Table of Contents
NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Economics Chapter 2 Sectors of the Indian Economy
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics chapter 2 Sectors of the Indian Economy, are crafted by our experienced faculty after thorough research. Students struggling to solve the exercise problems can refer to these NCERT Solutions for Sectors of the Indian Economy class 10. These class 10 Economics chapter 2 questions and answers will help them articulate their responses effectively and prepare efficiently for their CBSE exams. By referring to these NCERT Solutions for class 10 Economics chapter 2, students can enhance their understanding and performance in economics class 10 chapter 2.

Sectors of Indian Economy Class 10 Questions Answers
Here are all the Class 1o Economics chapter 2 Sectors of Indian Economy question and answer:
Ques 1. Fill in the blanks using the correct option given in the bracket:
(i) Employment in the service sector _________ increased to the same extent as production. (has / has not)
(ii) Workers in the _________ sector do not produce goods. (tertiary / agricultural)
(iii) Most of the workers in the _________ sector enjoy job security. (organized / unorganized)
(iv) A _________ proportion of labourers in India are working in the unorganized sector. (large / small)
(v) Cotton is a _________ product and cloth is a _________ product. (natural /manufactured)
(vi) The activities in primary, secondary and tertiary sectors are_________ (independent / interdependent)
- has not
- tertiary
- organized
- large
- natural, manufactured
- interdependent
Ques 2. Choose the most appropriate answer.
(a) The sectors are classified into public and private sectors on the basis of:
(i) employment conditions
(ii) the nature of the economic activity
(iii) ownership of enterprises
(iv) number of workers employed in the enterprise
(b) Production of a commodity, mostly through the natural process, is an activity in _________ sector.
(i) primary
(ii) secondary
(iii) tertiary
Also Read: NCERT Solutions for Class 10
(c) GDP is the total value of _________ produced during a particular year.
(i) all goods and services
(ii) all final goods and services
(iii) all intermediate goods and services
(iv) all intermediate and final goods and services
(d) In terms of GDP the share of tertiary sector in 2013-14 is between _________ per cent.
(i) 20 to 30
(ii) 30 to 40
(iii) 50 to 60
(iv) 60 to 70
Match the following:
| Problems faced by farming sector | Some possible measures |
| 1. Unirrigated land | (a) Setting up agro-based mills |
| 2. Low prices for crops | (b) Cooperative marketing societies |
| 3. Debt burden | (c) Procurement of food grains by government |
| 4. No job in the offseason | (d) Construction of canals by the government |
| 5. Compelled to sell their grains to the local traders soon after harvest | (e) Banks to provide credit with low interest |
Answer:
| Problems faced by the farming sector | Some possible measures |
| 1. Unirrigated land | (d) Construction of canals by the government |
| 2. Low prices for crops | (c) Procurement of food grains by government |
| 3. Debt burden | (e) Banks to provide credit with low interest |
| 4. No job in the offseason | (a) Setting up agro-based mills |
| 5. Compelled to sell their grains to the local traders soon after harvest | (b) Cooperative marketing societies |
Ques 4. Find the odd one out and say why.
(i) Tourist guide, dhobi, tailor, potter
Ans. Tourist Guide is the odd one out because he or she is appointed by the Government Department but tailor, dhobi, and potter own their private work.
(ii) Teacher, doctor, vegetable vendor, lawyer
Ans. The Vegetable vendor is the odd one out because he works in the primary sector, while jobs of teacher, lawyer, and doctor come under the tertiary sector.
(iii) Postman, cobbler, soldier, police constable
Ans. Cobbler is the odd one out because he works in the private sector while the postman, soldier, and police constable work for the public sector or the organized sector.
