Table of Contents
Nitrogen is one of the most abundant elements on Earth. This element is important for the survival of all living organisms. Nitrogen forms an essential component of amino acids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
The percentage of nitrogen present in the atmosphere is 78%. However, more is needed for the plants to directly utilize it for its purpose. Hence, this is where nitrogen fixation and nitrogen metabolism come into play.
What is Nitrogen Fixation?
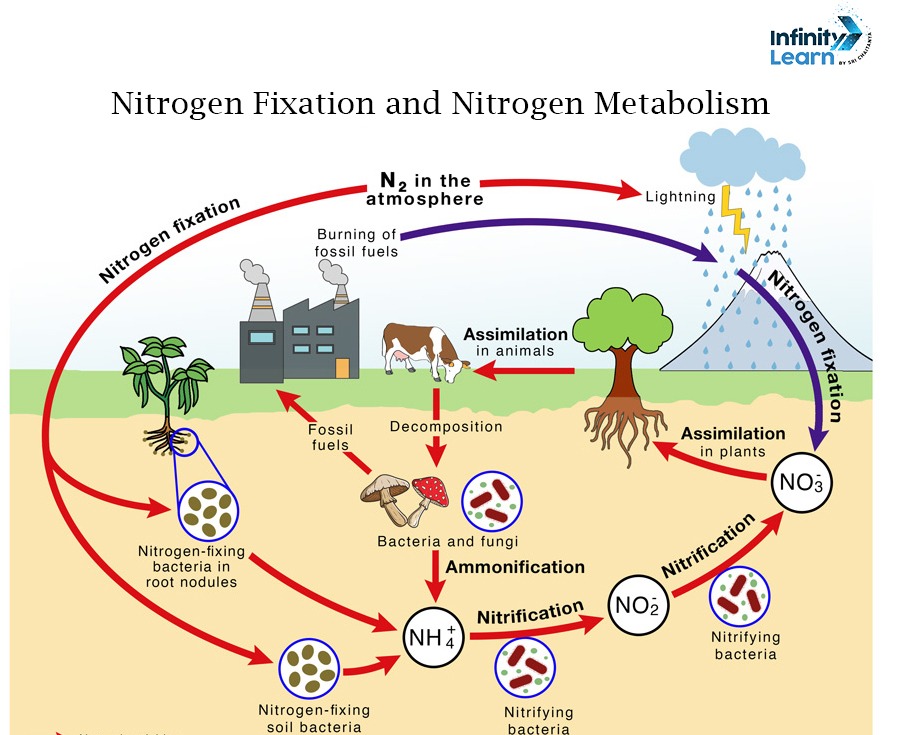
Nitrogen fixation is the process through which atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is converted into ammonia. It also gets converted into other nitrogenous compounds that plants, animals, and microbes can use. This process is important for incorporating nitrogen into plants or biological systems.
What Are The Types Of Nitrogen Fixation?
Fixing nitrogen can be achieved by lightning, industrial fixation, or biological fixation. The three nitrogen fixation processes are briefly discussed below.
Biological Nitrogen Fixation
Biological processes are the primary way of fixing nitrogen from the environment. The enzyme nitrogenase facilitates the fixation of nitrogen by certain bacteria and archaea. Diazotrophy is the term used to describe these species.
- Symbiotic Nitrogen Fixation – Nitrogen-fixing bacteria like Rhizobium, form symbiotic relations with plants, like legumes. Bacterias reside in the root nodules and convert nitrogen gas into ammonia.
- Free-Living Nitrogen Fixation – Bacterias like cyanobacteria can fix nitrogen without the need for a host plant. Examples include Azotobacter and Anabaena.
Industrial Nitrogen Fixation
A high-temperature and pressure industrial process is called the Haber-Bosch process. It is used to create ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen gases.
In addition to being a major component of the global nitrogen cycle, this ammonia is utilized to make fertilizers.
Atmospheric Nitrogen Fixation
The energy required to transform atmospheric nitrogen into nitrogen oxides (NO and NO₂) is produced by lightning.
Rainwater dissolves these nitrogen oxides. Later, they find their way into the soil as nitrates that plants can use.
How Nitrogen is Utilized in Living Organisms?
After the process of nitrogen fixation, it enters the nitrogen cycle involving the transformation of biochemicals. These transformation helps living organisms to use nitrogen properly.
The living organisms utilize nitrogen in three steps – ammonification, nitrification, and denitrification. These steps are briefly discussed below.
Ammonification
The process of ammonification is a part of the nitrogen cycle. It gives organisms the amount of nitrogen they require to exist.
