Table of Contents
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Biology Solved 2016 Set 4
Section A
1. We have usually red blood flowing through our bodies, but invertebrates like prawns, Pila have blue blood in them. Give reason for the blood being imparted blue colour.
2. The siblings differ from each other in certain features, though share some similarities as well. They also differ as well as resemble in certain characteristics to their parents. What is the source of these variations among them?
3. ‘Heart is considered as an endocrine gland’ state whether, the given statement is true or false. Support your answer with reason.
4. Name the actual sites of light and dark reactions inside the chloroplasts.
5. Where would you categorise an organism that may be cellular or acellular with
naked cytoplasm, multinucleate and saprophytic in nature?
Section B
6. Define sympodial axis. Where is it found?
7. Name the organelles which represent cell’s.
(i) Circulatory system (ii) Protein synthesis machinery
(iii) Powerhouse (iv) Disposal unit
(v) Control centre
8. Differentiate between red and white muscle fibres
9. (a) Name the most common pathway of respiration, in all living organisms.
(b) Where does it occur in a cell? What are its products?
or
Deficiency of certain nutrients leads to diseases or show deficiency symptoms in plants. However at times, the micronutrient like manganese when absorbed in larger quantities becomes toxic to the plant. Explain.
Section C
10. Give an account of types of meristematic tissue found in plants.
11. Illustrate a glycosidic, peptide and a phosphodiester bond.
12. Plants do not have specialised circulatory system for transport of substances, yet they transport substances. How?
13. What is the difference between electrical transmission and chemical transmission?
14. ‘Cell is an open dynamic system’. Justify the statement.
15. A student of taxonomy was puzzled when told by his professor to look for a key to identify a plant. He went to his friend to clarify, what ‘key’ the professor was referring to? What would the friend explain to him?
16. If a group of plants lacks photorespiration,
(a) Which of the cell in plant might be having RuBisCO enzyme
(b) In which cell the C02 fixation initially occurs?
(c) Describe some characteristic features of such plants.
17. Can you explain how a plant cell act as an osmotic system?
18. (a) Sand dollars, sea cucumbers and sea lilies are representatives of which phylum?
(b) What kind of symmetry do they exhibit in adults? Also name the locomotary organs in this phylum.
(c) Mention two characteristic features of this phylum
19. What would be expected to happen if
(a) GA3 is applied to rice seedlings.
(b) Dividing cells stop differentiating.
(c) You forget to add cytokinin to the the culture medium.
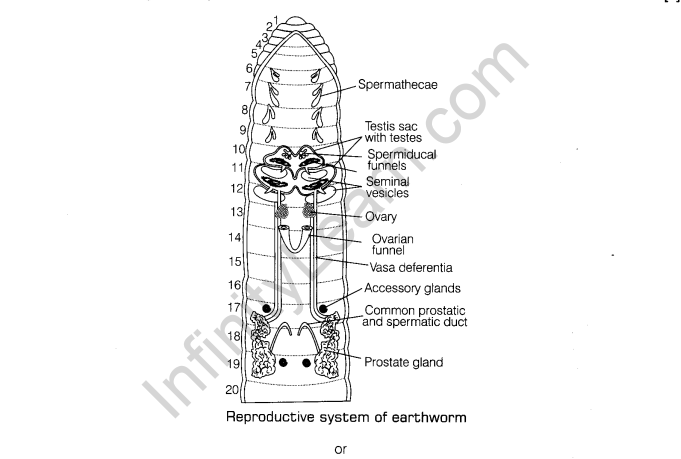
20. Draw a well labelled diagram of the reproductive organs of earthworm.
or
Identify and write about the appropriate type of tissues in column II according to the functions mentioned in column I.

21. During vacation, Pradeep visited his village where his grandfather lives. Next day he went with his grandfather to visit their sugarcane fields, which was the main crop there. All the fields of sugarcane showed poor yield and dwarf varieties. They were not juicy as well. He suggested his grandfather and other farmers of the village to apply growth regulators in order to increase the yield and quality of sugarcane.
(a) Which growth regulator Pradeep must have suggested them?
(b) What impact it would have on quality and yield of sugarcane?
(c) Name any two other applications of the hormone, useful in agriculture.
(d) What values are reflected by Pradeep?
