Table of Contents
Class 12 Chemical Kinetics Important Questions with Answers
Class 12 Chemistry exams with Important questions and answers for Chapter 4: Chemical Kinetics. Aligned with the CBSE curriculum and NCERT syllabus, these questions help you prepare for annual exams and entrance tests like NEET and JEE. Also access NCERT Solutions for Class 12 to score good marks in exam.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Define ‘rate of a reaction’. (Delhi 2010)
Answer: Rate of a reaction: Either, The change in the concentration of any one of the reactants or products per unit time is called rate of a reaction. Or, The rate of a chemical reaction is the change in the molar concentration of the species taking part in a reaction per unit time.
Question 2. Define ‘order of a reaction’. (All India 2011)
Answer: The sum of powers of the concentration of the reactants in the rate law expression is called the order of reaction.
Question 3. Define ‘activation energy’ of a reaction. (All India 2011)
Answer: The minimum extra amount of energy absorbed by the reactant molecules to form the activated complex is called activation energy.
The activation energy of the reaction decreases by the use of catalyst.
Question 4. Express the rate of the following reaction in terms of the formation of ammonia :
N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g) (Comptt. All India 2013)
Answer:
![]()
Question 5. If the rate constant of a reaction is k = 3 × 10-4 s-1, then identify the order of the reaction. (Comptt. All India 2013)
Answer: S-1 is the unit for rate constant of first order reaction.
Click Here: CBSE Syllabus For Class 12
Question 6. Write the unit of rate constant for a zero order reaction. (Comptt. All India 2013)
Answer: Mol L-1 S-1 is unit of rate constant for a zero order reaction.
Question 7. Define rate of reaction. (Comptt. Delhi 2016)
Answer: The change in concentration of reactant or product per unit time is called rate of reaction.
Question 8. Define rate constant (K). (Comptt. All India 2016)
Answer: Rate constant. It is defined as the rate of reaction when the concentration of reaction is taken as unity.
Question 9. For a reaction R → P, half-life (t1/2) is observed to be independent of the initial concentration of reactants. What is the order of reaction? (Delhi 2017)
Answer: The t1/2 of a first order reaction is independent of initial concentration of reactants.
Chemical Kinetics Class 12 Important Questions Short Answer Type -I [SA-I]
Question 10. A reaction is of second order with respect to a reactant. How will the rate of reaction be affected if the concentration of this reactant is
(i) doubled, (ii) reduced to half? (Delhi 2009)
Answer: Since Rate = K[A]2
For second order reaction Let [A] = a then Rate = Ka2
(i) If [A] = 2a then Rate = K (2a)2 = 4 Ka2
Rate of reaction becomes 4 times
(ii) If [A] = \(\frac{a}{2}\) then Rate = K \(\left(\frac{a}{2}\right)^{2}=\frac{\mathrm{K} a^{2}}{4}\)
∴ Rate of reaction will be \(\frac{1}{4}^{\text { th }}\) .
Question 11. Define the following :
(i) Elementary step in a reaction
(ii) Rate of a reaction (All India 2009)
Answer:
(i) Elementary step in a reaction: Those reactions which take place in one step are called elementary reactions.
Example : Reaction between H2, and I2 to form 2HI
H2 + I2 → 2HI
(ii) Rate of a reaction: The change in the concentration of any one of the reactants or products per unit time is called rate of reaction.
Question 12. Define the following :
(i) Order of a reaction
(ii) Activation energy of a reaction (All India 2009)
Answer:
(i) Order of a reaction :
- It is the sum of powers of molar concentrations of reacting species in the rate equation of the reaction.
- It may be a whole number, zero, fractional, positive or negative.
- It is experimentally determined.
- It is meant for the reaction and not for its individual steps.
(ii) Activation energy of a reaction: The minimum extra amount of energy absorbed by the reactant molecules to form the activated complex is called activation energy.
Question 13. A reaction is of first order in reactant A and of second order in reactant B. How is the rate of this reaction affected when (i) the concentration of B alone is increased to three times (ii) the concentrations of A as well as B are doubled? (Delhi 2010)
Answer:
r = K[A]1 [B]2
(i) When concentration of B increases to 3 times, the rate of reaction becomes 9 times
r = KA(3B)2 ∴ r = 9KAB2 = 9 times
(ii) r = K(2A) (2B)2 ∴ r = 8KAB2 = 8 times
Question 14. The rate constant for a reaction of zero order in A is 0.0030 mol L-1 s-1. How long will it take for the initial concentration of A to fall from 0.10 M to 0.075 M? (Delhi 2010)
Answer:
For a zero order reaction,

Question 15. Distinguish between ‘rate expression’ and ‘rate constant’ of a reaction. (Delhi 2011)
Answer:
Rate expression: The expression which expresses the rate of reaction in terms of molar concentrations of the reactants with each term raised to their power, which may or may not be same as the stoichiometric coefficient of that reactant in the balanced chemical equation.
Rate constant: The rate of reaction when the molar concentration of each reactant is taken as unity.
