Section A
1. Define plasmolysis.
2. Show the hierarchical arrangement of taxonomic categories in ascending order.
3. Name the pigment responsible for the colour of carrot.
4. Write the floral formula for the family-Fabaceae
5. Give another name for anaerobic respiration. How much energy is yielded from the food by this process?
Section B
6. The cross section of a plant material, when observed under the microscope shows the following features.
7. Write down some secondary functions of leaves.
8. Patients of cardiovascular diseases are usually recommended to use vegetable oils with polyunsaturated fatty acids. Give reasons.
9. ‘Photosynthesis is essential for sustaining life on earth’. Justify the statement with at least two reasons in support.
or
While examining the mitotic stage in a tissue, one finds some cells with 16 chromosomes and some with 32 chromosomes. What possible reasons could you assign to this difference in chromosome number?
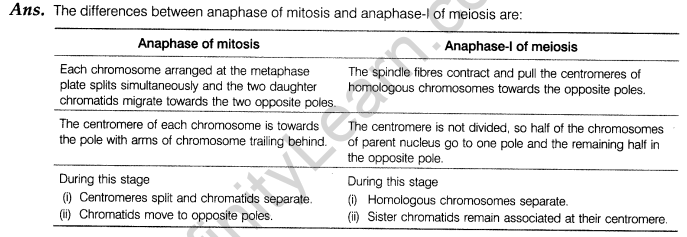
10. List any three differences between anaphase of mitosis and anaphase-I of meiosis.
11. Give an account of type of body wall and body cavity found in sponges.
or
Describe some general features of cartilaginous fishes.
12. Apart from being a plant hormone having physiological role, gibberellins are also used in agriculture to increase the yield. What role do these hormones play when applied externally in crop fields? .
13. (a) Define nerve impulse and explain the factors on which it depends.
(b) What do you understand by synergistic effect? Give example.
14. Mention two important functions of each of the given elements along with their deficiency symptoms
(a) P
(b) Fe
(c) Zn
15. With the help of a neatly labelled diagram, explain the structure of adipose tissue.
16. ‘Mitochondria are the powerhouse of the cell.’ Justify the statement.
17. (a) What is meant by threshold stimulus in muscle contraction?
(b) Give difference between actin and myosin.
18. Define turgor pressure. State any three advantages by which it is useful to green plants.
or
Explain giving reasons, why the rate of transpiration is more on sunny and windy day as compared to calm and cool day, even when they are appropriately watered.
19. Explain the concept of activation energy with the help of a graph.
20. What is the role played by renin-angiotensin in the regulation of functioning of kidney?
21. Arun’s grandfather while on a walk in morning collapsed in the garden. Arun spotted him and called their neighbour Dr. S Rakesh who took him to nearby clinic. After examining him, he gave him an injection and asked Arun to properly take care of his diet and exercise regime, else he would have to take these injections regularly, so as to control his increasing levels of sugar.
(a) Name the injection that doctor might have given to Arun’s grandfather.
(b) What is the role of the given hormone in controlling sugar levels in blood?
(c) What precautions are advised by doctor to control the disease? .
(d) What values are reflected by Arun’s behaviour?
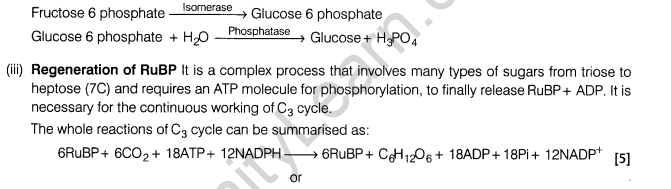
22. Describe the C3 cycle of carbon fixation in plants.
or
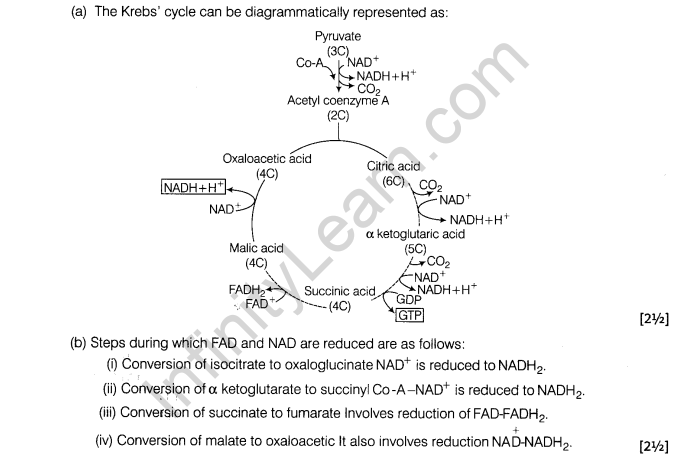
(a) Explain Krebs’ cycle in diagrammatic representation.