Section D
22. Briefly describe the events taking place in meiotic division. Where does it occur?
or
Calcium plays a very important role in the formation of bones. Write on the role of endocrine glands and hormones responsible for maintaining calcium homeostasis.
23. List differences between the natural and artificial system of classification in plants.
or
Point out the differences in the anatomy of leaf of peepal (Ficus religiosa) and maize (Zea mays). Draw the diagrams and label the differences
Answers
Section A
1. We have usually red blood flowing through our bodies, but invertebrates like prawns, Pila have blue blood in them. Give reason for the blood being imparted blue colour.
Ans. The invertebrates like prawns, Pila, etc., contain a blue copper protein complex pigment called haemocyanin, which imparts blue colour to their blood.
2. The siblings differ from each other in certain features, though share some similarities as well. They also differ as well as resemble in certain characteristics to their parents. What is the source of these variations among them? [1]
Ans. During meiosis (reductional division), the homologous chromosomes get synapsed and crossing over takes place between non-sister chromatids resulting in recombination. Which brings about genetic variability.
3. ‘Heart is considered as an endocrine gland’ state whether, the given statement is true or false. Support your answer with reason.[1]
Ans. Heart is considered as an endocrine gland as its cells, i.e. cardiocytes secrete a peptidal hormone Atrial Natriuretic Factor (ANF), which regulates the volume of blood through increased excretion of ions and water.
4. Name the actual sites of light and dark reactions inside the chloroplasts.[1]
Ans. The light reaction takes place in grana or thylakoids containing the photosystems and electron carriers in their membrane while, the dark reactions occur in stroma of chloroplast.
5. Where would you categorise an organism that may be cellular or acellular with naked cytoplasm, multinucleate and saprophytic in nature? [1]
Ans. The above given characteristics are those of slime molds and could be categorised under kingdom-Protista.
Section B
6. Define sympodial axis. Where is it found?[2]
Ans. When the peduncle of flower is formed by the fusion of bases of axillary branches and main axis, it is called sympodial axis. It is found in uniparous or monochasial cymose type of inflorescence.
7. Name the organelles which represent cell’s.[2]
(i) Circulatory system (ii) Protein synthesis machinery
(iii) Powerhouse (iv) Disposal unit
(v) Control centre
Ans. The organelles that represent cell’s.
(i) Circulatory system is endoplasmic reticulum.
(ii) Protein synthesis machinery is ribosomes.
(iii) Powerhouse is mitochondria.
(iv) Disposal unit is lysosomes.
(v) Control centre is hypothalamus.
8. Differentiate between red and white muscle fibres.
Ans. The differences between red and white muscles fibres are:

9. (a) Name the most common pathway of respiration, in all living organisms.[1]
(b) Where does it occur in a cell? What are its products?[1]
or
Deficiency of certain nutrients leads to diseases or show deficiency symptoms in plants. However at times, the micronutrient like manganese when absorbed in larger quantities becomes toxic to the plant. Explain.[2]
Ans. (a) The most common pathway of respiration, in all living organisms is glycolysis.
(b) Glycolysis occurs in cytoplasm of cell. It produces two molecules of pyruvic acid which may either enter Krebs’ cycle in the presence of 02 (aerobic respiration) or undergo fermentation (anaerobic respiration).
or
Since, manganese is a micronutrient, it is required in trace amounts only. When absorbed in large quantities by plants, it becomes toxic which is expressed as brown spots surrounded by chlorotic veins. Further, manganese also competes with magnesium and iron for absorption.
Therefore, excess of manganese induces deficiency of iron, magnesium as well as calcium translocation in plants.
Section C
10. Give an account of types of meristematic tissue found in plants. [3 x 1]
Ans. Meristems are divided into thrfee types on the basis of position in the plant body:
(a) Apical meristem The apical meristem is located at the apices/tips of roots and shoots. It has following functions:
(i) Forms the primary tissues of the plant and help in growth in length.
(ii) Certain cells of apical meristem constitute the axillary buds present in the axils of leaves.
(b) Intercalary meristem It occurs in between mature tissues, at the bases of internodes and leaf sheaths of grasses and other monocots. They help to regenerate the part of grasses, eaten by herbivores and help in primary growth of plants.
(c) Lateral meristem It is arranged parallel to the sides of the organs of plants. The lateral meristem is responsible for increase in the diameter of an organ.
