Table of Contents
Earth has a wide variety of living things, ranging from tiny one-celled creatures to more complex plants and animals. However, when we look closely at the smallest parts of life, we find that they all share two important things: DNA and RNA. The main difference between DNA and RNA is that DNA is like a double rope, while RNA is like a single rope.
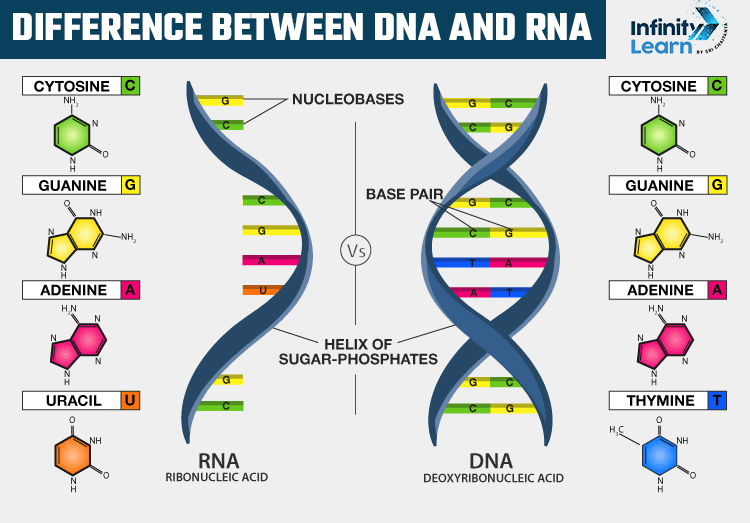
Difference Between DNA and RNA
| DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) | RNA (Ribonucleic acid) |
| Definition | |
| It is a long polymer with a deoxyribose and phosphate backbone, and four unique bases: thymine, adenine, cytosine, and guanine. | It is a polymer with a ribose and phosphate backbone, and four different bases: uracil, cytosine, adenine, and guanine. |
| Location | |
| It is located in the nucleus and mitochondria of a cell. | It can be found in the cytoplasm, nucleus, and ribosomes. |
| Sugar Component | |
| It contains 2-deoxyribose. | It contains Ribose. |
| Function | |
| DNA is responsible for the transmission of genetic information and serves as a medium for long-term storage. | RNA plays a crucial role in transmitting the genetic code necessary for protein synthesis from the nucleus to the ribosome. |
| Predominant Structure | |
| DNA is a double-stranded molecule with a long chain of nucleotides. | RNA is a single-stranded molecule with a shorter chain of nucleotides. |
| Propagation | |
| DNA can replicate itself, it is self-replicating. | RNA cannot replicate itself. Instead, it is synthesized from DNA when needed. |
| Nitrogenous Bases and Pairing | |
| The base pairing is as follows: GC (Guanine pairs with Cytosine), A-T (Adenine pairs with Thymine). | The base pairing is as follows: GC (Guanine pairs with Cytosine), A-U (Adenine pairs with Uracil). |
DNA
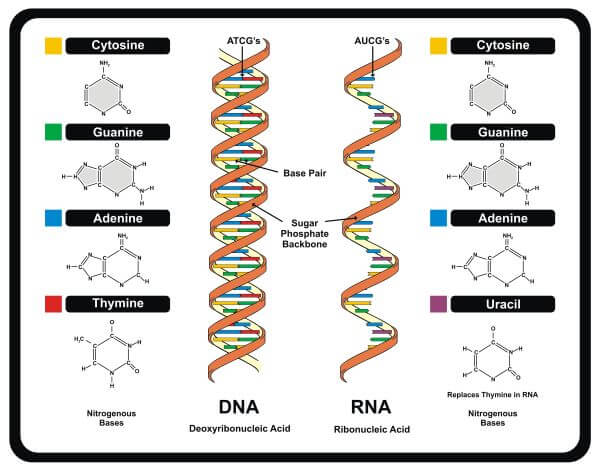
Within cells, DNA, also known as Deoxyribonucleic acid, acts as the fundamental plan for making proteins. DNA is made up of deoxyribose sugar, phosphates, and a distinctive sequence of the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T).