(b) During which steps of Krebs’ cycle, NAD and FAD are reduced?
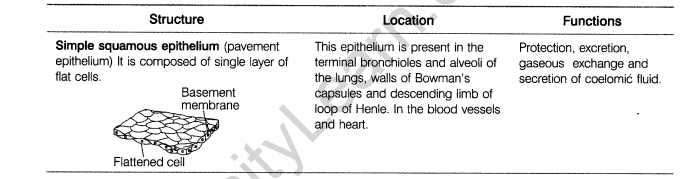
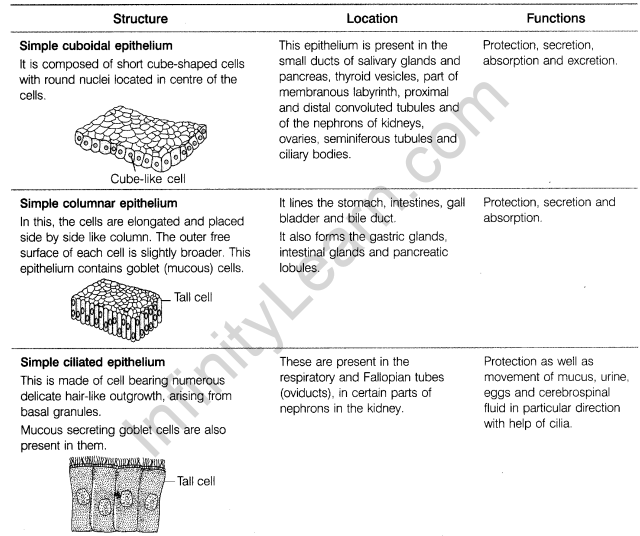
23. Describe the various types of simple epithelial tissues in animals, with the help of a labelled diagram.
or
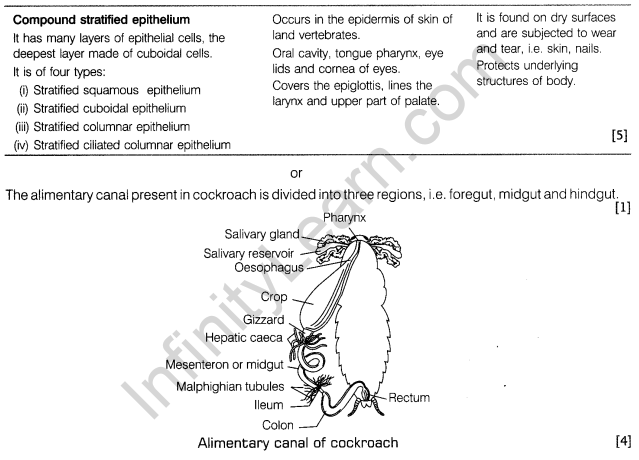
Draw the digestive system of cockroach. In how many parts is the alimentary canal of cockroach divided?
Answers
Section A
1. Define plasmolysis. [1]
Ans. Plasmolysis is defined as the process of outward movement of water from the cell, when cell is placed in hypertonic solution.
2. Show the hierarchical arrangement of taxonomic categories in ascending order.
Ans. The taxonomic categories used in the process of classification can be arranged in ascending order as per following hierarchical order;


5. Give another name for anaerobic respiration. How much energy is yielded from the food by this process?
Ans. Another name for anaerobic respiration is fermentation. Approximately, 5% of food’s energy is yielded by this process
Section B
6. The cross section of a plant material, when observed under the microscope shows the following features. [2]
(a) Radially arranged vascular bundles
(b) Four xylem strands with exarch condition of protoxylem
To which plant’s part, these features can be assigned?
Ans. If the cross section of a plant material shows features like radially arranged vascular bundles and four xylem strands with exarch protoxylem, it can be identified as a section of dicot root. Other features that help in confirmation of specimen as dicot root are:
(i) The presence of root hairs (ii) Endodermis with casparian strips
(iii) The absence of pith
7. Write down some secondary functions of leaves.[1/2 x 4]
Ans. Secondary functions of leaves are:
(i) Leaves store food as in the leaf base, e.g onion.
(ii) Leaves change into phyllodes to protect against transpiration.
(iii) In some leaves like of Euphorbia, the young leaves are brightly coloured to attract insects for pollination.
(iv) Storage of water in the cells of some succulent plants, e.g. ,
8. Patients of cardiovascular diseases are usually recommended to use vegetable oils with polyunsaturated fatty acids. Give reasons.[2]
Ans. Vegetable oils contain polyunsaturated fatty acids having one or more double bonds. Due to this property, the chances or frequency of clotting of blood decrease, which finally reduces the possibility of blockage of arteries.
