Table of Contents
Class 6 Science Chapter 1 Food Where Does It Come From Extra Questions
Class 6 Science Chapter 1 Food: Where Does It Come From?, introduces students to the basics of food sources, varieties, and nutrition. To deepen understanding, extra questions such as multiple-choice questions (MCQs) and short answers are very helpful. These extra questions, aligned with the CBSE syllabus, help students review key concepts from the chapter and prepare for exams. Using resources like “Class 6 Food: Where Does It Come From Extra Questions with Answers” allows students to test their knowledge and improve their grasp of how food affects living things and ecosystems. This approach is crucial for building a strong foundation in science.
Class 6 Food Where Does It Come From Extra Questions with Answers
Below are the food where does it come from extra questions with answers from outside NCERT textbook for deepen the concepts.
Food Where Does It Come From Class 6 Extra Questions Science Chapter 1
Here are long and short NCERT extra questions for class 6 science Chapter 1 Food Where Does It Come From
Food Variety – Extra Questions on Food Where Does It Come From
Question 1. Define the term food.
Ans.
Food refers to substances consumed by humans and animals to obtain energy, promote growth, and maintain good health.
Question 2. What do you mean by food habit?
Ans.
A food habit is the practice of consuming specific types of food based on personal preference and availability.
Question 3. Define the term ingredients.
Ans.
Ingredients are the components used to prepare a specific dish.
Question 4. Explain the importance of food for living organisms.
Ans.
Food is essential for living organisms for several reasons:
- It provides energy for various activities.
- It supports growth.
- It aids in the repair and replacement of damaged body parts.
- It offers protection against infections and diseases.
Question 5. Whether plants or animals give us more varieties of food? Explain.
Ans.
Animals provide us with limited food varieties such as meat, eggs, milk, honey, and others. In contrast, plants offer a broader array of foods, including cereals, pulses, fruits, oils, fats, vegetables, sugar, and many other products. Therefore, plants supply a greater variety of food options.
Question 6. Why should we eat cooked food?
Ans.
Cooked food is preferable because it is easier to digest, kills harmful germs, and enhances the taste of the food.
Question 7. Write the food habits of the people in Tamil Nadu and Punjab.
Ans.
Tamil Nadu: Typical foods include Idli, Dosa, Sambhar, Banana Chips, and Coconut oil.
Punjab: Common foods are Lassi, Paratha, Pulses, and Chapatis.
Activity 1.
Ask your friends in the school about the items they would be eating during a day. See if you can also get this information from friends staying in different states of India.
List all the items in your notebook as given in Table 1.1, for as many friends as possible.
| Name of the student/friend | Food item eaten in a day |
| T.S. Sree Kumar (Kerala) | Idli, dosa, curd, rice, sambar, etc. |
| Sarthak Sharma (Uttar Pradesh) | Vegetable, dal, chapati, curd, rice, etc. |
| Sanchit Bose (W. Bengal) | Fish curry, rice, vegetable, etc. |
| Sohan Singh (Punjab) | Makki roti, rajma, sarson saag, curd, ghee, etc. |
| P. Prasada Rao (Andhra Pradesh) | Rice, tuar dal, rasam, kunduru, ghee, pickle, etc. |
Activity 2.
Choose some of the items you listed in below table and try to find out what ingredients are used to prepare these, by discussing with your friends and elders at home. List them in table. Some examples are given here. Add some more items to this list.
| Food item | Ingredients |
| Roti/chapati | Atta, water |
| Dal | Pulses, water, salt, oil/ghee, spices |
| Idli | Rice, urad dal, salt, water |
| Fish curry | Fish, spices, oil/ghee, salt, water |
Food Materials and Sources – Extra Questions on Food Where Does It Come From
Question 1.
Name the animals which provide us milk.
Ans.:
Key animals that produce milk include cows, buffaloes, goats, and camels.
Question 2.
Name the animals which give us meat.
Ans.:
Significant sources of meat include goats, sheep, and pigs.
Question 3.
Name some other animals that give us food.
Ans.:
Apart from providing milk and meat, various animals offer additional food products. For instance:
- Birds such as chickens, fowls, and ducks supply both eggs and meat.
- Fish are a source of meat.
- Bees produce honey.
Question 4.
What are the two main sources of food?
Ans.:
The primary sources of food are:
- Plants: From which we obtain fruits, vegetables, and pulses.
- Animals: From which we derive milk, eggs, and meat.
Question 5.
Name two sugar-producing plants.
Ans.:
The two main plants that produce sugar are:
- Sugarcane.
- Sugar beet.
Activity 3.