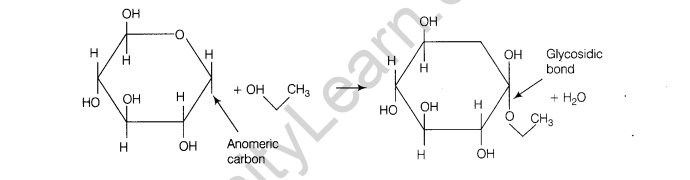
11. Illustrate a glycosidic, peptide and a phosphodiester bond.
Ans. Glycosidic Bond It is formed between two C-atoms of two adjacent monosaccharides, thus it forms a polysaccharide by linking individual monosaccharides. This bond is formed by dehydration, i.e. removal of water.
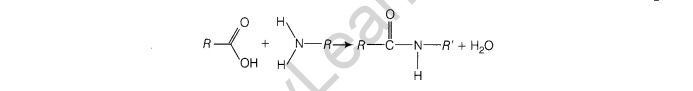
Peptide Bond A peptide bond (amide bond) is a chemical bond formed when the carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the amine group of the other molecule, thereby releasing a molecule of water (H2 O)
Phosphodiester Bond A phosphodiester bond is a group of strong covalent bonds between a phosphate group and two other molecules over two ester bonds. In DNA and RNA, the phosphodiester bond is the linkage between the 3′ carbon atom of one sugar molecule and the 5 carbon of another, deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA. [3 x 1]
12. Plants do not have specialised circulatory system for transport of substances, yet they transport substances. How? [3]
Ans. In the absence of specialised circulatory system as in higher animals, the root system in plaRts play an important role in absorption of water and nutrients from the soil either actively or passively and transport them to various parts of the plants. Transportation of substances, e.g. water, nutrients and food over long distances including upward and downward movements is achieved through vascular system comprising of xylem and phloem.
13. What is the difference between electrical transmission and chemical transmission?
14. ‘Cell is an open dynamic system’. Justify the statement. [3]
Ans. Ceil allows exchange including entry and exit of matter and energy from its surroundings. It takes up water, oxygen, food, salts for growth and division and energy to carry out its metabolic processes. It also releases its waste matter and secretions to outside along with heat (energy). The exchange of matter or substances between the cell and its environment is dynamic as it varies in direction and rate as per the requirements of a cell. Thus, a cell attains a steady-state wherein the internal conditions of cell remain constant. Hence, cell is considered to be an open dynamic system.
15. A student of taxonomy was puzzled when told by his professor to look for a key to identify a plant. He went to his friend to clarify, what ‘key’ the professor was referring to? What would the friend explain to him?
Ans. In this question, the word ‘key’ stands for taxonomic keys. In systematics, a taxonomic key is a device for diagnosting alternate characters which provide an easy means of identification for unknown organisms. The concept of key was introduced by Ray.
The taxonomic keys help an individual in the identification, nomenclature and classification of a newly discovered plant or animal specimen. Separate taxonomic keys are required for each taxonomic category. Keys are analytical in nature.
16. If a group of plants lacks photorespiration,
(a) Which of the cell in plant might be having RuBisCO enzyme
(b) In which cell the C02 fixation initially occurs?
(c) Describe some characteristic features of such plants.[3 x l]
Ans. (a) If a group of plants lack photorespiration, then the bundle sheath cells might be possessing RuBisCO.
(b) C02 fixation in such plants initially occurs in mesophyll cells.
(c) Such plants are known as C4 plants, which possess following characteristic features.
(d) Mostly tropical, that can tolerate high temperatures.
(e) Leaves of such plants show Kranz anatomy having large number of chloroplasts, thick walls impervious to gaseous exchange and no intercellular spaces.
17. Can you explain how a plant cell act as an osmotic system?[3]
Ans. (a) A plant cell has a cell membrane and cell wall as its boundary. The cell wall is freely permeable to water, hence it is not a barrier to movement, while the plasma membrane is selectively permeable,
(b) In plant cells, the cells usually contains a large central vacuole, whose contents, the vacuolar sap, contribute to the solute potential of the cell. The difference between in the concentration of vacuolar sap and external solution results in osmosis.
18. (a) Sand dollars, sea cucumbers and sea lilies are representatives of which phylum?
(b) What kind of symmetry do they exhibit in adults? Also name the locomotary organs in this phylum.
