Table of Contents
Introduction to Condensation
Condensation meaning is a heat transfer process that converts a gas into a liquid. This is normally accomplished by lowering the pressure on the gas. The most typical condensing application is in refrigeration and air conditioning systems, where heat transfer from objects is critical.
Condensing is also used in steam turbines and jet engines to transform high-pressure steam into a liquid that may be used in the engine’s combustion chambers.
Let’s go into the article to understand condensation, its meaning, method, and relevance using condensation examples.
Condenser
A condenser (or AC condenser) is the outside portion of an air conditioner or heat pump that, depending on the time of year, either releases or gathers heat.
Split air conditioners and heat pump condensers use the same fundamental components. A condenser coil, the compressor, a cooling system, and other controls are all housed in the condenser cabinet. The condenser coil can be composed of copper tubing with aluminium fins or all-aluminum tubing to transfer heat quickly.
Condenser fan
A condenser fan is a kind of fan that is placed near the condenser, as the name implies. Condenser fan purpose is to eliminate heat from the refrigerant within the hollow passageways of the condenser. When your air conditioner is turned on, the refrigerant in its evaporator coil absorbs heat from the inside of your home.

Condenser microphone
Condenser microphones are sound-capture devices that use a particularly sensitive vibrating diaphragm to capture sound. Condenser microphones are among the most powerful recording studio microphones, capable of recording virtually any instrument.
Condensation definition
Condensation definition is also as follows:
- Condensation occurs when a gas transforms into a liquid.
- Condensations are characterized as reactions in which two molecules combine with the loss of water.
- Condensation is the process of removing heat from a system in such a way that vapour is turned into liquid.
Aldol condensation reaction
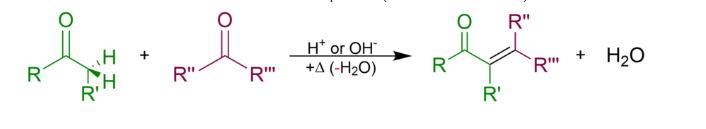
In organic chemistry, an aldol condensation reaction is a condensation process in which two carbonyl moieties (of aldehydes or ketones) react to generate a -hydroxyaldehyde or -hydroxyketone (an aldol reaction), which is subsequently dehydrated to give a conjugated enone.
The entire aldol condensation reaction equation (where Rs can be H) is as follows:
Benzoin condensation
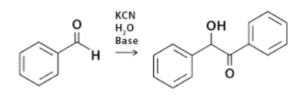
Benzoin condensation is the reaction between two types of aromatic aldehydes, particularly benzaldehyde, in the presence of a catalyst (either a nucleophile or heterocyclic) to create an aromatic parent molecule. It is known as the benzoin condensation reaction.
The coupling process that occurs between aldehydes to generate parent benzoin is what that benzoin condensation reaction is really about. In this situation, the benzaldehyde is engaged in this homocoupling mechanism. The benzoin condensation reaction is shown as:
Cross aldol condensation
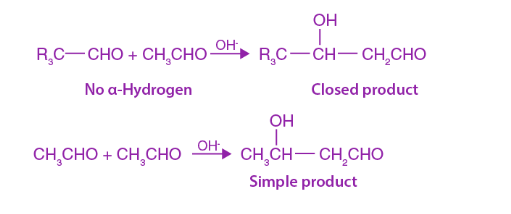
The Cross aldol condensation is the condensation process of two distinct molecules of a ketone or aldehyde in a protic solvent that includes water or alcohol. When condensation proceeds between two separate carbonyl molecules, this is known as cross aldol condensation.
Claisen condensation
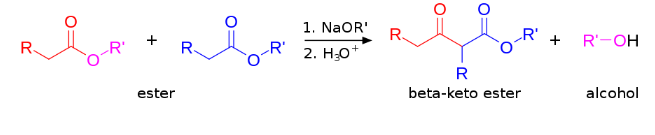
Claisen condensation is a carbon-carbon bond forming reaction that occurs between 2 esters or a single ester and another carbonyl molecule in the presence of a strong base.
The reaction yields either a -keto ester or a -diketone. The Claisen condensation reaction scheme is shown as:
Condensed milk price
There are different condensed milk prices depending upon the company and brand. Bigbasket offers the best price of Rs 63 for Amul Mithai Mate 200 gm.
Condensation examples
Condensation examples consist of the aldol condensation and the Knoevenagel condensation, both of which produce water as a byproduct, as well as the Claisen condensation and the Dieckman condensation (intramolecular Claisen condensation), all of which produce alcohols as a byproduct.
Frequently Asked Questions on Condensation
What is condensation with example?
Condensation is the transformation of water vapour into liquid. It is the opposite of evaporation, in which liquid water turns into a vapour. Esterification is a type of condensation reaction that produces an ester from an alcohol with a carboxylic acid.
What is aldol condensation reaction short note class 12?
An aldol condensation reaction occurs when an enolate ion reacts with a carbonyl compound to form a -hydroxy ketone , -hydroxy aldehyde, which is subsequently dehydrated to form a conjugated enone.
What is benzoin condensation with example?
The benzoin condensation reaction is typically initiated by aromatic aldehydes or glyoxals and results in the creation of an acyloin. Benzaldehyde is transformed to benzoin in the classic example.
What is cross aldol condensation class 12?
Cross-aldol condensation occurs when aldol condensation occurs between two separate aldehydes, two different ketones, as well as an aldehyde and a ketones. When both reactants contain -hydrogens, four chemicals are formed as byproducts.
What is an example of Claisen condensation?
The production of ethyl acetoacetate or acetoacetic ester is a common instance of claisen condensation. 3-oxobutanoate is another name for it.