Ammonification is the process by which nitrogen-containing compounds from decaying organic matter are broken down into simpler compounds. The product formed is ammonia, by tiny creatures such as bacteria or other types of decomposing organisms.
These less complex materials support the ecology. Ammonification, very simply, is the process of turning naturally occurring nitrogen compounds into ammonia.
Nitrification
Nitrification is a natural process carried out by nitrifying bacteria. It is a crucial phase in the soil’s nitrogen cycle.
The natural process of nitrification is brought about by specialist autotrophic bacteria in the environment. Ammonia is transformed into nitrites (NO2–) and subsequently nitrates (NO3–) throughout this aerobic process.
What Are The Factors Affecting the Nitrification Process?
Several factors affect the nitrification process. Temperature, moisture content, pH, oxygen availability, and other factors are responsible for putting impact on the process. They are briefly discussed below.
Temperature
Temperature plays an important role in the activity of bacteria like – Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter.
- The nitrification occurs mainly at temperature ranges of 25°C and 30°C.
- Nitrification slows down significantly below 15°C.
- It almost completely ends below 5°C.
pH levels
The nitrifying bacteria are very sensitive to pH levels. They tend to show the following variations and responses.
- The ideal pH for nitrification is between 6.5 and 8.5
- Nitrification slows down and ammonia oxidation decreases below pH 6.
- High pH (beyond 9) can prevent nitrifying bacteria from growing.
- This can cause an accumulation of ammonia that can become hazardous.
Availability of Oxygen
Oxygen-deficient environments slow or stop the nitrification of bacteria.
- Although oxygen concentrations are necessary, proper aeration is more important.
- A dissolved oxygen concentration of at least 2 mg/L is required for nitrification.
Moisture content
Moisture holding capacity is important for nitrification for terrestrial organisms.
- Nitrification occurs best in well-aerated soils.
- The soil must contain 40–60% water (based on soil water-holding capacity).
- Excess moisture can create anaerobic conditions.
- Thus, limiting oxygen availability and slowing nitrification.
Salinity
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria are inhibited by saline conditions.
- They cannot survive in osmotic stress, causing them to die.
- In low-salinity conditions, nitrification can occur.
- However, it is sensitive to salt accumulation, especially in agricultural areas.
Importance of Nitrogen Fixation and Metabolism in Agriculture
For agriculture and food production, nitrogen fixation and metabolism serve as important processes.
Nitrogen is necessary for plants to flourish, yet it is often lacking in soils. Because of this, farmers must use nitrogen fertilizers to provide their crops with the nutrients they require.
Mentioned below are the importance of nitrogen fixation and metabolism in agriculture.
- Legumes fix nitrogen, hence crop rotation with them can organically replenish the soil in sustainable agricultural practices.
- The use of artificial fertilizers reduces due to nitrogen fixation, which could pollute the environment.
- Nitrogen is a component of chlorophyll, which is required for carrying out photosynthesis.
- For the production of crops high in protein, such as lentils, beans, and soybeans, nitrogen fixation is needed.
- Also, to synthesize vital macromolecules for growth and reproduction, such as proteins, amino acids, and nucleic acids (DNA and RNA), plants need nitrogen.
FAQs on Nitrogen Fixation and Nitrogen Metabolism
What is nitrogen fixation?
The process that turns atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into ammonia is known as nitrogen fixation. Additionally, it is transformed into various nitrogenous chemicals that are useful to microorganisms, plants, and animals. Nitrogen incorporation into plants or biological systems depends on this process.
Why is nitrogen fixation important for plants?
Amino acids, proteins, nucleic acids, and chlorophyll all contain significant amounts of nitrogen. But plants cannot directly absorb nitrogen from the atmosphere. Nitrogen fixation converts nitrogen into forms that are useful to plants, such as nitrate or ammonia. Plants can better absorb nitrogen and flourish as a result of this.
What are nitrifying bacteria, and what role do they play?
The nitrogen cycle depends on nitrifying microorganisms such as Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter. Ammonia is converted to nitrite by Nitrosomonas. Next, nitrite is converted to nitrate by Nitrobacter. These microbes aid in converting nitrogen into forms that are absorbed and utilized by plants
What is nitrogen metabolism?
The mechanism that enables organisms to use nitrogen is known as nitrogen metabolism. Nitrogen undergoes many transformations after it is fixed. These processes are referred to as denitrification, assimilation, nitrification, and ammonification. These processes assist plants and animals in using nitrogen to produce DNA, proteins, and other essential compounds.
What are the different types of nitrogen fixation?
The three types of nitrogen fixation are biological, industrial, and atmospheric fixation








