Table of Contents
Introduction to Flower
A flower is the reproductive structure found in flowering plants, also known as angiosperms. It is typically a brightly colored structure composed of petals, sepals, stamens, and pistils. Flowers serve the purpose of facilitating the process of sexual reproduction in plants.
Brief overview of a flower
A flower is the reproductive structure of a flowering plant or angiosperm. It is composed of various parts, including petals, sepals, stamens, and pistils.
The primary function of a flower is sexual reproduction. Pollinators, attracted by the petals and sometimes the fragrance, transfer pollen from the stamens to the stigma. This fertilizes the ovules inside the ovary, leading to the development of seeds. The ovary often develops into a fruit, aiding in seed dispersal.
Labelled diagram of a flower
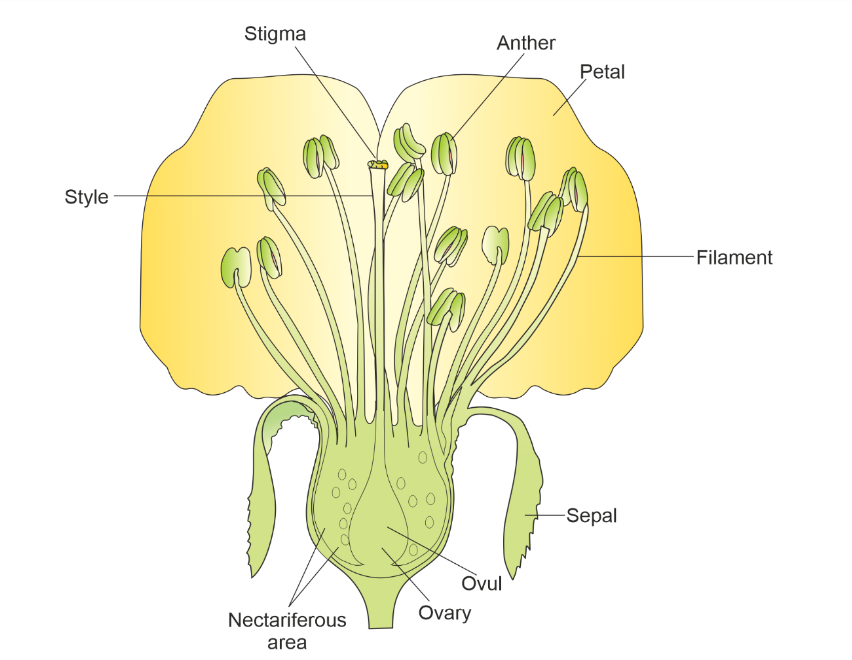
Whorls of a flower
The whorls of a flower refer to the different sets or arrangements of floral parts found within the flower. These whorls are organized in concentric circles or layers. The typical flower consists of four whorls: the calyx, corolla, androecium, and gynoecium.
- Calyx: The calyx is the outermost whorl of the flower. It consists of sepals, which are usually green and protect the developing bud. The sepals may be separate or fused together, forming a cup-like structure.
- Corolla: The corolla is the second whorl, located inside the calyx. It consists of petals, which are often colorful and fragrant. The petals attract pollinators and are usually larger and more visually appealing than the sepals.
- Androecium: The androecium is the third whorl and represents the male reproductive organs of the flower. It is composed of stamens, which consist of a filament and an anther. The anther produces pollen grains, which contain the male gametes (sperm cells).
- Gynoecium: The gynoecium is the innermost whorl and represents the female reproductive organs of the flower. It is composed of one or more carpels, which may be separate or fused. Each carpel consists of three parts: the stigma, style, and ovary. The stigma receives pollen, the style connects the stigma to the ovary, and the ovary contains ovules, which develop into seeds after fertilization.
The number of floral parts in each whorl can vary among different species. Some flowers may lack certain whorls or have modified structures.
Classification of flowers
Based on the number of floral whorls present, flowers can be classified into different types:
- Complete Flowers: These flowers have all four whorls—calyx, corolla, androecium, and gynoecium—present. They are considered “perfect” flowers because they contain both male and female reproductive structures. Complete flowers are commonly found in many flowering plants.
- Incomplete Flowers: In contrast to complete flowers, incomplete flowers lack one or more of the whorls. They may lack either the calyx, corolla, androecium, or gynoecium.
Functions of flowers
Flowers serve several important functions in the life cycle of flowering plants (angiosperms). Here are the key functions of flowers:
- The primary function of flowers is to facilitate sexual reproduction in plants. The male reproductive organs (stamens) produce pollen containing the male gametes, while the female reproductive organ (pistil) contains the ovary, which holds the ovules. The transfer of pollen from the stamen to the stigma of the same or another flower allows fertilization to occur, leading to the development of seeds and subsequent plant offspring.
- Flowers have evolved a variety of characteristics to attract pollinators, such as bees, butterflies, birds, and insects. They use colorful petals, attractive shapes, patterns, and fragrances to entice pollinators to visit and interact with the flower. Pollinators help transfer pollen from one flower to another, promoting cross-pollination and genetic diversity.
- Flowers employ mechanisms to ensure the dispersal of pollen to increase the chances of successful pollination. Some flowers release their pollen into the air, relying on wind as a pollination agent (anemophily). Others produce sticky or textured pollen that easily adheres to the bodies of visiting animals or insects (zoophily). Insects and animals inadvertently transport this pollen to other flowers as they move from one source of nectar to another, aiding in cross-pollination.
- Genetic Variation and Adaptation: Flowers and their reproductive processes, including cross-pollination, contribute to genetic variation within plant populations. This genetic diversity enables plants to adapt to changing environmental conditions, resist diseases, and improve their overall fitness.
Pollination
Pollination is the process by which pollen, containing the male gametes (sperm cells), is transferred from the anther of the stamen to the stigma of the pistil in flowering plants. This transfer of pollen is crucial for successful sexual reproduction and the formation of seeds.
Frequently asked questions on Flower
What are the different whorls of a flower?
The different whorls of a flowers are: Calyx Corolla Androecium Gynoecium
Is flower produced by all plants?
No, flowers are only present in angiosperms. It is not present in any other group of plants.
What are the uses of a flower?
Flowers have ornamental value, symbolize emotions, provide fragrances, offer medicinal properties, enhance culinary creations, support pollinators, contribute to cultural traditions, represent celebrations, convey messages, decorate spaces, inspire perfumes, beautify gardens, and serve as a vital part of the global floral industry.
Classify flowers depending on the presence of or absence of reproductive whorls.
Depending on the presence of or absence of reproductive whorls flowers are classified into: a. Staminate Flowers: These flowers lack the gynoecium (pistil) and have only the male reproductive structure (androecium). They produce pollen but lack the ability to produce seeds. b. Pistillate Flowers: Pistillate flowers lack the androecium (stamens) and have only the female reproductive structure (gynoecium). They possess the pistil (stigma, style, and ovary) but do not produce pollen. c. Neutral Flowers: These flowers lack functional reproductive structures altogether. They do not possess either the androecium (stamens) or the gynoecium (pistil). Neutral flowers often serve other purposes, such as attracting pollinators with their colorful petals or producing nectar.
What are accessory whorls of a flower?
The calyx and corolla are the accessory whorls of a flower as they are not directly involved in in reproduction.