(iv) MTNL, Indian Railways, Air India, Jet Airways, All India Radio
Ans. Jet Airways is the odd one out because it is owned by a private company and MTNL, Indian Railways, Air India, and All India Radio are owned by the Government of India
Also Check: NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Understanding of Economic Development Chapter 4
Ques 5. A research scholar looked at the working people in the city of Surat and found the following.
| Place of work | Nature of employment | Percentage of working people |
| In offices and factories registered with the government | Organized | 15 |
| Own shops, offices, clinics in marketplaces with formal license | 15 | |
| People working on the street, construction workers, domestic workers | 20 | |
| Working in small workshops is usually not registered with the government |
Complete the table. What is the percentage of workers in the unorganized sector in this city?
Answer:
| Place of work | Nature of employment | Percentage of working people |
| In offices and factories registered with the government | Organized | 15 |
| Own shops, offices, clinics in marketplaces with formal license | Organized | 15 |
| People working on the street, construction workers, domestic workers | Unorganized | |
| Working in small workshops is usually not registered with the government | Unorganized |
Ques 6. Do you think the classification of economic activities into primary, secondary and tertiary is useful? Explain how.
Ans.
- The classification of economic activities into primary, secondary, and tertiary is useful, as it helps to classify the different occupations that are taken up by the people in the country and how much each sector contributes to the growth of the country.
- It is also important because it helps in asserting which sector contributes the most to the GDP and which sector has the scope to employ more people and increase the National Income.
Ques 7. For each of the sectors that we came across in this chapter why should one focus on employment and GDP? Could there be other issues that should be examined? Discuss.
Ans. Employment and GDP are two of the most important factors in the development of a country. Employment and GDP are used to calculate the overall productivity and National income of a country. If a country has a high employment rate, its GDP, National Income, and per capita income will automatically increase. Hence, these are the two things that have been given major emphasis in this chapter.
Other issues which should be examined are as follows:
i) Health care facilities
ii) Education
iii) Poverty
iv) Food Production
v) Nourishment
Ques 8. Make a long list of all kinds of work that you find adults around you doing for a living. In what way can you classify them? Explain your choice.
Ans. When we see people around us, we can classify the activities they perform into three sectors: primary, secondary, and tertiary.
- Activities like cleaning, agriculture, selling vegetables are examples of the primary sector.
- Manufacturing of goods is an example of the secondary sector.
- Teaching, mining, banking, transportation are all examples of the tertiary sector.
Ques 9. How is the tertiary sector different from other sectors? Illustrate with a few examples.
Ans.
- The are activities that help in the development of the primary and secondary sectors are called tertiary activities.
- These activities are different from the primary and secondary sector activities. These activities, by themselves, do not produce a good but they are an aid or support for the production process. For example, goods that are produced in the primary or secondary sector would need to be transported by trucks or trains and then sold in wholesale and retail shops.
- These transportation facilities and shopkeepers come under the tertiary sector. They do not produce goods but play a very important role in selling and bringing those goods to the market.
Ques 10. What do you understand by disguised unemployment? Explain with an example each from the urban and rural areas.
Ans. The situation of underemployment, where people are apparently working but all of them are made to work less than their potential is called disguised unemployment. In this case, the person considers himself employed but is actually not working.
- In rural areas, where agriculture is the main source of income, this kind of unemployment can be seen often. If a piece of land requires only three people to work on it and instead five people are working on it, then the two extra people are said to be in a situation of disguised unemployment.
- In urban areas, disguised unemployment is seen when painters, plumbers, electricians are unable to find work on a daily basis and work way less than their potential.
Class 10 co
Ques 11. Distinguish between open unemployment and disguised unemployment.
Ans. Open unemployment is when a person is willing to work, is educated but is unable to get a job and work. This kind of unemployment is visible. On the other hand, disguised unemployment is when a person is apparently working but is made to work less than his or her potential. This kind of employment is quite evident in villages where people working in farms consider themselves employed but are actually working less than their potential.
Ques 12. “Tertiary sector is not playing any significant role in the development of Indian economy.” Do you agree? Give reasons in support of your answer.
Ans. No, this is not correct. The tertiary sector is playing a significant role in the development of the Indian Economy. In the year 2003, the tertiary sector replaced the primary sector as the most producing sector in the country. A few reasons to support this are given below:
- The primary and secondary sectors can only flourish if the tertiary sector is there to support them.
