A flower is the reproductive structure found in flowering plants, also known as angiosperms. It is typically a brightly colored structure composed of petals, sepals, stamens, and pistils. Flowers serve the purpose of facilitating the process of sexual reproduction in plants.
Brief overview of a flower
A flower is the reproductive structure of a flowering plant or angiosperm. It is composed of various parts, including petals, sepals, stamens, and pistils.
The primary function of a flower is sexual reproduction. Pollinators, attracted by the petals and sometimes the fragrance, transfer pollen from the stamens to the stigma. This fertilizes the ovules inside the ovary, leading to the development of seeds. The ovary often develops into a fruit, aiding in seed dispersal.
Labelled diagram of a flower
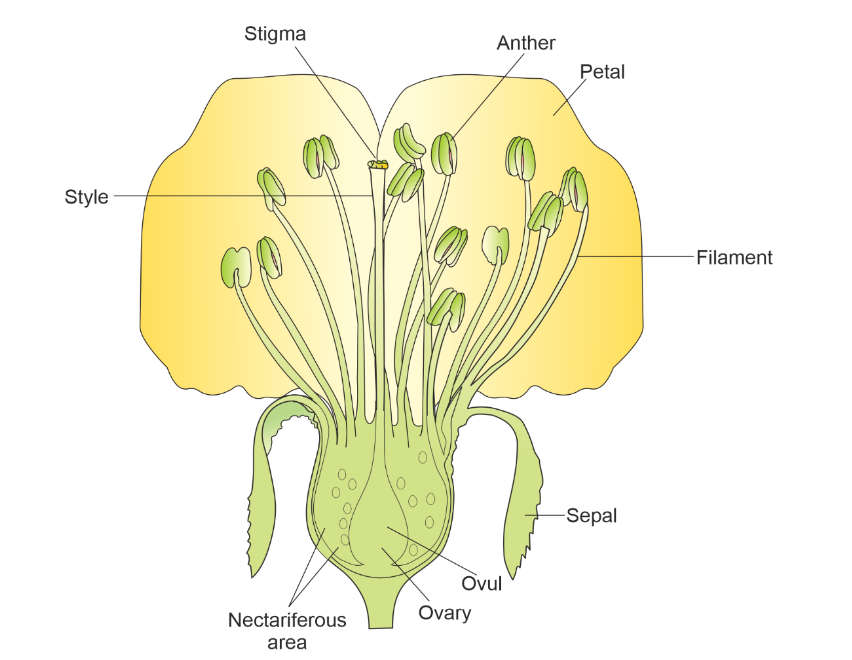
Whorls of a flower
The whorls of a flower refer to the different sets or arrangements of floral parts found within the flower. These whorls are organized in concentric circles or layers. The typical flower consists of four whorls: the calyx, corolla, androecium, and gynoecium.
- Calyx: The calyx is the outermost whorl of the flower. It consists of sepals, which are usually green and protect the developing bud. The sepals may be separate or fused together, forming a cup-like structure.
- Corolla: The corolla is the second whorl, located inside the calyx. It consists of petals, which are often colorful and fragrant. The petals attract pollinators and are usually larger and more visually appealing than the sepals.
- Androecium: The androecium is the third whorl and represents the male reproductive organs of the flower. It is composed of stamens, which consist of a filament and an anther. The anther produces pollen grains, which contain the male gametes (sperm cells).
- Gynoecium: The gynoecium is the innermost whorl and represents the female reproductive organs of the flower. It is composed of one or more carpels, which may be separate or fused. Each carpel consists of three parts: the stigma, style, and ovary. The stigma receives pollen, the style connects the stigma to the ovary, and the ovary contains ovules, which develop into seeds after fertilization.
The number of floral parts in each whorl can vary among different species. Some flowers may lack certain whorls or have modified structures.
Classification of flowers
Based on the number of floral whorls present, flowers can be classified into different types:
- Complete Flowers: These flowers have all four whorls—calyx, corolla, androecium, and gynoecium—present. They are considered “perfect” flowers because they contain both male and female reproductive structures. Complete flowers are commonly found in many flowering plants.
- Incomplete Flowers: In contrast to complete flowers, incomplete flowers lack one or more of the whorls. They may lack either the calyx, corolla, androecium, or gynoecium.
Structure of a Flower
Flowers typically consist of four main parts:
- Sepals: These are the outermost part of the flower and usually green. Sepals protect the flower in its bud stage and can sometimes support the petals when in bloom.
- Petals: Often brightly colored, petals attract pollinators like bees and butterflies. Their vivid colors and fragrances play a critical role in facilitating pollination.
- Stamens: This is the male reproductive part of the flower, consisting of two main components:
- Anther: The top part that produces pollen.
- Filament: The stalk that supports the anther.
- Pistil: This is the female reproductive part of the flower, composed of:
- Stigma: The sticky top that traps pollen.
- Style: A tube-like structure that connects the stigma to the ovary.
- Ovary: Contains ovules, which, after fertilization, develop into seeds.
Types of Flowers
Flowers are classified based on several factors:
- Complete vs. Incomplete Flowers:
- Complete flowers have all four parts: sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils.
- Incomplete flowers lack one or more of these parts.
- Bisexual vs. Unisexual Flowers:
- Bisexual flowers (or perfect flowers) contain both stamens and pistils.
- Unisexual flowers have either stamens or pistils but not both. They are further divided into:
- Male flowers: Contain stamens but no pistil.
- Female flowers: Contain pistils but no stamens.
Functions of a Flower
The primary function of a flower is to aid in the process of reproduction through pollination and fertilization. Key functions include:
- Pollination: Flowers attract pollinators through their color, scent, and nectar. Pollinators transfer pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another, enabling fertilization.
- Fertilization: After pollination, the pollen grain travels down the style to the ovary, where it fertilizes the ovules, resulting in seed formation.
- Seed and Fruit Development: Once fertilized, the ovules develop into seeds, and the ovary matures into a fruit, which helps in seed dispersal.
Pollination
Pollination is the process by which pollen, containing the male gametes (sperm cells), is transferred from the anther of the stamen to the stigma of the pistil in flowering plants. This transfer of pollen is crucial for successful sexual reproduction and the formation of seeds.
FAQs on Flower
What are the 10 parts of a flower and their functions?
The ten parts include petals, sepals, stamens, anthers, filaments, pistils, styles, stigmas, ovules, and ovaries. Each part has a role in reproduction and attracting pollinators.
What are the two functions of the flower of a plant?
Flowers help in reproduction and attract pollinators like bees and butterflies.
What is the main function of the style in a flower?
The style connects the stigma to the ovary and helps transport pollen for fertilization.
What are the 4 parts of the flower?
The four main parts are petals, sepals, stamens, and pistils.
Do flowers have 5 basic parts?
Yes, flowers typically have five basic parts: petals, sepals, stamens, pistils, and ovules.
What are the 7 parts of a plant and their functions?
The seven parts are roots (absorb water), stems (support), leaves (photosynthesis), flowers (reproduction), fruits (protect seeds), seeds (grow new plants), and nodes (growth points).
How are flowers pollinated?
Flowers are pollinated when pollen from the anther reaches the stigma, often by wind, insects, or animals.
What type of pollination occurs in flowers?
Pollination can be self-pollination (within the same flower) or cross-pollination (between different flowers).
What is flower pollination called?
Flower pollination is called 'pollination.' It is the process that helps fertilize plants to produce seeds.