Let us take the food items listed earlier and try to find out where they come from— the ingredients and their sources. Some examples are shown in Table 1.3. Fill in the blanks in Table 1.3 and add more examples to this list.
Table 1.3: Ingredients used to prepare food items and their sources
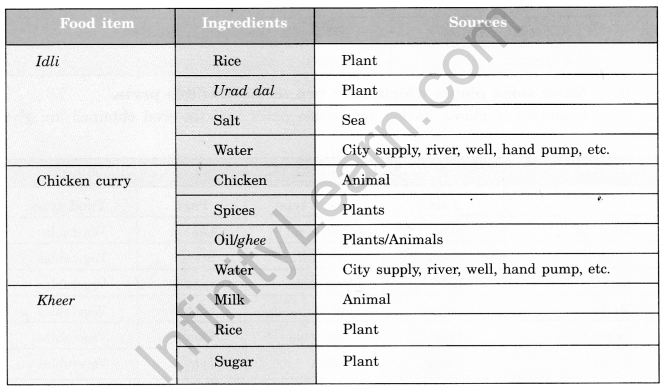
Plant Parts and Animal Products as Food – Extra Questions on Food Where Does It Come From
Question 1.
Write the names of the plants that provide us:
- Vegetables
- Fruits
- Cereals or grains
- Pulses
- Oil or fat.
Ans.:
The different types of food derived from plants include:
- Vegetables: Examples include tomatoes, cabbages, spinach, potatoes, etc.
- Fruits: Examples include bananas, grapes, apples, etc.
- Cereals or grains: Examples include rice, wheat, barley, ragi, etc.
- Pulses: Examples include gram, peas, beans, etc.
- Oil or fat: Examples include mustard, groundnut, sunflower, etc.
Question 2.
Which part of the plants do we eat generally?
Write the names of some more edible parts of the plants.
Ans.:
Typically, we consume the fruits of many plants. In addition to fruits, we also consume other plant parts such as flowers, leaves, roots, rhizomes, and stems. Examples of various edible parts of plants include:
| Edible part of plants | Examples |
| 1. Roots | Beet, Carrot, Sweet potato, Radish, etc. |
| 2. Stem | Onion, Potato, Ginger, Sugarcane, etc. |
| 3. Leaves | Spinach, Soya-methi, Bathua, etc. |
| 4. Flowers | Cauliflower |
| 5. Seeds | Mustard, Sweet pea, Lotus, Groundnut |
| 6. Fruits | Banana, Mango, Apple, etc. |
Question 3.
Name some plants which have two or more edible parts.
Answer:
Examples of plants having two edible parts, and the food obtained are given below:
| Name of plant | First edible part | Second edible part | ||
| Part | Food type | Part | Food type | |
| Mustard | Seeds | Spices, oil | Leaves | Vegetables |
| Lotus | Seeds | Dry fruit | Stem | Vegetables |
| Radish | Root | Vegetable | Leaves | Vegetables |
| Methi | Seeds | Spices | Leaves | Vegetables |
| Drum stick | Fruit | Vegetable | Flowers | Vegetables |
| Gram | Seeds | Pulse | Leaves | Vegetables |
Question 4.
What is honey? What is its importance?
Ans.: Honey is a sweet, liquid substance produced by bees from the nectar they collect from flowers. It contains water, sugar, minerals, and enzymes, making it easily digestible. Honey is valued in medicine for its antiseptic properties, which inhibit the growth of microorganisms.
Question 5.
From where does honey come? How is it produced and collected?
Ans.: Honey is obtained from honey bees. These bees build their nests, known as hives, on tall trees and buildings. Worker bees gather nectar from flowers and store it in these hives. Honey bees can also be kept in artificial hives for easier management. Honey is harvested from these hives either manually or using a mechanical extractor.

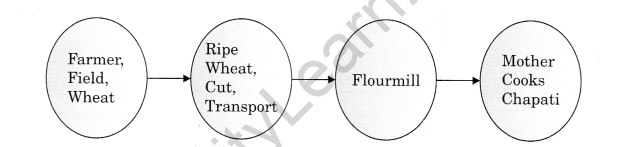
Question 6.
We know that every item that we eat is contributed by a number of persons. Show various contributors involved when we eat a chapati (through a flow chart).