- The tertiary sector adds up a lot to the National income of the country.
- Education, which is the basis of everything, comes under the tertiary sector. A person working as a teacher comes under the tertiary sector.
- This sector provides the maximum employment opportunities to the people in the country.
Ques 13. Service sector in India employs two different kinds of people. Who are these?
Ans. Service sector in India employs two different types of people. These people are:
- Highly Skilled labour, which includes teachers, bankers, IT officials, etc. These people are permanently employed.
- Less Skilled Labour, which includes vendors, electricians, plumber, etc. These people are not permanently employed.
Ques 14. Workers are exploited in the unorganized sector. Do you agree with this view? Give reasons in support of your answer.
Ans. The unorganized sector is characterized by small and scattered units, which are largely outside the control of the government. There are rules and regulations but these are not followed. Jobs here are low-paid and not regular. Hence, it is correct to say that workers are exploited in the unorganized sector because more work is taken from them in comparison to what they are paid. They have no provisions or extra pay for overtime and no medical benefits. The biggest problem in working in this sector is that there is no job security.
Ques 15. How are the activities in the economy classified on the basis of employment conditions?
Ans. On the basis of the employment conditions, the economy can be classified into two sectors:
- Organised Sector: Enterprises registered under the Government of India, who have an employee-friendly environment and are provided with various facilities including high wages.
- Unorganised Sector: Small and scattered units which are temporary. The employees in this sector are paid less.
Ques 16. Compare the employment conditions prevailing in the organized and unorganized sectors.
Ans. In the organized sector, the employees are given higher wages, medical facilities, a healthy working environment, and their jobs are permanent. They are not liable to look for a new source of income each day. In the unorganized sector, the wages are low, the employees are exploited, no extra income for extra time is given, no medical facilities are provided and the work environment is unhealthy.
Ques 17. Explain the objective of implementing the NREGA 2005.
Ans. The National Rural Employment Guarantee Act, 2005 was introduced with an aim to ensure guaranteed 100 days of employment in a year to all those who are in need of work. It also states that in the case of employment not being provided under this act, employment wages will be given to those left unemployed. Additional employment opportunities need to be created for people in villages and smaller towns.
Ques 18. Using examples from your area compare and contrast the activities and functions of private and public sectors.
Ans.
| S.No | Public Sector | S.No | Private Sector |
| 1 | It is controlled and managed by the government. | 1 | It is controlled and managed by an individual or a group of individuals. |
| 2 | The main aim of the sector is public welfare. | 2 | The main aim of the sector is to earn maximum profits. |
| 3 | The sector provides basic facilities like education, health, food, and security to the people. | 3 | The sector provides consumer goods for the people. |
| 4 | For example, the Indian Railways, the Post Office, and the BSNL. | 4 | For example, the Reliance, TISCO, etc. |
Ques 19. Discuss and fill the following table giving one example each from your area.
| Well managed organization | Badly managed organization |
| Public sector | |
| Private Sector |
Ans. Student Activity
Ques 20. Give a few examples of public sector activities and explain why the government has taken them up.
Ans.
- In the public sector, the government owns most of the assets and provides all the services. The public sector activities are set for the betterment of the public itself. The reason the government has taken up the public sector is so that basic facilities can be provided to the people of the country at a reasonable cost.
- There are several things needed by society as a whole but which the private sector will not provide at a reasonable cost.
- Banks, transport, irrigation, electricity, water, and all the basic things that are necessary for people, come under the public sector. Providing these facilities to its citizens is the responsibility of the Government.
Ques 21. Explain how the public sector contributes to the economic development of a nation.
Ans.
- The public sector is the sector that comes under the government of India. The Government has to provide the basic necessities of people including water, electricity, irrigation, at a reasonable rate so that the poorer section also can avail these facilities.
- If these departments are left unattended, it will result in the downfall of the economy of a country because the growth of the country would hamper.
- The economic development of a country depends upon the development of the people and if people are deprived of the basic necessities, the country’s economic development would be affected.