Question 16. What do you understand by the rate law and rate constant of a reaction? Identify the order of a reaction if the units of its rate constant are : (i) L-1 mol s-1 (ii) L mol-1 s-1 (All India 2011)
Answer: The rate of reaction is found to depend on α concentration of term of reactant A and β concentration term of reactant B
Then Rate of reaction ∝ [A]α [B]β
or Rate = K [A]α [B]β
This expression is called Rate law.
‘K’ in this expression is called Rate constant. Rate constant’s unit :
(i) Unit = L-1 mol s-1 → Zero order reaction
(ii) Unit = L mol-1 s-1 → Second order reaction.
Question 17. The thermal decomposition of HCO2H is a first order reaction with a rate constant of 2.4 × 10-3 s-1 at a certain temperature. Calculate how long will it take for three-fourths of initial quantity of HCO2 H to decompose. (log 0.25 = -0.6021) (All India 2011)
Answer: Given : K = 2.4 × 10-3

Question 18. A reaction is of second order with respect to a reactant. How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of the reactant is reduced to half? What is the unit of rate constant for such a reaction? (All India 2011)
Answer:
Rate = K [A]2 = Ka2
If [A] = \(\frac{1}{2}\)a Rate = K \(\left(\frac{a}{2}\right)^{2}=\frac{1}{4}\) Ka2
∴ Rate = 1/4th (one fourth of origina rate)
The unit of rate constant is L mol-1 s-1
Question 19. What do you understand by the ‘order of a reaction’? Identify the reaction order from each of the following units of reaction rate constant:
(i) L-1 mol s-1 (ii) L mol-1 s-1 (Delhi 2012)
Answer:
Order of reaction: The sum of powers of the concentration of the reactants in the rate law expression is called the order of that chemical reaction.
r = K[A]x[B]y Order = x + y
(i) Zero order
(ii) Second order
Question 20. A reaction is of second order with respect to a reactant. How is its rate affected if the concentration of the reactant is (i) doubled (ii) reduced to half? (All India 2012)
Answer:
As Formula, r = K[R|2 …(Given)
(i) R’ = 2R ⇒ r = K[2R]-1 = 4KR-1
∴ Rate becomes 4 times than original rate
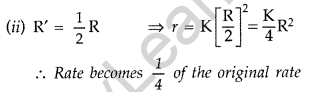
Question 21. What is meant by rate of a reaction? Differentiate between average rate and instantaneous rate of a reaction. (Comptt. All India 2012)
Answer:
Rate of reaction: It is the change in concentration of the reactants or products in a unit time. Average rate : Average rate depends upon the change in concentration of reactants or products and the time taken for the change to occur. R → P
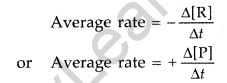
Instantaneous rate: It is defined as the rate of change in concentration of any one of the reactant or product at a particular moment of time.
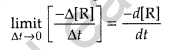
More Resources for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology
- NCERT Books
- NCERT Books for Class 12
Question 22.
(a) For a reaction A + B → P, the rate law is given by, r = k[A]1/2 [B]2.
What is the order of this reaction?
(b) A first order reaction is found to have a rate constant k = 5.5 × 10-14 s-1. Find the half life of the reaction. (All India 2013)
Answer:
(a) According to the formula : r = k[A]1/2 [B]2
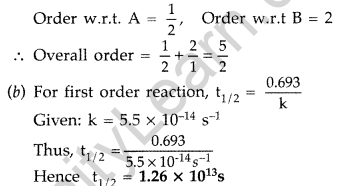
Question 23. Rate constant k for a first order reaction has been found to be 2.54 × 10-3 sec-1. Calculate its 3/4th life, (log 4 = 0.6020). (Comptt. India 2013)
Answer: For first order reaction:

Question 24. A first order gas phase reaction : A2B2(g) → 2A(g) + 2B(g) at the temperature 400°C has the rate constant k = 2.0 × 10-4 sec-1. What percentage of A2B2 is decomposed on heating for 900 seconds? (Antilog 0.0781 = 1.197) (Comptt. All India 2013)
Answer: Since the reaction is of the first order

Question 25. Write two differences between ‘order of reaction’ and ‘molecularity of reaction’. (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
| Order of reaction | Molecularity of reaction |
| (i) It is the sum of tire concentration terms on which die rate of reaction actually depends. | It is the number of atoms, ions or molecules that must collide with one another simultaneously so as to result into a chemical reaction. |
| (ii) It can be fractional as well as zero. | it is always a whole number. |
Question 26. Define the following terms :
(a) Pseudo first order reaction.
(b) Half life period of reaction (t1/2). (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
(a) Those reactions which are not truly of the first order but under certain conditions become first order reactions are called pseudo first order reaction.
(b) The time taken for half of the reaction to complete is called half life period.
Question 27. Explain the following terms :
(i) Rate constant (k)
(ii) Half life period of a reaction (t1/2) (Delhi 2014)
Answer:
(i) Rate constant (k): It is a proportionality constant and is equal to the rate of reaction when the molar concentration of each of the reactants is unity.