(c) Mention two characteristic features of this phylum.[3 x 1]
Ans. (a) Sand dollars, sea cucumbers and sea lilies are representatives of phylum-Echinodermata.
(b) The adults of this phylum exhibit pentamerous radial symmetry. The locomotory organs is tube feet.
(c) The two characteristic features of phylum- Echinodermata are
(i) Single layered and ciliated epidermis, covering the thick dermis layer comprising of mesodermal endoskeleton of calcareous plates, often possesing spines. Thus, named Echinodermata.
(ii) They are enterocoelous and contains a water filled ambulacral or water vascular system.
19. What would be expected to happen if
(a) GA3 is applied to rice seedlings.
(b) Dividing cells stop differentiating.
(c) You forget to add cytokinin to the the culture medium.[3 x 1]
Ans. (a) The rice seedlings show extraordinary elongation of stem and leaf sheaths.
(b) Tissue and organ differentiation will not take place.
(c) No root and shoot formation will take place in the callus.
20. Draw a well labelled diagram of the reproductive organs of earthworm. [3×1]
or
Identify and write about the appropriate type of tissues in column II according to the functions mentioned in column I.

Ans. Earthworm being a hermaphrodite bears both testis and ovaries in the same individual.
(a) Simple columnar epithelium This epithelium lines the stomach, intestine, gall bladder, etc. It forms gastric and intestinal glands, where it has a secretary role and is called as glandular epithelium. In intestinal mucosa, this epithelium has microvilli which increase the absorptive surface area and is called brush bordered columnar epithelium.
(b) Stratified epithelium These are made up of more than one layer of epithelial cells (also called compound epithelium). They cover the surface where constant wear and tear take place. They mainly function as a protective epithelium.
(c) Connective tissue It is the tissue which connects different tissues or organs and provides support to various structures in animal body. These tissues are mesodermal in origin and consist of living cells and extra cellular matrix, e.g. blood is a fluid or vascular connective tissue.
21. During vacation, Pradeep visited his village where his grandfather lives. Next day he went with his grandfather to visit their sugarcane fields, which was the main crop there. All the fields of sugarcane showed poor yield and dwarf varieties. They were not juicy as well. He suggested his grandfather and other farmers of the village to apply growth regulators in order to increase the yield and quality of sugarcane.
(a) Which growth regulator Pradeep must have suggested them?
(b) What impact it would have on quality and yield of sugarcane?
(c) Name any two other applications of the hormone, useful in agriculture.
(d) What values are reflected by Pradeep?
Ans. (a) Pradeep would have suggested the plant growth regulator, gibberellins to be applied in sugarcane in his class to real life problem. [4×1]
(b) Gibberellins increase the length of stem as well as the sugar content thereby making them juicy, thus improving the quantity as well as quality of sugarcanes.
(c) The other applications of gibberellins in agriculture are
(i) Delay of senescence so, that fruits stay ripe for longer period.
(ii) Helps to improve and elongate shape of fruits like apple.
(d) Pradeep is smart, responsible and well attentive. He intelligently applied the knowledge he acquired
Section D
22. Briefly describe the events taking place in meiotic division. Where does it occur?[5]
or
Calcium plays a very important role in the formation of bones. Write on the role of endocrine glands and hormones responsible for maintaining calcium homeostasis.[5]
Ans. Meiotic division takes place in germ cells. The number of chromosomes is reduced to half in daughter cells. Meiotic cell division is divided into two phases, i.e. meiosis-l and II.
In the meiotic-l division, the homologous chromosomes pair to form bivalent. Exchange of genetic material takes place. The chromosomes, separate and get distributed into daughter cells.
Long prophase-l is divided info five sub-stages, i.e. leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene and diakinesis. During metaphase-l, the bivalents arrange themselves on equatorial plate with their arms on the plate, but the centromere is directed towards opposite pole. It is followed by anaphase-l.
