Table of Contents
Introduction to Swarts Reaction
Organic chemistry is a vital branch of chemistry. We deal with a lot of carbon-based reactions in organic chemistry. Organic reactions are the name given to these chemical processes.
Organic reactions are classified into five types: substitution, elimination, addition, radical, and oxidation-reduction. The Swarts reaction is an example of one of these, and we will go over it in detail in this post.
So, first and foremost, define it.
Explain Swarts Reaction
It is a method of converting alkyl chloride and alkyl bromide to alkyl fluoride. It is an organic reaction known as swarts fluorination and halogen exchange reaction. It was given its name after Frederic Jean Edmond Swarts, who described and defined this response for the first time in 1892. Swarts reaction is an abbreviation for Swarts reaction.
It is the most effective method for producing alkyl fluorides. To start this reaction, we could heat alkyl chloride or alkyl bromide in the presence of heavy metal fluorides. Heavy metal fluorides containing mercurous fluoride or silver fluoride can be employed. If we employ light metal fluorides, the reaction will proceed forward, but the quantity will be reduced. This is also called Haloalkanes Swart Reaction.
Swarts Reaction Definition
Swarts Reaction is a type of organic reaction in which alkyl chlorides/alkyl bromides are converted to alkyl fluorides. Frederick Jean Edmond Swarts reported this method in 1892.
Swarts Reaction Reagent
The Swarts Reaction Reagent is a combination of antimony trifluoride (SbF3) and chlorine (Cl2).
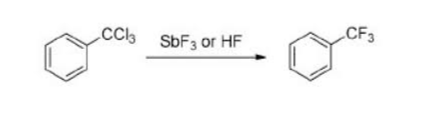
Swarts Reaction Equation
The Swarts Reaction Equation is as follows:
Swarts Reaction Mechanism
Mechanism of Swarts Reaction proceeds according to the SN2 reaction. The metal-fluorine link is broken, and a new bond is formed between carbon and fluorine. Displaced chlorine or bromine atoms form bonds with the metal. Swarts rule states that the fluoride formed during fluorination frequently has a lower boiling point compared to the comparable chloride.
In Haloalkanes Swart Reactions, the chlorinated hydrocarbons can be reacted with metallic fluorides to form fluorinated hydrocarbons. As a result, Swarts fluorination is suitable to totally replace fluorine with chlorine or bromine in alkyl chlorides or alkyl bromides.
Also Check For:
Finkelstein and Swarts Reaction
The Finkelstein and Swarts Reaction are both engaged in the synthesis of alkyl halides. These reactions describe the exchange of halides between organic and inorganic molecules in order to generate new alkyl halides. The following are the differences in Finkelstein and Swarts reactions:
| Swarts Reaction | Finkelstein Reaction |
| It produces alkyl fluoride. | It produces alkyl iodide. |
| The reactants that are included in this reaction are alkyl chloride or alkyl bromide, as well as a fluorinating agent such as antimony fluoride. | Primary halides, secondary halides, and alkyl halides are suitable reactants for this reaction, while benzyl halides, tertiary reactions, vinyl, and aryl halides are not. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Swarts Reaction
What is swarts reaction?
Swarts reaction is commonly used to synthesize alkyl fluorides from alkyl chlorides or alkyl bromides. The alkyl chloride/bromide is heated in the presence of heavy metal fluoride to achieve this.
What is the formula for Swarts reagent?
In the presence of Sb salts with an oxidation state of +5, antimony trifluoride (SbF3) is widely employed to substitute chlorines with fluorines. (SbCl5) Swarts reagent is an antimony trifluoride (SbF3) and chlorine (Cl2) combination.
What is swarts reaction Class 12 example?
Swarts reaction: The best way to synthesize alkyl fluorides is to heat alkyl chloride/bromide in the presence of a metallic fluoride, such as AgF, Hg2F, CdF2, or SbF5. This is known as the swarts reaction.
What is Finkelstein & Swartz reaction?
Swarts and Finkelstein reactions. Swarts and Finkelstein reactions are halogen exchange reactions that involve alkyl halides. Swarts' reaction: RX+MF → RF+MX.
What is Finkelstein reaction haloalkanes?
Another important name reaction in organic chemistry is the Finkelstein reaction. It is employed in the synthesis of haloalkanes and alkyl halides. It is a halogen exchange reaction that substitutes nucleophilic bimolecular (SN2 reaction). It takes its name from German chemist Hans Finkelstein.








