Table of Contents
Introduction
Modern Periodic Table: The physical and chemical properties of elements are periodic functions depending on their atomic numbers, according to modern periodic law.
Scientists ordered elements across each row in ascending order of atomic number from left to right, and they noticed that the same properties repeated at regular intervals.
The modern periodic table, often known as the long version, is based on modern periodic law. The table is an arrangement of elements arranged in increasing atomic number order. The modern periodic table is the periodic table in its current form. There are 18 vertical columns and seven horizontal rows in total.
Modern Periodic Law Definition
The current Periodic law can be stated as follows:
“Elements’ physical and chemical properties are periodic functions of their atomic numbers.”
The number of electrons or protons in a neutral atom is represented by the atomic number. Scientists now have a comprehensive understanding of quantum numbers and the electrical structure of elements in the periodic table after discovering the fundamental unit of elements.
Chemists discovered a resemblance between the 94 naturally occurring chemical elements after learning the periodic law. People became more interested in the chemistry of these elements due to their similarity. Scientists created various artificial elements. A new periodic table based on modern periodic laws was constructed by altering Mendeleev’s periodic table.
Father of modern periodic table
Dmitri Mendeleev, the father of modern periodic table, was born in Siberia. He was the youngest of fourteen children still alive. Dmitri’s father lost his sight shortly after his birth. Dmitri’s father died unexpectedly when he was thirteen.
He would study chemistry at his father’s alma mater, the Main Pedagogical Institute (not St. Petersburg University). He received his degree in chemistry in 1865, following various illnesses and the loss of his mother.
Modern periodic table image
The modern periodic table looks like the following:
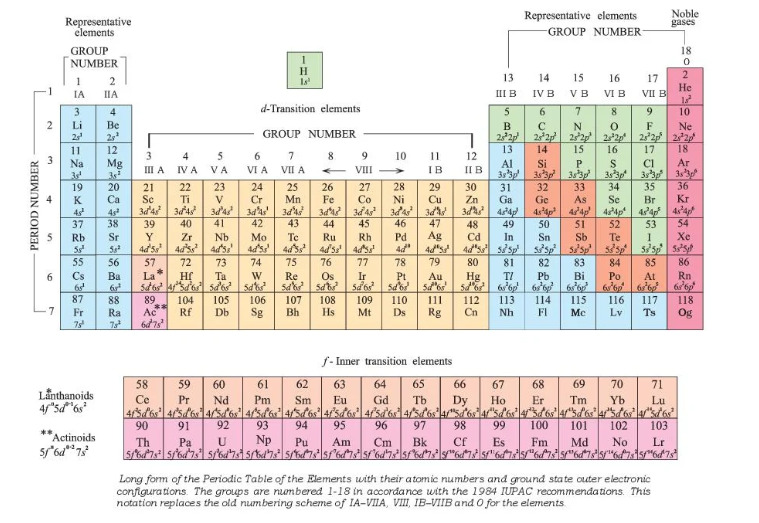
Examining the Table
Each element is denoted by a chemical symbol consisting of one or two characters.The first letter of a sign is always capitalised whereas the second letter, if any, is always lowercase.
Cu, for example, is the symbol for copper. It is an abbreviation for cuprum, the Latin word for copper. The number above each symbol in the table represents the symbol’s unique atomic number. Notice how the atomic numbers in the table rise from left to right and from top to bottom.
Periodic Trends in the Modern Periodic Table
Periodic table trends are predictable patterns in the properties of periodic table elements. The electrical configuration of elements determines periodic trends. They result from variations in the atomic structure of elements with their appropriate periodic table periods (horizontal rows) and groups (vertical columns).
Periodic trends are based on the periodic law, which asserts that if the chemical elements are listed in increasing atomic number order (from left to right), then their physical and chemical properties will be a periodic function of their atomic numbers.
Conclusion
The modern periodic table is used to organize all known elements. Elements are organized in the table by increasing atomic number. Each element is represented by its chemical symbol in the current periodic table. The number above each symbol represents its atomic number.
Atomic numbers in the table grow from left to right and from top to bottom. Periods are rows in the periodic table. If we move from left to right across a period, we observe that each element has one more proton than the element before it.
Groups are the columns of the periodic table. Elements in the same group have similar characteristics. There are three different types of elements including metals, metalloids, and nonmetals. Elements in each class share certain fundamental features.
FAQs on Modern Periodic Table
What is the modern periodic table?
Modern periodic law is the foundation of the modern periodic table, often known as the enlarged version. The table is organised in ascending atomic number order. It is made up of 18 vertical columns and 7 horizontal rows.
Who is the creator of the present periodic table?
Dimitri Mendeleev (1834-1907) Dmitri Mendeleev, who discovered the modern periodic table, was born in Siberia. He was the youngest of fourteen children. Dmitri's father lost his sight not long after he was born.
What is Henry Moseley's modern periodic table?
The chemical and physical properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic numbers, according to modern periodic law. Henry Moseley proposed it in 1913 based on his X-ray studies. The modern periodic table has 18 groups (vertical columns) and seven periods (horizontal rows).
What are the distinctions between the periodic tables of Mendeleev and Moseley?
Chemical elements are arranged in the Mendeleev periodic table according to their atomic masses. The chemical elements in the Moseley periodic table are organized according to their atomic numbers. Mendeleev's periodic table only had 56 chemical elements.