9. ‘Photosynthesis is essential for sustaining life on earth’. Justify the statement with at least two reasons in support. [2]
or
While examining the mitotic stage in a tissue, one finds some cells with 16 chromosomes and some with 32 chromosomes. What possible reasons could you assign to this difference in chromosome number?
Ans. Photosynthesis is essential for sustaining life on earth because:
(i) It is the only process that utilises solar energy and convert it into chemical energy which is stored in the form of food, i.e. carbohydrates. This food is manufactured for all living beings on earth. [1]
(ii) Secondly, it releases oxygen as byproduct into the atmosphere, which is essential for all organisms to sustain life.
or
Such a condition may arise in case of a mosaic or mosaicism, which denotes the presence of two or more populations of cells with different genotypes in one individual.
It can result from various mechanisms including non-disjunction, anaphase lagging and endoreplication. It may also result from a mutation during development which is propagated to only a subset of the adults cells.
Section C
10. List any three differences between anaphase of mitosis and anaphase-I of meiosis.
11. Give an account of type of body wall and body cavity found in sponges.[3]
or
Describe some general features of cartilaginous fishes. [3]
Ans. The body wall of sponges contains outer dermal layer or pinacoderm and inner gastral layer or choanoderm. The pinacoderm contains flat cells called pinacocytes and choanoderm consists of spherical cells with collar from which a flagellum emerges out.
The body cavity in sponges is a large cavity called spongocoel or paragastric cavity. It opens to the outside by a terminal opening called osculum.
or
The general features of cartilaginous fishes are:
(i) Cartilaginous endoskeleton is present.
(ii) These are mostly marine, poikilothermic animals,
(iii) Notochord is persistent throughout life.
(iv) Placoid scales are present.
(v) Air bladder is absent.
(vi) Tail fin is always heterocercal.
12. Apart from being a plant hormone having physiological role, gibberellins are also used in agriculture to increase the yield. What role do these hormones play when applied externally in crop fields? .
Ans. Gibberellins are useful in agriculture in the following ways:
(i) Application of gibberellins increases the length of the stem and increase the yield of sugar in sugarcane.
(ii) Gibberellins delay senescence and the fruits can be left on the trees for longer duration, so as to increase the market period.
(iii) It can cause fruits like apple to elongate and improve in shape
13. (a) Define nerve impulse and explain the factors on which it depends.
(b) What do you understand by synergistic effect? Give example.
Ans. (a) Nerve impulse is defined as a wave of electrochemical disturbance that passes along a neuron, during conduction of an excitation. The conduction of nerve impulse depends on:
(i) Permeability of axon membrane.
(ii) Osmotic equilibrium between the axoplasm and extracellular fluid present outside the axon.
(b) Synergistic effect is a type of hormonal interaction, where two or more hormones complement each other’s actions and both are needed for full expression of the hormone effects, e.g-. the production, secretion and ejection of milk by mammary glands require the synergistic effects of oestrogens, progesterone, prolactin and oxytocin.
14. Mention two important functions of each of the given elements along with their deficiency symptoms
(a) P
(b) Fe
(c) Zn
Ans. The important functions of elements given are as follows:
Mention two important functions of each of the given elements along with their deficiency symptoms.
(a) Phosphorus (P) It forms the constituent of cell membrane protein, nucleic acids, nucleotides, ATR NADP and energy rich compounds.
Deficiency symptoms It causes poor growth, leaves become dull green and chlorosis occurs.[1]
(b) Iron (Fe) It helps in chlorophyll synthesis, cytochrome synthesis, ferredoxin synthesis, activates enzyme and activates catalase.
Deficiency symptoms It results in chlorosis. [1]
(c) Zinc (Zn) It activates enzyme synthesis. It is a constituent of carbonic anhydrase. This is also a constituent-of dehydrogenase.
Deficiency symptoms Leaves are not properly formed.
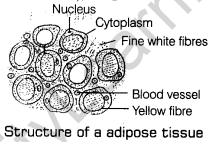
15. With the help of a neatly labelled diagram, explain the structure gf adipose tissue.
Ans. Adipose tissue is a fat storing connective tissue. Its matrix is packed with large, spherical or oval fat cells or adipocytes. The fibres are few in number and form a loose network for supporting fat laden cells. This tissue is found in the subcutaneous parts, in the mesenteries, covering of the heart and around the blood vessels and kidneys. The adipose tissue mainly stores reserve food. It acts as shock absorbing cushion around the heart, kidneys, eyeball, etc.
16. ‘Mitochondria are the powerhouse of the cell.’ Justify the statement.
Ans. Mitochondria are known as powerhouse of the cell because they generate ATR the energy currency of the cell. Terminal oxidation takes place through oxidative phosphorylation, thus producing ATR Even the reduced coenzymes produced in cytosol through glycolysis, transfer their reducing power to mitochondria for ATP synthesis. ATP synthesised inside mitochondria provides energy for all cellular activities including over coming tendency for entropy. Flence, these are known as powerhouse of the cell.