Structure & Composition of DNA
DNA contains the instructions needed for living things to grow, develop, and make more of themselves. These instructions are found in every cell and are passed from parents to their children.
DNA is made up of building blocks called nucleotides, which have three parts: a nitrogen group, a phosphate group, and a sugar group. The order of these nitrogen bases – thymine (T), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and adenine (A) – is very important because it determines our genetic code.
Genes are formed by the specific order of these nitrogen bases in DNA, and this order is essential for making proteins. RNA is another molecule that reads the genetic information in DNA to create proteins.
The nucleotides link together to create two long strands that twist into a shape like a spiral ladder, called a double-helix. In this ladder, the sugar and phosphate parts make the sides, and the rungs are formed by the nitrogen bases.
The bases on one strand connect with the bases on the other strand: guanine pairs with cytosine, and adenine pairs with thymine.
DNA molecules are very long, so they are tightly packed into structures called chromosomes. Each chromosome contains a single DNA molecule. In humans, we have 23 pairs of chromosomes inside the nucleus of our cells.
Types of DNA
Sure, here’s a simplified version of the information:
- A-DNA: This type of DNA is found in conditions with 75% humidity. When there’s a lot of salt or dehydration, it forms 11 pairs of building blocks, with each pair rising about 2.56Å. It has the widest helix shape among all DNA, measuring 23Å. It’s a right-handed helix that turns 32.70 times per pair.
- B-DNA: This is the most common DNA type. It’s found in regular conditions with neutral pH and normal salt levels. It has 10 building block pairs per twist and a helix width of 20Å. The famous Watson-Crick double helix model is based on B-DNA.
- C-DNA: This DNA appears at 66% humidity and when there are a few ions like lithium. It twists with about 9.33 pairs per turn and has a helix width of 19Å, rising about 3.320 per pair.
- D-DNA: This is a rare variant of DNA. It twists with 8 pairs, tilting away from the center by about 3.03Å.
- Z-DNA: This DNA type is found in very salty environments. Unlike A, B, and C-DNA, it’s a left-handed helix. Its backbone forms a zig-zag pattern, made up of dinucleotides instead of single building blocks seen in other forms.
RNA
Ribonucleic acid, commonly known as RNA, plays a crucial role in making proteins in living cells. It carries instructions from DNA to control the production of proteins.
RNA is made up of long chains of molecules, including ribose sugar, phosphates, and four different nitrogen bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and uracil (U). While DNA and RNA share some of these nitrogen bases (A, G, and C), DNA typically contains thymine, while RNA typically contains uracil.
Types of RNA
Not all genes in cells are used to make RNA. There are different kinds of RNA, and each type comes from its own type of gene:
- Transfer RNA (tRNA) – tRNA brings amino acids to ribosomes during the process of making proteins.
- Messenger RNA (mRNA) – mRNA carries the instructions for making a chain of amino acids, which then form a protein.
- Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – rRNA helps build ribosomes, which are like protein-making factories in the cell. They read the mRNA instructions and put together the amino acids.
- Small nuclear RNA (snRNA) – snRNA combines with proteins to help process RNA in eukaryotic cells, which are a type of cell with a defined nucleus.
FAQs on Difference Between DNA and RNA
What is the Difference between DNA and RNA?
DNA has two strands, creating a double twist, whereas RNA generally has only one strand. In DNA, the sugar is called deoxyribose, while in RNA, it's ribose. Additionally, DNA has the bases adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine, while RNA has adenine, uracil, cytosine, and guanine.
What is the functional difference between DNA and RNA?
DNA and RNA have distinct roles in our bodies. DNA stores and transfers genetic information, while RNA encodes amino acids and serves as a go-between for DNA and ribosomes to create proteins.
Where are DNA and RNA found?
DNA can be found inside the cell's nucleus and in the mitochondria, while RNA is present in the cytoplasm, nucleus, and ribosomes.
Why is DNA a better genetic material than RNA?
The DNA's sugar, called deoxyribose, has one fewer oxygen-rich hydroxyl group. DNA is a steadier type of genetic material. In contrast, RNA has ribose sugar and is more prone to reacting. So, DNA is a superior genetic material compared to RNA.