Answer:
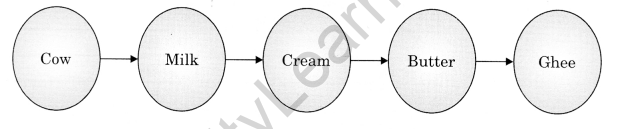
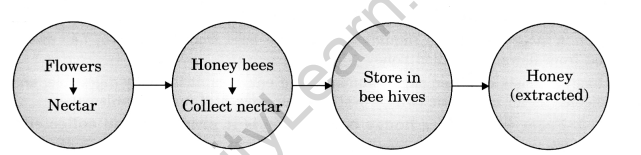
Question 7.
Make flow charts for the preparation of (a) ghee (b) honey.
Answer:
(a)
(b)
Question 8.
Which parts of a plant are eaten as food?
Ans.: The parts of a plant that are commonly consumed as food include:
- Roots
- Stems
- Leaves
- Flowers
- Fruits
- Seeds
- Spices
Question 9.
Define sprouted seeds.
Ans.: Sprouted seeds are germinating seeds characterized by the emergence of a white structure, known as the radicle, from the seed. This initial stage of growth marks the beginning of a seed’s development into a new plant.
What do Animals Eat? – Extra Questions on Food Where Does It Come From
Question 1. Explain the terms: Herbivores, Carnivores, and Omnivores.
Ans.
- Herbivores: These are animals that exclusively consume plant materials such as leaves, fruits, flowers, and seeds. Examples include deer, cows, and rats.
- Carnivores: These animals primarily feed on other animals. Notable examples are tigers and lions.
- Omnivores: These animals have a diet that includes both plant and animal origin foods. Examples include humans, cats, and crows.
Question 2. What do you know about vegetarian and non-vegetarian habits?
Ans. Humans are naturally omnivorous, capable of consuming both plant-based and animal-based foods. However, dietary choices often vary based on religious beliefs or cultural practices. This leads to two main dietary patterns:
- Vegetarian: Individuals who refrain from consuming meat, fish, and eggs.
- Non-vegetarian: Individuals who include meat, fish, and eggs in their diet.
Question 3. Define Scavengers and Parasites with examples.
Ans.
- Scavengers: These animals consume dead organisms and thereby contribute to the cleaning of the environment. Examples include crows, jackals, and hyenas.
- Parasites: These organisms live on or inside other living hosts, deriving their nutrients at the host’s expense. Common examples are fleas, leeches, mosquitoes, and bed-bugs.
Question 4. What are known as ‘energy-rich food’?
Ans. Cereals are considered ‘energy-rich foods’ because they are major sources of energy. Examples include rice, wheat, jowar, and maize.
Question 5. One day you were busy from morning to evening. You couldn’t have your lunch. How did you feel? Elaborate your experience.
Ans. On a particularly busy day, I missed my lunch, which left me feeling extremely fatigued and exhausted by day’s end. The lack of food made me weak and unable to perform tasks effectively, with my hunger reaching an alarming level.
Question 6. Suppose one of your friends had only one chapati, some rice, and one bowl of pulses for his daily meal. Do you think that by eating such a meal he can work and play the whole day?
Ans. The diet described is inadequate for sustaining energy throughout a full day of work and play. Such a limited intake of food will likely result in quick exhaustion due to insufficient energy provisions.
Activity 6.
Several animals are listed in Table 1.5. For some of them, the type of food they eat is also given. Fill in the blanks in the table.
Table 1.5: Animal and their Food
| Name of the animal | Food the animal eats |
| Buffalo | Grass, oilcake, hay, grains |
| Cat | Small animals, birds, milk |
| Rat | Grains, bread |
| Lion | Flesh of animals |
| Tiger | Flesh of animals |
| Spider | Small insects |
| House lizard | Small insects |
| Cow | Grass, leaves, hay, mustard, cake |
| Human beings | Rice, pulses, chapati, idli, dosa, bread, eggs |
| Butterfly | Nectar |
| Crow | Small insects, grains, meat |
| Others (Dog) | Meat, biscuit, bread |
Activity 7.
Have a look again at Table 1.5 and group the animals entered here as follows. Place animals which eat only plants or plant products.
- Buffalo, cow and butterfly.
Objective Type Questions – Extra Questions on Food Where Does It Come From
Question 1.
Match the following items given in Column A with that in Column B:
| Column A | Column B |
| Lion | Nectar |
| Deer | Fruit juice |
| Man | Human faecal |
| Female mosquito | Plants |
| Butterfly | Human blood |
| Human infant | Both plants and animals |
| Male mosquito | Animals |
| Pig | Mother’s milk |
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
| Lion | Animals |
| Deer | Plants |
| Man | Both plants and animals |
| Female mosquito | Human blood |
| Butterfly | Nectar |
| Human infant | Mothers milk |
| Male mosquito | Fruit juice |
| Pig | Human feecal |
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words:
- We feel …………….. when we have no food for some time.
