Table of Contents
Boric Acid Formula
Boric acid, also known as hydrogen borate or boracic acid, is a white crystalline solid with the chemical formula H3BO3. It has diverse applications, including use as an antiseptic, insecticide, flame retardant, buffering agent, and neutron absorber. It is found naturally in volcanic regions and hot springs. Boric acid is known for its low toxicity and historical use dating back to ancient times.
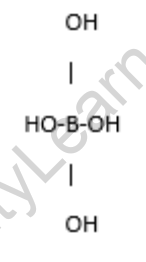
The formula of Boric Acid
H3BO3
The formula indicates that boric acid is composed of three hydrogen atoms (H) bonded to a central boron atom (B), which is further bonded to three hydroxyl groups (OH).
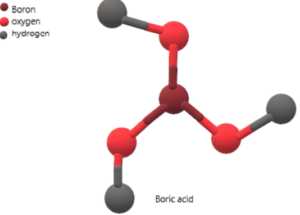
Structure of Boric Acid
The structure of boric acid consists of a trigonal planar boron atom with three hydroxyl groups attached to it.
Physical properties of Boric Acid
- State: Boric acid exists as a white crystalline solid at room temperature. It is commonly found in the form of fine powder or large crystals.
- Melting Point: The melting point of boric acid is relatively low, around 170-176°C (338-349°F). At this temperature, boric acid undergoes a phase transition from a solid to a liquid state.
- Boiling Point: Upon further heating, boric acid does not boil directly. Instead, it undergoes sublimation, where it transitions from a solid to a vapor without passing through the liquid phase. The sublimation point of boric acid is around 300-320°C (572-608°F).
- Density: The density of boric acid varies depending on its crystalline form and the presence of any impurities. Typically, it has a density of about 1.435 g/cm³.
- Solubility: Boric acid is moderately soluble in water. The solubility increases with temperature. At room temperature, approximately 3.5 grams of boric acid can dissolve in 100 grams of water, forming a slightly acidic solution.
- Hygroscopicity: Boric acid exhibits hygroscopic properties, meaning it can absorb moisture from the surrounding air. This hygroscopic nature allows it to readily dissolve in humid environments.
- Crystal Structure: Boric acid crystals have a layered structure. The layers are composed of planar boron atoms with attached hydroxyl groups. The layers are held together by weak hydrogen bonding.
Chemical properties of Boric Acid
- Solubility: Boric acid is soluble in water and other polar solvents.
- Acidity: It is a weak acid and acts as a proton donor, releasing hydrogen ions (H+) in aqueous solutions.
- Buffering capacity: Boric acid exhibits buffering properties, helping to maintain a stable pH in solutions.
- Reaction with bases: It reacts with bases to form borates.
Uses of Boric Acid
Antiseptic and preservative: Boric acid has antiseptic properties and is used as an ingredient in topical antiseptic solutions and ointments. It also acts as a preservative in pharmaceuticals and cosmetics.
- Insecticide: Boric acid is used as an insecticide to control pests like cockroaches, ants, termites, and silverfish. It disrupts their digestive system and causes dehydration.
- Flame retardant: Boric acid is used as a flame retardant in various materials, including cellulose insulation, textiles, and polymers.
- Glass and ceramic production: It is employed as a flux in the production of glass and ceramics to lower the melting point and improve their thermal and chemical stability.
- Medical applications: Boric acid solutions are sometimes used as an eyewash to relieve eye irritation and treat certain eye infections.
Boric acid should be handled with care, as excessive exposure or ingestion can be toxic. Pregnant women and young children should avoid direct contact with boric acid due to potential risks.
Solved Examples on Boric Acid
Example 1: What happens when Boric Acid dissolved in water?
Solution:
When boric acid is dissolved in water, it undergoes dissociation to form hydrogen ions (H+) and borate ions (BO3-).
H3BO3 + H2O ⇌ H+ + [B(OH)4]-
Example 2: Reaction with Sodium Hydroxide
When boric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), a salt called sodium borate and water are formed.
H3BO3 + 3NaOH → Na3BO3 + 3H2O
In this reaction, one molecule of boric acid reacts with three molecules of sodium hydroxide to produce one molecule of sodium borate and three molecules of water.
Frequently asked questions on Boric Acid
What is boric acid used for?
Boric acid is used for antiseptic purposes, insect control, and as an eye wash.
Is boric acid the same as borax?
No, boric acid and borax are different; borax is a mineral, while boric acid is derived from borax.
What is another name for boric acid?
Another name for boric acid is hydrogen borate.
What is the main purpose of boric acid?
The main purpose of boric acid is for its antiseptic, insecticidal, and eye-cleansing properties.
Which acid kills cockroach?
Boric acid is effective in killing cockroaches.
Is borax used for carrom powder?
Yes, borax can be used in carrom powder to reduce friction on the board.
Is boric acid safe for hair?
Boric acid isn't typically used for hair and may be harmful, always consult a healthcare provider before use.
Is boric acid used for skin?
Boric acid can be used for minor skin infections, but use cautiously and consult a healthcare provider before use.