Now, the homologous chromosomes repel each other, move to the opposite poles with both their chromatids. In this way each pole gets half the chromosomes number of the parent cell
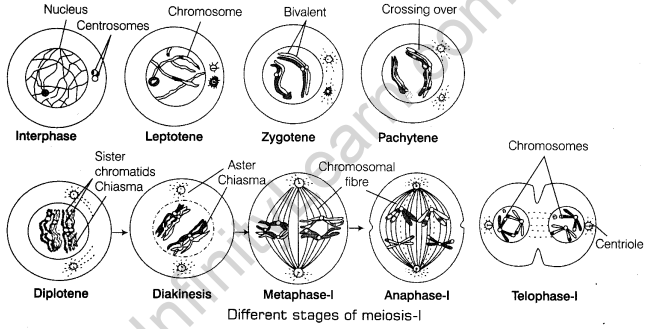
In telophase-l, the nuclear envelope and nucleolus are appear. The centromere of each chromosome breaks, separating the chromatids, one each to a daughter cell. The meiosis-ll is similar to mitotic divisions, where equational division takes place. During prophase-ll, chromosomes become compact. In metaphase-ll, chromosomes align at equator or metaphase plate.
In anaphase-ll, shortening of chromosomes and movement towards opposite poles occurs. Telophase-ll is the last phase and reverse of prophase, with the formation of nuclear envelope, nucleoli, rRNA, etc.
Cytokinesis After nuclear division, the cytoplasm and organelles also divides and are equally distributed to four cells.
As a result of meiotic division, the four daughter cells are formed with half the chromosome number (haploid) in each cell.
or
The endocrine glands and hormones that are responsible for maintaining calcium homeostasis, are thyroid and parathyroid glands and their associated hormones are calcitonin and Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) respectively.
(i) Parathyroid glands are the glands developed from the endoderm of the embryo. The cells or parathyroid glands are of two types, i.e. chief cells and oxyphil cells. The chief cells of the parathyroid glands secrete Parathyroid Hormone (PTH).
This hormone (PTH) is involved in regulating calcium and phosphate balance between the blood and other tissue. It mobilises the release of calcium into the blood from bones. PTH increases calcium reabsorption by the body organs like intestine and kidneys.
(ii) Thyroid gland is the largest endocrine gland located anterior to the thyroid cartilage of the larynx in the neck. This gland plays a vital role in maintaining calcium homeostasis. It releases thyrocalcitonin hormone produced by the parafollicular cells, also called ‘C’ cells.
The hormone is secreted when the calcium level in blood are high. It is a 32 amino acid peptide hormone that lowers the calcium level by suppressing release of calcium ions from the bones. Thus, calcitonin has an action opposite to that of the parathyroid hormone on calcium homoeostasis.
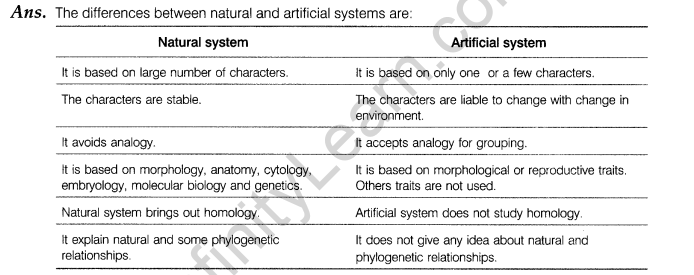
23. List differences between the natural and artificial system of classification in plants.
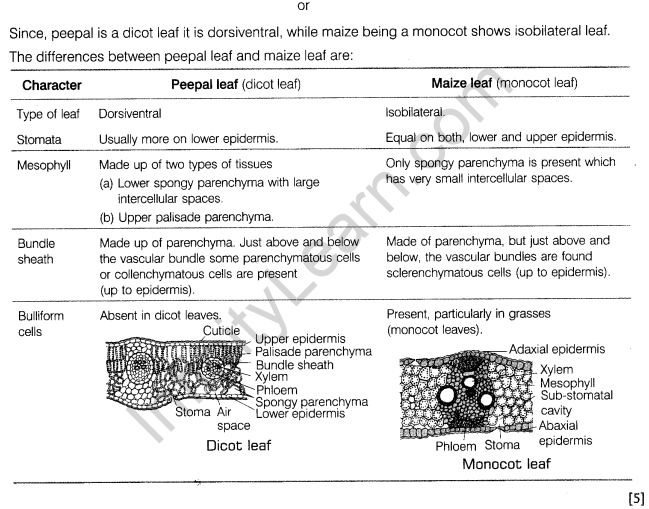
or
Point out the differences in the anatomy of leaf of peepal (Ficus religiosa) and maize (Zea mays). Draw the diagrams and label the differences