17. (a) What is meant by threshold stimulus in muscle contraction?
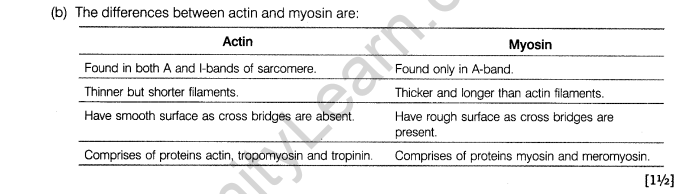
(b) Give difference between actin and myosin.
Ans. (a) During contraction, the muscle fibre requires a specific minimum strength or intensity of the stimulus or nerve impulse, which is called threshold stimulus. If the stimulus is below this intensity, the contraction fails to occur.
18. Define turgor pressure. State any three advantages by which it is useful to green plants.
or
Explain giving reasons, why the rate of transpiration is more on sunny and windy day as compared to calm and cool day, even when they are appropriately watered.
Ans. The pressure that develops due to osmotic entry of water into a cell is called turgor pressure.
The turgor pressure is useful to plants in many ways. Some of its advantages are:
(i) It keeps the cells and their organelles extended or stretched, so as to help in proper functioning of cell.
(ii) It is essential for cell enlargement during growth.
(iii) It helps in opening and closing of stomata by regulating the turgidity of guard cells.
or
On a sunny day, the temperature is high which leads to increased evaporation in the form of transpiration from the leaves. This happens to lower the temperature of plant. The windy days takes away the moisture from the surroundings causing the leaf to transpire more, releasing moisture into the atmosphere. Therefore, even if the plants are appropriately watered, they transpire more on a sunny and windy day. However, on 4 cool and calm day is reduced the temperature and humidity is not as high, thereby the loss of water through transpiration.
19. Explain the concept of activation energy with the help of a graph.
Ans.
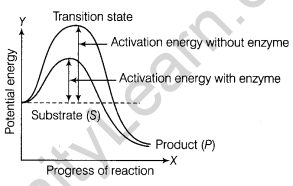
The external supply of energy required for the initiation of chemical reaction is called activation energy.
It increases the kinetic energy of the system and thus the rate of reaction. Enzymes lower the activation energy needed for a reaction. It can be explained with the help of graph.
Thus, it is evident from the graph that activation energy required is much less in the presence of an enzyme, thus increasing the rate of transition of substrate to product.
20. What is the role played by renin-angiotensin in the regulation of functioning of kidney?
Ans. Renin is released from the Juxtaglomerular Apparatus (JGA) on activation by fall in the glomerular blood pressure/flow. Renin converts angiotensinogen in blood to angiotensin-l and further to angiotensin-ll. Angiotensin-ll, being a powerful vasoconstrictor, increases the glomerular blood pressure and thereby Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR).
Angiotensin-ll also activates the adrenal cortex to release aldosterone. Aldosterone causes reabsorption of Na+ and water from the distal parts of the tubule. This also leads to an increase in blood pressure and GFR. This complex mechanism is generally known as Renin-Angiotensin Aldosterone System (RAAS).
21. Arun’s grandfather while on a walk in morning collapsed in the garden. Arun spotted him and called their neighbour Dr. S Rakesh who took him to nearby clinic. After examining him, he gave him an injection and asked Arun to properly take care of his diet and exercise regime, else he would have to take these injections regularly, so as to control his increasing levels of sugar.
(a) Name the injection that doctor might have given to Arun’s grandfather.
(b) What is the role of the given hormone in controlling sugar levels in blood?
(c) What precautions are advised by doctor to control the disease?
(d) What values are reflected by Arun’s behaviour?
Ans. (a) The doctor might have given insulin injection to Arun’s grandfather.
(b) Insulin stimulates the movement of glucose from blood to liver cells and adipose tissue, thus lowering the blood glucose level.
(c) Precautions advised by doctor to control diabetes are: ‘
(i) Regular exercise (ii) Balanced diet (iii) Reduced sugar intake
(d) Arun is alert, attentive and also protective and caring towards his grandfather. [4×1]
Section D
22. Describe the C3 cycle of carbon fixation in plants.
or
(a) Explain Krebs’ cycle in diagrammatic representation.
(b) During which steps of Krebs’ cycle, NAD and FAD are reduced?
23. Describe the various types of simple epithelial tissues in animals, with the help of a labelled diagram.
or
Draw the digestive system of cockroach. In how many parts is the alimentary canal of cockroach divided?
Ans. The various types of simple epithelial tissues along with their structure and functions can be summarised as :