Table of Contents
The Ghaggar River flows through northern India, beginning in the Siwalik (Shiwalik) Range in northwestern Himachal Pradesh. It travels roughly 200 miles (320 km) southwest through Haryana, where it merges with the Saraswati River. Eventually, the Ghaggar dissipates into the Great Indian (Thar) Desert. Near the town of Sirsa, it supplies water to two irrigation canals that reach into Rajasthan. Historically, it is thought that the Ghaggar was once a tributary of the Indus River. The river’s flow is seasonal, primarily relying on monsoon rains.
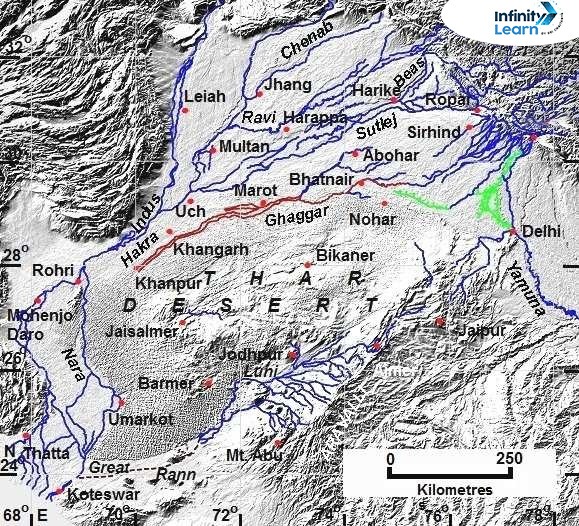
Ghaggar/Dead River
The Ghaggar River is a seasonal river that flows through northern India and parts of Pakistan. It originates in the Shivalik Hills of Himachal Pradesh and flows through the states of Punjab, Haryana, and Rajasthan before disappearing into the Thar Desert. Historians often identify this River as the Vedic Saraswati River. Additionally, researchers believe that the Sutlej and Yamuna Rivers once flowed into the Ghaggar-Hakra riverbed, further enhancing its historical importance.
Don’t Miss: National River of India
Ghaggar River Route Map
On a map, the Ghaggar River can be seen starting from the Shivalik Hills and flowing southwest through Punjab and Haryana, finally dispersing in the dry regions of Rajasthan.
Is Ghaggar River also known as Saraswati River?
Yes, many archaeologists and geologists, including Philip and Virdi (2006) and K.S. Valdiya (2013), have identified the Ghaggar River as the Saraswati River mentioned in ancient texts. Gregory Possehl affirms this view, citing linguistic, archaeological, and historical evidence that identifies the Vedic Saraswati River with the modern Ghaggar or Hakra.
Also Check: Kaveri River
Why is Ghaggar River Famous
The Ghaggar River holds historical & cultural significance and influences the region. It was once thought to be a tributary of the Indus River but now flows seasonally, mainly during the monsoon. Encroachment poses a significant issue for this River and its tributaries like the Tangri and Markanda, particularly in parts of Haryana, where it frequently earns the designation of a “dead river.” However, during the monsoon season, these rivers reclaim their floodplains, resulting in substantial flooding and damage. This underscores their enduring presence and underscores the challenges of managing natural waterways in densely populated areas.
Also Check: Subarnarekha River
Tributaries of the Ghaggar River
1. Kaushalya River
The Kaushalya River is a small river that starts in the lower Shivalik Hills of Haryana. It joins the Ghaggar River near the town of Pinjore.
2. Markanda River
The Markanda River also originates in the Shivalik Hills. It flows through the state of Haryana and merges with the Ghaggar near Shatrana. This river is known for its flash floods during the monsoon season.
3. Sarsuti River
The Sarsuti River is often linked with the mythological Saraswati River. It flows through the plains of Haryana and meets the Ghaggar River, contributing to its flow.
4. Tangri River
The Tangri River starts in the Shivalik Hills and runs through Haryana. It joins the Ghaggar River near the town of Ambala. Like other tributaries, it is seasonal and mainly flows during the monsoon.
5. Chautang River
The Chautang River, another tributary of the Ghaggar, flows through Haryana. It is considered to follow an ancient riverbed and adds to the Ghaggar’s flow during the rainy season.
Key Facts about Dead River
- Seasonal Flow: The Ghaggar River is primarily a monsoon-fed river, meaning it flows mainly during the rainy season.
- Historical Significance: Historians believe that the G. River basin was the site of the ancient Saraswati River mentioned in the Rigveda. This area is also home to many Indus Valley Civilization sites.
- Agricultural Importance: Despite its seasonal nature, the river is crucial for irrigation in the regions it traverses.
- Disappearance: Unlike most rivers, the Ghaggar does not reach the sea. It vanishes into the sands of the Thar Desert, with no definite endpoint.
- Known as Ghaggar in India before the Ottu barrage.
- Called Hakra in Pakistan downstream of the barrage.
- It Dries up in the Great Indian Thar Desert.
- Understanding this River provides insight into its historical, geographical, and cultural significance in northern India.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is special about Ghaggar River?
Historians identify the Ghaggar River with the ancient Saraswati River of Vedic literature, highlighting its historical significance. It flows seasonally through northern India, impacting agricultural practices and local ecosystems.
What is the ending point of Ghaggar River?
The Ghaggar River eventually dissipates into the Great Indian (Thar) Desert in Rajasthan, India, after flowing through Punjab and Haryana.
What is the new name of Dead River?
The Dead River is known as the Hakra River. Downstream of the Ottu barrage in Pakistan, the Dead River is known as the Hakra River.
What is the drainage system of Dead/Ghaggar River?
The Ghaggar/Saraswati River basin drains parts of Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, and Rajasthan, contributing to the region's agricultural and ecological systems.
Where does the Dead river start and end?
This River originates in the Siwalik Hills of Himachal Pradesh, India, and ends in the Thar Desert of Rajasthan, India.
Is Ghaggar river a Saraswati River?
Archaeological and geological research identifies this river as the ancient Saraswati River mentioned in Vedic texts.
Which glacier is the Ghaggar river from?
This River does not originate from a glacier. It starts in the Siwalik Hills of Himachal Pradesh, fed by rainfall and seasonal streams.
What are the major tributaries of the Ghaggar River?
It is fed by several tributaries originating in the Shivalik Hills, such as the Kaushalya, Markanda, Sarsuti, Tangri, and Chautang Rivers. These tributaries contribute to the Ghaggar's flow as it passes through Haryana..