- Government encourages small and large industries to flourish and provides employment opportunities to all the sections of society.
Ques22. The workers in the unorganized sector need protection on the following issues: wages, safety, and health. Explain with examples.
Ans. The unorganized sector is characterized by small and scattered units, which are largely outside the control of the government. There are rules and regulations but these are not followed.
The workers in the unorganized sector need protection:
- Wages: For example, here wages are low and even not regular and there is the absence of provision for overtime, paid leave, etc. Hence proper and fixed wages should be given to these workers so that they can grow and contribute to the growth of the country.
- Safety: For example, workers working in mines or crackers factories always face the element of risk.
- Health: Health is a very important factor for the growth and development of the country. The unorganized sector is given no medical security and if any accident occurs while they are working, the employer is not responsible for their health. For example – there is no sick leave for labourers working on daily wages.
Ques 23. A study in Ahmedabad found that out of 15,00,000 workers in the city, 11,00,000 worked in the unorganized sector. The total income of the city in this year (1997-1998) was Rs 60,000 million. Out of this Rs 32,000 million was generated in the organized sector. Present this data as a table. What kind of ways should be thought of for generating more employment in the city?
Ans.
| Total Workers | Workers in the Unorganized Sector | Total Income of City (1997-1998) | Income generated by organised sector | Income generated by unorganised sector |
| 15,00,000 | 11,00,000 | 60,000 million | 32,000 million | 28,000 million |
The table clearly shows that the income generated in the unorganized sector is close to 50% of the total income of Ahmedabad. In order to increase employment opportunities for the people more industries should be set up, proper education must be provided to all and proper facilities under the public sector must be provided to all.
Ques 24. The following table gives the GDP in Rupees (Crores) by the three sectors: Year Primary Secondary Tertiary 2000 52,000 48,500 1,33,500 2013 8,00,500 10,74,000 38,68,000
1. Calculate the share of the three sectors in GDP for 2000 and 2013.
Ans. In 2000, primary sector = 22.22%, secondary sector = 20.73%, tertiary sector = 57.04% And In 2013, primary sector = 13.94%, secondary sector = 18.70%, tertiary sector = 67.36%
2. Show the data as a bar diagram similar to Graph 2 in the chapter.
Ans. 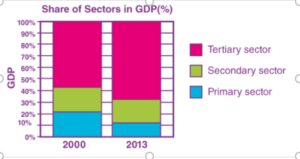 3. What conclusions can we draw from the bar graph?
3. What conclusions can we draw from the bar graph?
Ans. We can draw the conclusion that the share of the tertiary sector in the GDP has increased by 10%, while that of the primary sector has almost halved. The secondary sector has grown by about 2% in the last 13 years.
More CBSE Class 10 Study Materials
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solution for Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 English
- NCERT Books for Class 10
FAQs on NCERT Solutions Class 10 Economics Chapter 2 Sectors of Indian Economy
What are the sectors of the Indian economy Chapter 2?
The Indian economy is divided into three sectors: Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary. The primary sector includes activities like agriculture and mining, which are based on natural resources. The secondary sector involves industries that manufacture goods, like factories and construction. The tertiary sector, or service sector, includes services such as banking, healthcare, and education that support the economy.
What is the name of chapter 2 of economics class 10?
Chapter 2 of the Class 10 Economics book is titled Sectors of the Indian Economy. It explains the roles of these three sectors and how they contribute to the country's economic development.
What are the sectors of the Indian economy short notes?
The sectors of the Indian economy are categorized into the primary sector, which deals with natural resources; the secondary sector, which focuses on manufacturing; and the tertiary sector, which provides services. Together, these sectors drive the country's economic growth.
What is the full form of GDP?
GDP stands for Gross Domestic Product. It represents the total value of all goods and services produced within a country over a specific period, typically one year.
How to calculate GDP?
GDP is calculated by adding up all the expenditures made in the economy. This includes consumption, investments, government spending, and net exports (exports minus imports). It measures the economic output of a country.








