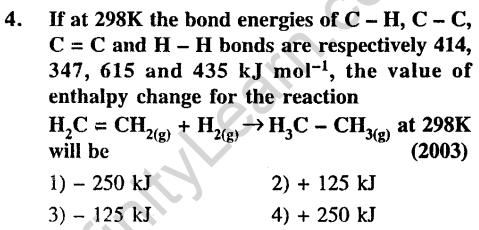
Thermodynamics and Chemical Energitics- JEE Main MCQ’S & Solutions in Chemistry
1.A heat engine absorbs heat Q, at temperature T, and heat Q2 at temperature Tr Work done by the engine is J(Q, + Q2). This data (2002)
(1)violates 1st law of thermodynamics
(2)violates Is‘ law of thermodynamics if Q, is -ve
(3)violates 1st law of thermodynamics if Q2 is -ve
(4)does not violates Is‘ law of thermodynamics
Ans.(1) Some mechanical energy is always converted (lost) to other forms of energy.
2.If an endothermic reaction is non-spontaneous at freezing point of water and becomes feasible at its boiling point, then (2002)
(1)A H is – ve, A S is + ve
(2)AH and AS both are + ve
(3)AH and AS both are – ve
(4)AH is + ve, AS is – ve
Ans.(2) At low temperature the AS is -ve which makes AG positive (AG = AH-TAS). But at higher temperature AS is +ve which makes the AG negative (condition for spontaneity).

Ans.(4) AH negative shows that the reaction is spontaneous. Higher value for Zn shows that the reaction is more feasible.
Ans.
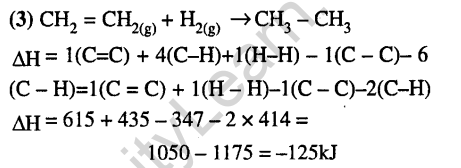

Ans.(1) For spontaneous reaction, dS > 0. AG and dG should be negative, i.e. < 0

Ans.(3) AG=-2.303 RT logK .
7.The enthalpy change for a reaction does not depend upon (2003)
(1)use of different reactants for the same product
(2)the nature of intermediate reaction steps
(3)the differences in initial or final temperature of involved substances
(4)the physical states of reactants and products
Ans.(2) Hess law of heat summation.
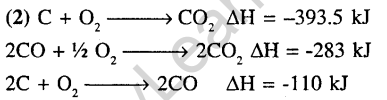
8.The enthalpies of combustion of carbon and carbon monoxide are -393.5 and -283 kj mol*1 respectively. The enthalpy of formation of carbon monoxide per mole is (2004)
(1)5 kJ 2)-110.5 kJ
3) -676.5 kJ 4) 676.5 kJ
Ans.

Ans.(1) For a spontaneous change AG is negative and Ece„ is positive.
10.Consider the reaction : N2 + 3H2——— > 2NH3 carried out at constant temperature and pressure. If AH and AU are the enthalpy and internal energy changes for the reaction, which of the following expressions is true ?
1) AH = 0 2) AH = AU (2005)
3) AH< AU 4) AH> AU
Ans.
Ans.

Ans.(1) Energy required to get H and C atoms.
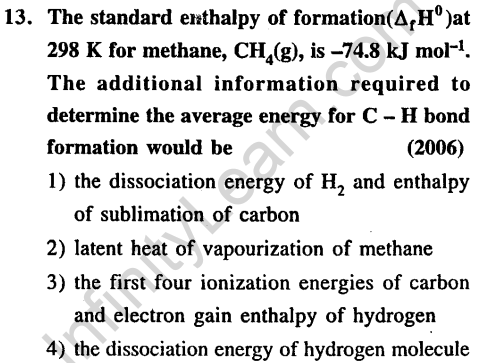
Ans.
Ans.
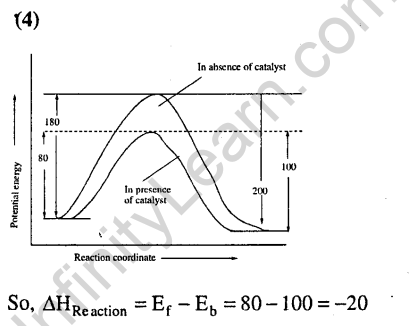

Ans.
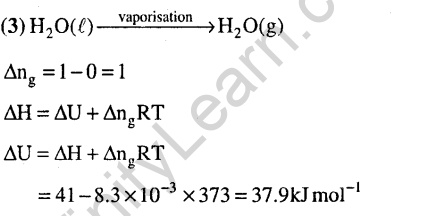
16.Identify the correct statement regarding a spontaneous process (2007)
(1)For a spontaneous process in an isolated system, the change in entropy is positive
(2)Endothermic processes are never spontaneous
(3)Exothermic processes are always spontaneous (4)Lowering of energy in the reaction process is the only criterion for spontaneity
Ans.(1) For a spontaneous process in an isolated system, the change in entropy is positive.