- ……………. living beings need food.
- Children need food for ………………. .
- If food is not given for long, most of the known living beings will ……………. .
- We get ……………… after eating food.
- Different organisms eat …………….. kinds of food.
- Mustard ………………….. are used as spices and oil.
- We get food from ………………… as well as animals.
- We use ……………… energy when we run than when we walk.
- We use ……………… energy when we sleep.
- Each of us should make sure not to ……………… food.
- Human beings are ……………. .
Ans.:
- weak
- All
- growth
- die
- energy
- different
- seeds
- Plants
- more
- less
- waste
- omnivore
Question 3.
State -whether the statements given below are True or False:
- Different people have different choices of food.
- If a person does not get food he feels weak and is likely to fall ill.
- Human beings, animals, birds, insects, etc. eat the same type of food.
- There is no effect on our ability to do work even if we do not eat food for a day.
- Lion is omnivorous.
- Plants give us more varieties of food than animals.
- Cooked food can be easily consumed and absorbed by our body.
- There is a range of food items eaten over various states of India.
- For every item that we eat there are a number of persons who have contributed.
- Leaves absorb sunlight and prepare food using chlorophyll.
Ans.:
- True
- True
- False
- False
- False
- True
- True
- True
- True
- True
Class 6 Food Where Does Tt Come From MCQ Extra Questions
Question 1. Which part of a mustard plant is edible?
- Seeds and flowers
- Leaves and flowers
- Seeds and leaves
- Stem and roots
Ans.:
Seeds of mustard are used for oil and spices while leaves are used as vegetables.
Question 2. Honey bees are often seen sitting on flowers. Why do they do so?
- They like flowers
- They lay eggs on flowers
- They suck nectar from flowers
- All of these
Ans.:
Bees collect nectar from flowers and convert it into honey.
Question 3. Which one is the best for health?
- Boiled seeds
- Roasted seeds
- Wet swollen seeds
- Sprouted seeds
Ans.:
Sprouted seeds are the best for health.
Question 4. Which one of the following set comprises only herbivorous animals?
- Cow, goat, rabbit, deer
- Cow, goat, rabbit, wolf
- Wolf, goat, rabbit, deer
- Cow, crow, crane, camel
Ans.:
Wolf and crow are not herbivorous.
Question 5. Animals which eat both plants and flesh of other animals are called
- herbivores
- carnivores
- omnivores
- sanguinivores
Ans.:
Animals which eat both plants and flesh of other animals are called omnivores.
Question 6. Human beings are
- herbivores
- carnivores
- omnivores
- decomposers
Ans.:
Human beings eat herbs as well as meat and eggs.
Question 7. Which one of the following sets is not correct?
- Cow, rabbit, deer, goat
- Tiger, lion, wolf, panther
- Bear, crow, cat
- Rabbit, deer, cat, wolf
Ans.:
All other sets have only one type of animals.
Question 8. Which one is not a food for a squirrel?
- Grains
- Small insects
- Fruits
- All of these
Ans.:
Squirrel is a herbivorous animal.
Question 9 .Rearing and management of fishes in large scale is called
- agriculture
- apiculture
- pisciculture
- horticulture
Ans.:
c. pisciculture.
Question 10. Which of the following is a root vegetable?
- Potato
- Carrot
- Cucumber
- Onion
Ans.:
b. Carrot
| Other Resources for Class 6 | |
| NCERT Syllabus for Class 6 | NCERT Solutions Class 6 |
| Worksheet for Class 6 All subjects | CBSE Notes Class 6 |
| NCERT Books for Class 6 | Online Tuition for Class 6 |
FAQs on Class 6 Science Chapter 1 Food Where Does It Come From Extra Questions
Where does it come from food class 6?
In Food: Where Does It Come From? for Class 6, we learn about the different sources of food, including plants and animals, and how food reaches our tables.
Why is it called food?
It is called food because it provides the necessary nutrients that organisms need to survive, grow, and maintain good health.
Where is food coming from?
Food comes from various sources; plants provide fruits, vegetables, and grains, while animals provide meat, dairy, and eggs.
Why choose Infinity Learn for class 6 food where does it come from extra questions?
Infinity Learn offers comprehensive resources for Class 6 that enhance understanding through extra questions, helping students grasp concepts in Food: Where Does It Come From? effectively.
What is the purpose of food?
The purpose of food is to supply energy and nutrients to our bodies. It helps in growth, repairs tissues, and keeps our systems functioning properly.









