster? What is its mode of action?
Solution:
Bacterium Streptococcus produces an enzyme known as streptokinase is widely used as an anti-clotting agent. It can break down clots and prevent clot-associated diseases like heart attacks.
14. What are biofertilizers? Give two examples.
Solution:
Bio fertilizers are used to provide additional supplements for increasing the nutrient content in the soil which helps in the overall development and growth of the plants. Rhizobium and nostoc are examples of biofertilizers.
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Why is aerobic degradation more important than anaerobic degradation for the treatment of large volumes of wastewater rich in organic matter? Discuss.
Solution:
Aerobic degradation is more important than anaerobic degradation for the treatment of large volumes of wastewaters rich in organic matter because:
i) By aerobic degradation, the major part of the organic sludge is digested in the wastewater
ii) After the aerobic degradation of the decomposers, they get separated along with the organic matter which is rich in nutrients.
iii) Biological oxygen demand (BOD) is reduced during the aerobic degradation which makes the water more suitable for aquatic organisms.
iv) Activated sludge is produced in the aerobic degradation that produces gases like methane and carbon dioxide which are the main constituents of the biogas.
2. (a) Discuss the major programs that the Ministry of Environment and Forests, Government of India, has initiated for saving major Indian rivers from pollution.
(b) Ganga has recently been declared the national river. Discuss the implication with respect to pollution of this river.
Solution:
(a) The Ministry of Environment and Forests, Government of India has initiated two plans:
i. Ganga Action Plan
ii. Yamuna Action Plan
These plans were planned to involve a large number of sewage treatment plants. Ganga and Yamuna are very important rivers in terms of flora, fauna and as a tourist and religious attraction spot.
(b) The river Ganga is the largest river in India which covers a total distance of approximately 2520 km across India and Bangladesh and it provides the habitat for more than 140 different species of fish and about 90 different species of amphibians and many endangered species. So that the river Ganga considered as the largest river and requires to be free from the pollution.
3. Draw a diagrammatic sketch of the biogas plant, and label its various components given below: Gas Holder, Sludge Chamber, Digester, Dung + water chamber.
Solution:
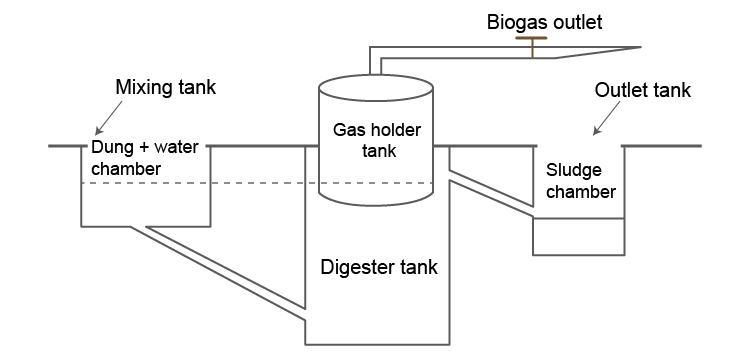
4. Describe the main ideas behind the biological control of pests and diseases.
Solution:
The main ideas behind the biological control of pests and diseases are to control the number of pests by introducing the natural predators to the environment for this pest. Examples are:
i) The Ladybird beetle is used to control the population of insects like Aphids.
ii. Nucleopolyhydro viruses (NPVs) are being used to kill insects such as caterpillars and butterflies which damage the plants and crops. This virus will damage the insect’s midguts.
5. (a) What would happen if a large volume of untreated sewage is discharged into a river?
(b) In what way anaerobic sludge digestion is important in sewage treatments?
Solution:
a) The Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) will get higher which would lead to the death of organisms such as fishes due to low availability of oxygen in the water. Waterborne diseases like cholera and dysentery as people drink water directly from the river will be spread.
b) Anaerobic sludge digestion is important in sewage treatments because it decreases the Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) and the sludge digestion occurs in the presence of anaerobic bacteria and when the sludge is digested the anaerobic bacteria releases a mixture of gases like methane(CH3), carbon dioxide(CO2) and hydrogen sulphide(H2S). These are the main constituents of biogas.
6. Which type of food would have lactic acid bacteria? Discuss their useful application.
Solution:
Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) is widely used to ferment or culture food products. Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) are found in curd. Its useful applications are:
i) The Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) is a type of bacteria which can convert milk into curd by producing an enzyme called lactase.
ii) Some people will suffer from the condition called lactose tolerance which gets allergic to lactose. So the bacteria will help to remove or convert lactose.
iii) Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) increases the vitamin B12 content and they are present in our digestive system also.
Microbes are small living organisms that cannot be seen with the naked eye but need to be observed through a high powered microscope. Bacteria is one of the most prevalent microbes which also has its uses in helping out humans by nitrifying and ammonifying the soil. They are also used in the process of curdling cheese and butter and in the production of antibiotics. Thus, they have many uses that can be utilised commercially by humans.
Important topics of Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare are:
- Microbes in Household Products
- Microbes in Industrial Products
- Microbes in Sewage Treatment
- Microbes in Production of Biogas
- Microbes as Biocontrol Agents
- Microbes as Bio-fertilizers.
The main concepts that are covered in this Chapter are listed below:
- Microbes in Household Products
- Microbes in Industrial Products
- Microbes in Sewage Treatment
- Microbes in Production of Biogas
- Microbes as Biocontrol Agents
- Microbes as Biofertilizers
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Solutions – Download Free PDF can be used as a quick reference to help students understand complicated concepts.
The main features of NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 10
Microbes in Human Welfare are listed below:
- The exact answer is a layout by solutions.
- In support of CBSE exam preparations, it is an extremely helpful tool.
- It is readily available.
- Downloading of solutions is free.
- The answers are simple and to the point.
- To learn rapidly and remember effectively use pointers.
NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 FAQs
How to solve the questions present in Chapter 10 of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Biology faster?
Students in Class 12 should answer the questions in the NCERT textbook to gain an understanding of the key concepts covered. If students have any concerns when solving the problems, they can consult our experts' NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Biology, which contain detailed solutions to each problem. The solutions include detailed explanations for each step to ensure that students understand how to solve problems without trouble.
What are the key features of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 10?
The key features of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 are listed below – The answers have been created by a team of highly qualified Biology experts. Based on the most recent term – II CBSE Syllabus – the solutions are accurate and error-free. Every significant topic is taught in clear English to ensure that students do well on their second-term exams. Using our experts' NCERT Exemplar Solutions, students gain a complete comprehension of key ideas.
Mention the topics included in Chapter 10 of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Biology.
The main topics that are covered in Chapter 10 of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Biology are as follows– Microbes in Household Products Microbes in Industrial Products Microbes in Sewage Treatment Microbes in Production of Biogas Microbes as Biocontrol Agents Microbes as Bio fertilizers
Why Opt for Infinity Learn?
In this chapter Infinity Learn provides videos, notes, NCERT text book solutions, other practice book solutions and assignments that help you learn the concepts and to memorise the concepts for entrance exams and board exams. Most important, Infinity learn provide instant doubt support by subject experts.