Ans.(4) We know, AG = AH – TAS.So, lets find the equilibrium temperature, i.e., at which AG = 0; AH = TAS;

Ans.
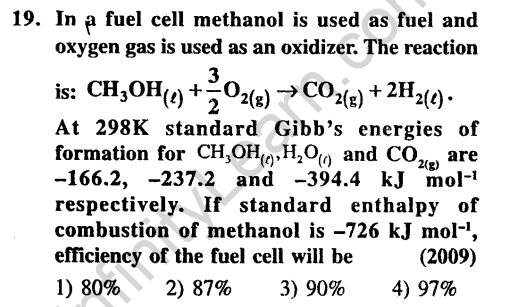
Ans.
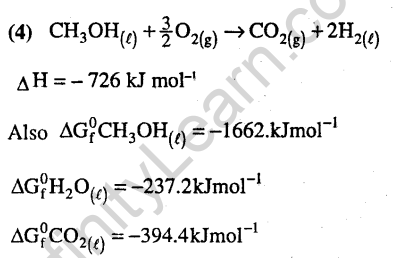
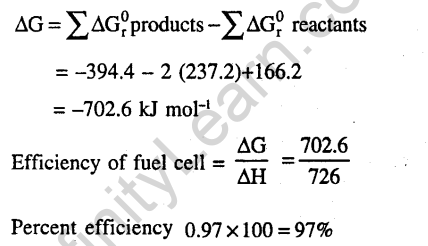
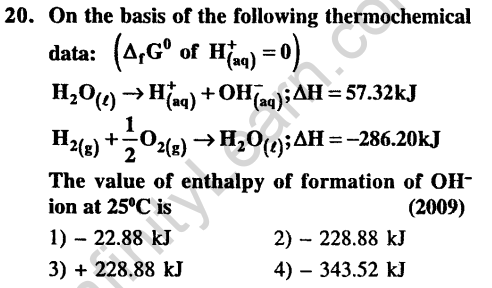
Ans.
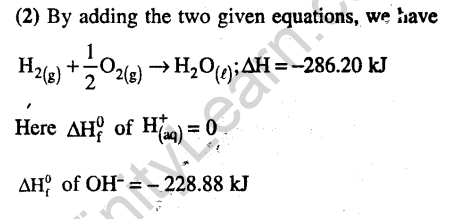

Ans.(2) Enthalpy of formation of NH3=-46 kJ/mole N2 + 3H2 2NH3 AHf = -2.x 46kJmol
Bond breaking is endothermic and bond formation is exothermic.Assuming ‘x’ is the bond energy of N-H bond (kJ mol-1)
712 + (3 x 436) – 6x = -46 x 2 Therefore, x – 352 kJ/mol
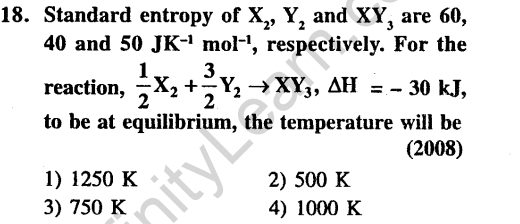
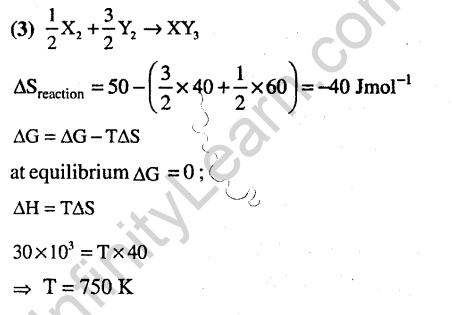
22.For a particular reversible reaction at temperature T, AH and AS were found to be both +ve. If Te is the temperature at equilibrium, the reaction would be spontaneous when (2010)
1) T > T 2) T > T
3) T is 5 times T 4) T = T
Ans.(2) AG = AH = TAS at equilibrium, AG = 0 .For a reaction to be spontaneous AG should be negative. Therefore, T > T
23.The entropy change involved in the isothermal reversible expansion of 2 moles of an ideal gas from a volume of 10 dm3 to a volume of 100 dm3 at 27°C is (2011)
1) 32.3 J moHK-1 2) 42.3 J mol-‘K”1
3) 38.3 J mol-1K-1 4) 35.8 J mol-1K_1
Ans.

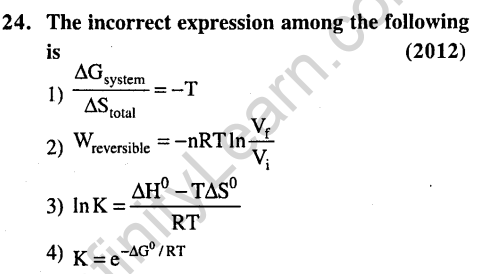
Ans.
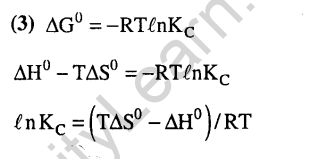

25.A position filled with 0.04 mol of an ideal gas expands reversibly from 50.0 mL to 375 mL at a constant temperature of 37.0#C. As it does so, it absorbs 208J of heat. The values of q and w for the process will be (2013)(R = 8.314J/molK and
In 7.5 = 2.01)
(1)q = + 208J, w = – 208 J
(2)q = – 208J, w = – 208 J
(3)q = – 208J, w = + 208 J
(4)q = + 208J, w = + 208 J
Ans. (1) Work done by system is negative

Ans.

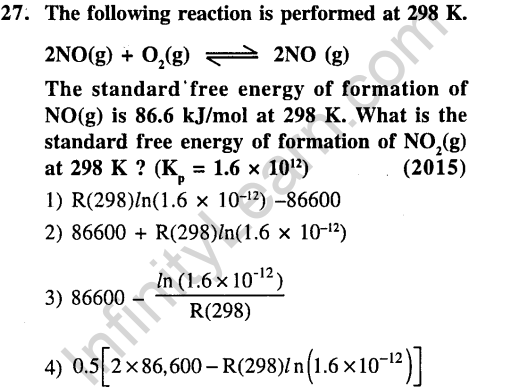
Ans.