Table of Contents
Introduction to Ionic Bonds
Ionic bonds are a sort of chemical binding that arises between oppositely charged ions. In this post, we will go through the definition, properties, formation, and instances of ionic bonding in depth.
We will also go over the key differences between ionic and covalent bonds, as well as the structure and properties of ionic bonds. Understanding the structure of ionic bonding can help you grasp the underlying forces that drive chemical processes and the properties of diverse substances.
Ionic Bond Definition
An ionic bond is a type of chemical bond that occurs between two atoms when one atom transfers electrons to another atom. This transfer of electrons creates two oppositely charged ions – a positively charged cation and a negatively charged anion. The attraction between these ions creates an electrostatic force that holds the atoms together in a stable compound.
Ionic Bond Examples
Ionic bonds are commonly found in compounds composed of metal and non-metal elements. For example, sodium chloride (NaCl) is a classic example of an ionic compound. In this case, sodium (Na) donates an electron to chlorine (Cl), resulting in the formation of Na+ and Cl- ions, which are held together by electrostatic forces. Hence, ionic bonds form between Na+ and Cl- ions.
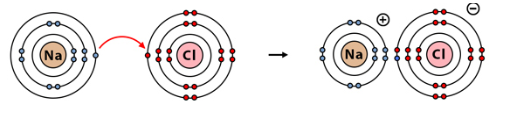
Formation of Ionic Bond
The formation of Ionic bond happens through a process known as ionization or ion formation. This occurs when an atom gains or loses electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. The atoms involved in the bond undergo a complete transfer of valence electrons, resulting in the formation of ions with opposite charges.
The Structure Associated with Ionic Bonding
The structure normally associated with ionic bonding is called giant lattice. In an ionic bond, the atoms are held together in a regular, repeating pattern called a crystal lattice. This structure is formed due to the strong electrostatic attraction between the positively and negatively charged ions. The arrangement of ions in the crystal lattice contributes to the properties of the ionic compound.
Ionic Bond Properties
Ionic bonds have several distinct key characteristics:
- They have high melting and boiling temperatures and are normally solid at room temperature.
- They are very good conductors of electricity when dissolved in water or melted.
- The strong electrostatic forces between ions result in the stability and rigidity of ionic compounds.
- Ionic compounds tend to form crystalline structures and have a tendency to dissociate into ions when dissolved in water.
- They also have a high degree of electrical conductivity in a molten or aqueous state.
Ionic Bond vs Covalent Bond
There are two main difference between Ionic and Covalent Bonds. The main difference lies in the way electrons are shared between atoms. In ionic bonds, electrons are transferred from one atom to another, leading to the formation of ions. In contrast, covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms.
Ionic bonds are more usually formed between a metal and a nonmetal, whereas covalent connections are most commonly formed between nonmetal atoms. The complete transfer of electrons in ionic bonds results in ions with opposing charges. Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms, creating a stable electron configuration.
Conclusion
Ionic bonds play a crucial role in the formation of many compounds, contributing to their unique properties and characteristics. Understanding the concept of ionic bonding is essential in chemistry as it helps explain the behavior of various substances. By exploring the definition, properties, examples, and differences of covalent bonds, you have gained a comprehensive understanding of ionic bonds and their significance in chemical reactions.
Frequently Asked Questions on Ionic Bond
What is an ionic bond and what are its properties?
Ionic bond, also known as electrovalent bond, is a type of connection generated in a chemical molecule by the electrostatic attraction of oppositely charged ions. A bond is created when the valence (outermost) electrons of one atom are irreversibly transferred to another.
What is the difference between ionic and covalent bonds electronegativity?
An ionic bond is formed when there is an electronegativity difference of 2 or more on the Pauling scale between two atoms. A covalent bond is formed when the difference between two atoms is smaller than two.
Is it true that ionic bonding acts in all directions?
Strong electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions hold an ionic lattice together. The forces in the lattice act in all directions. This is known as ionic bonding.
Which bond is stronger ionic or covalent?
Ionic bonds are generally significantly stronger than covalent bonds. Ionic bonds are created by total electron transfer, whereas covalent bonds are formed through electron sharing. Electrostatic force exists between ionic bonds, whereas Van der Waals force exists between covalent bonds.