(ii) Half life period of a reaction (t1/2): The time taken for half of the reaction to complete is called half life penod.(R)t
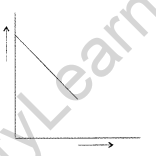
Question 28. For a chemical reaction R → P, the variation in the f concentration (R) vs. time (f) plot is given as
(i) Predict the order of the reaction.
(ii) What is the slope of the curve? (All India 2014)
Answer:
(i) It is zero order reaction.
(ii) Slope of the curve = -K
Question 29.
(a) For a reaction, A + B → Product, the rate law is given by, Rate = k[A]1[B]2. What is the order of the reaction?
(b) Write the unit of rate constant ‘k’ for the first order reaction. (Comptt. Delhi 2014)
Answer:
(a) For a reaction, A + B
Rate = k [A]1 [B]2
This is the third order of reaction.
(b) Unit of rate constant for first order reaction is S-1
Question 30. Define the following terms :
(i) Rate constant (k)
(ii) Activation energy (Ea) (Comptt. Delhi 2014)
Answer:
(i) Rate constant (k): It is a proportionality constant and is equal to the rate of reaction when the molar concentration of each of the reactants is unity.
(ii) Activation energy (Ea): The minimum extra amount of energy absorbed by the reactant molecules to form the activated complex is called activation energy.
Question 31. How does a change in temperature affect the rate, of a reaction? How can this effect on the rate constant of a reaction be represented quantitatively? (Comptt. All India 2014)
Answer:
The rate constant of a reaction increases with increase of temperature and becomes nearly double for every 10° rise in temperature.
The effect can be represented quantitatively by Arhenius equation K = Ae-Ea/RT
Where [Ea = Activation energy of the reaction; A = Frequency factor]
Question 32. Define each of the following :
(i) Specific rate of a reaction
(ii) Energy of activation of a reaction (Comptt. All India 2014)
Answer:
(i) Specific rate of a reaction: Specific rate of reaction is the rate of reaction when the molar concentration of each of the reactants is unity.
(ii) Activation energy of a reaction: The minimum extra amount of energy absorbed by the reactant molecules so that their energy becomes equal to threshold value, is called activation energy.
Question 33. A reaction is of second order with respect to its reactant. How will its reaction rate be affected if the concentration of the reactant is (i) doubled (ii) reduced to half? (Comptt. All India 2014)
Answer:
Since Rate = K[A]2
For second order reaction Let [A] = a then Rate = Ka2
(i) If [A] = 2a then Rate = K (2a)2 = 4 Ka2
∴Rate of reaction becomes 4 times
(ii) If [A] = \(\frac{a}{2}\) then Rate = K \(\left(\frac{a}{2}\right)^{2}=\frac{\mathrm{K} a^{2}}{4}\)
∴ Rate of reaction will be \(\frac{1}{4}^{\text { th }}\) .
Question 34. Define the following terms :
(i) Half-life of a reaction (t1/2)
(ii) Rate constant (k) (Comptt. Delhi 2015)
Answer:
(i) Half-life of a reaction (t1/2): Half-life period (t1/2) is the time in which half of the substance has reacted and its concentration is reduced to one-half of its initial concentration.
(ii) Rate constant (k): Rate constant may be defined as the rate of reaction when the molar concentration of each reactant is taken as unity.
Question 35. Write units of rate constants for zero order and for the second order reactions if the concentration is expressed in mol L-1 and time in second. (Comptt. All India 2015)
Answer:
Using formula of rate constant,
K = [mol L-1]1 – n s-1 (n = order of rxn)
Unit for zero order reaction,
K = [mol L-1]1 – 0 s-1
K = [mol L-1] s-1 = mol L-1 s-1
Unit for second order reaction,
K = [mol L-1]1 – 2 = [mol L-1]-1 s-1
Question 36. For a reaction: 2NH2(g) \(\stackrel{\mathrm{Pt}}{\longrightarrow}\) N2(g) + 3H2(g)
Rate = k
(i) Write the order and molecularity of this reaction.
(ii) Write the unit of k. (Delhi 2016)
Answer:
2NH2(g) \(\stackrel{\mathrm{Pt}}{\longrightarrow}\) N2(g) + 3H2(g)
(i) It is a zero order reaction and its molecularity is two.
(ii) Unit of k is mol L-1 s-1.
Question 37. For a reaction: H2 + Cl2 \(\stackrel{\mathrm{hv}}{\longrightarrow}\) 2HCl
Rate = k
(i) Write the order and molecularity of this reaction.
(ii) Write the unit of k. (All India 2016)
Answer:
H2 + Cl2 \(\stackrel{\mathrm{hv}}{\longrightarrow}\) 2HCl
This reaction is zero order reaction and molecularity is two.
(ii) Unit of k = mol L-1 s-1
Question 38. For a chemical reaction R → P, variation in ln[R] vs time (f) plot is given below:
For this reaction:
(i) Predict the order of reaction
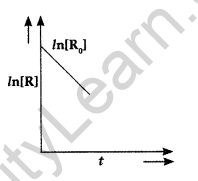
(ii) What is the unit of rate constant (k)? (Comptt. Delhi 2017)
Answer:
(i) It is zero order reaction.
(ii) The unit of rate constant (k) is mol L-1 S-1.





