Table of Contents
Vascular tissues are deemed as the essential lifeline of a plant. This is because they have the key purpose of transporting substances within the plant structure. Out of these tissues, the xylem and phloem are the most important tissues in a plant and both of them have very specific roles to play in the plant.
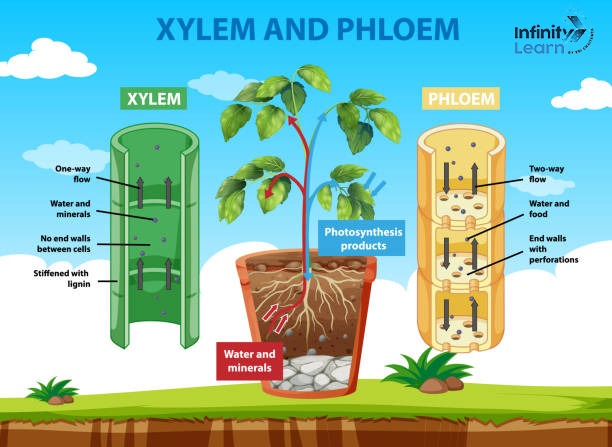
Xylem is mainly involved in the transport of water and dissolved minerals to various parts of the plant. It transports to the aerial parts and is involved in mechanical support of the plant.
On the other hand, phloem is used to transport sugar and other organic photosynthesis products from the source to the bottom, requiring energy.
Thus, the xylem and phloem components together are a transport system. Knowing about these tissues is important to anyone who wants to study plants, horticulture or agriculture, or has an interest in environmental matters.
Therefore, in this article, we will be discussing these two tissues in depth.
What is Xylem?
The xylem is one of the two main vascular tissues in plants that assist in the transportation of water and nutrients in plants. It is one of the vascular tissues, made up of some different types of cells namely:
- Tracheids
- Vessel elements
- Fibres
- Parenchyma cells
What is Transpiration?
In growth and development, the main use of xylem is to transfer water and dissolved minerals from the root to the leaf and other organs of the plant. This process is termed as transpiration by which the water evaporates from the leaves and causes a suction force by drawing up the water through the xylem vessels.
What is the Function of Xylem?
The function of the xylem is to transport water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the leaves of the other parts of the plant, as well as to provide structural support. Let us discuss some key roles and functions of Xylem tissues in the plant’s body.
- Role of Xylem in Water Transport:
- The xylem has an important skill for transporting water and dissolved material like minerals from the root towards the aerial part of the vascular plants.
- This process is important for the plant to be able to take water.
- It is important for photosynthesis and several vital physiological functions of the plant.
- Mechanism of Water Movement:
-
- When water gets into the roots it fills the xylem, starting its upward movements.
- The circulation of water within the xylem is facilitated by a process called transpiration and this is the evaporation of water on the surface of the leaves.
- This causes an area of low pressure known as ‘suction’.
- This draws water upward and thus it is able to rise up in defiance of gravity.
- Nutrient Transport:
- Apart from water transport, the xylem has another function of transporting of the mineral solution from the soil to different parts of the plant.
- These minerals are involved in the metabolic activities of plants such as the synthesis of enzymes and other important compounds.
- Structural Support Function:
- They play a role in providing support to the structure of a plant.
- The safety of tracheids and passed substances is covered by a special layer called lignin.
- Lignin is an organic polymer with high strength.
- This lignification enables the plant to become erect.
- It also withstands the effects of forces such as wind as well as bears the load of the leaves, flowers and fruits.
What is Phloem?
Phloem is a kind of vascular tissue present in plants. The major function is to transport organic solutes with sugars produced in the process of photosynthesis to other parts of the plant, tree, or shrub.
This transport process or Translocation, delivers energy in the parts required for growth, storage or for any other activity.
- Composition of Phloem Tissues:
Phloem is made of several kinds of cells, namely:
- Sieve tube elements
- Companion cells
- Phloem fibres
- Phloem parenchyma cells.
Sieve tube elements are involved in the actual transport of sugars. This is facilitated by companion cells that are involved in the process of loading and unloading the molecules in the sieve tubes.
- Direction of Movement:
- Bidirectional Movement- Unlike xylem, which transports substances in one direction only. Whereas, the phloem can transport substances up and downwards according to the needs of the plant.
What are the Functions of Phloem?
Phloem plays an essential role as it supports the plant in growth, reproduction and its ability to respond to the environment. Below are the pointers that provide the knowledge about the functions of phloem.
- Role in Nutrient:
- The other kind of vascular tissue in plants is phloem.
- It plays a major role in moving organic solutes across the plant, especially sugars synthesised in the process of photosynthesis.
- This process or pass is known as translocation.
- Whereby energy is channelled to appropriate areas such as growth, storage, and so on.
- Role in Growth and Storage:
- Phloem helps in growth, reproduction and the processes of the plant’s reaction to external conditions.
- The roots stems, flowers, and fruits of the plant get the nutrients they need to function.
- Role in Photosynthesis Product Distribution:
- The main function of phloem is to transport the products of photosynthesis to different parts of the plant.
- Also, it brings in nutrients and water to various organs as needed.
- Role in Energy and Storage:
- Transports organic products in different parts of the plant for growth, storage, or energy.
Xylem and Phloem FAQs
What is common between Xylem and Phloem?
Xylem and phloem are two primary vascular tissues that are present in plants and are accountable for the transportation of particular products in the plants.
Why is Xylem thicker than Phloem?
Xylem is thicker than phloem because it has lignin in the cell wall and so has more strength to combat outward pressures.
What are vascular tissues?
Vascular tissues are complex plant tissues that consist of xylem and phloem tissue with the function of transporting water, minerals and nutrients to body parts necessary for growth as well as for the existence of plants
What is the difference between Xylem and Phloem?
Xylem moves water and minerals from the roots to the aerial parts of the plant in unidirectional movement. Phloem transports sugars from the source leaves to the sink organs in the bidirectional movement.
Is xylem faster than phloem?
Yes, xylem transport is generally faster than phloem because of the transpiration pull driving force through the formation of the passive transport. Phloem is active, thus slower. Hence, translocation is an energy based process.









