Table of Contents
Introduction
It is a beta-hydroxy acid (BHA) and phenolic acid subclass. Salicylic acid was first isolated from the willow tree leaves of the genus Salix. Salicylic acid also known as 2 hydroxybenzoic acid was first isolated from the leaves of salix trees.
It is a free acid found in minor amounts in various plants and was primarily isolated from the bark of willow trees (Salix spp.), from which it derives its name. It functions as a plant hormone.
Salicylic acid is an organic carboxylic acid which forms crystals and possesses keratolytic, bacteriostatic, and fungicidal properties. Large consumption of salicylic acid can be damaging to our bodies and modest quantities can be used as an antiseptic and food preservative.
This topic will study salicylic acid, its structure, formula, physical and chemical properties, preparation process, side effects, and uses.
Overview of Salicylic Acid
It was obtained from the bark of the Willow tree. It gets its common name from many sources, including a metabolic result of salicin (an alcoholic -glycoside found in plants) and an active metabolite formed from acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin).
It appears in nature as pure, colourless crystals of an organic acid. This compound’s salt and ester derivatives, known as salicylates, are also commonly utilized in organic chemistry. It occurs naturally in plants as a growth hormone.
Salicylic Acid Structural Formula
Salicylic acid has the chemical formula C6H4(OH)COOH. The molecular formula is also written in condensed form as C7H6O3. Salicylic acid’s IUPAC name is 2-hydroxybenzoic acid.
All carbon atoms in salicylic acid’s benzene ring are sp2 hybridized. An intramolecular hydrogen bond can be formed in the salicylic acid. Salicylic acid can liberate a proton in an aqueous solution. The resultant carboxylate ion, COO-, interacts with the hydrogen atoms of the hydroxyl group intermolecularly.
Salicylic acid structure and uses
Salicylic acid structural formula
Salicylic acid structural formula can be visually represented as following:
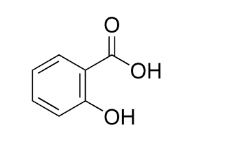
C7H6O3 Uses (Salicylic Acid)
- It is used in the medical industry to remove the skin’s outer layer.
- It is used to treat acne, dandruff, and rage.
- It acts as a preservative.
- It is used in the manufacture of medications such as aspirin.
- It is applied topically to relieve muscle and joint discomfort.
- It is used to treat pain from mouth ulcers.
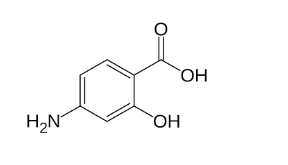
Para amino salicylic acid structure
Para-amino salicylic acid (PAS) is an amino derivative of salicylic acid. It features an amino group (-NH2) attached to the para position of the benzene ring. This modification enhances its antimicrobial properties and makes it effective in treating tuberculosis. The para amino salicylic acid structure is as follows:
Drawing the Structure of Salicylic Acid
To correctly represent the structure of salicylic acid, we have to draw a benzene ring with one carbon atom attached to a hydroxyl group -OH and then connect another carbon atom to a carboxylic acid group (COOH). This configuration showcases the arrangement of atoms and bonds within the molecule.
Conclusion
With its distinct structure and versatile applications, salicylic acid holds a prominent place in various fields. Understanding its structural formula, IUPAC name, and molecular composition allows us to appreciate its chemical properties and significance. Salicylic acid is a chemical that has numerous applications in the skincare, pharmaceutical, and industrial industries.
FAQs on Salicylic Acid Structure
What is the Structural Formula of Salicylic Acid?
The salicylic acid structural formula is (C6H4(OH)COOH).
What are the functional groups of Salicylic Acid?
A hydroxyl group (-OH group) is linked at the ortho position to the carboxylic acid functional group (-COOH group) on the benzene ring.
What is the salicylic acid structure and IUPAC name?
The IUPAC name for salicylic acid is 2-hydroxybenzoic acid. The salicylic acid formula structure can be represented as:
Does salicylic acid have a functional group structure?
The starting material for salicylic acid has two distinct functional groups: a carboxylic acid and a phenol. The top spectrum labels the absorption bands of O-H phenol (3230-3000 cm-1), O-H carboxylic acid (3000-2500 cm-1, 881 cm-1) and C=O carboxylic acid (1652 cm-1).









