Table of Contents
Ethylene Glycol Formula
Introduction
Ethylene glycol is an organic compound with the chemical formula C2H6O2. It is a colorless, odorless, and viscous liquid that is commonly used as an antifreeze and coolant in various applications. The formula C2H6O2 represents the composition of ethylene glycol, where there are two carbon atoms (C2), six hydrogen atoms (H6), and two oxygen atoms (O2). Ethylene glycol has a wide range of uses, including automotive and industrial cooling systems, heat transfer fluids, solvents, and as a raw material in the production of polyester fibers and resins. It is commonly known as ethylene glycol but also referred to as monoethylene glycol (MEG) or ethane-1,2-diol.
Structural Formula of Ethylene Glycol
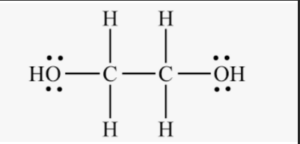
The structural formula of ethylene glycol(C2H6O2) is as shown above.
This formula represents two hydroxyl (OH) groups attached to a central carbon atom, with each carbon atom also bonded to two hydrogen atoms. The hydroxyl groups give ethylene glycol its characteristic properties and reactivity.
Uses of Ethylene Glycol
One of the primary uses of ethylene glycol is as an antifreeze and coolant in automotive and industrial cooling systems. It has a high boiling point and can effectively prevent the freezing or overheating of engine coolant, protecting the engine from damage.
Additionally, ethylene glycol is a key ingredient in the production of polyester fibers, resins, and polyethylene terephthalate (PET), which are used in textiles, packaging materials, plastic bottles, and more. It also finds applications as a solvent, humectant, and in some pharmaceutical formulations.
However, it’s important to note that ethylene glycol is toxic and should be handled with caution. Ingestion or absorption through the skin can lead to severe health effects, and it should be kept away from children and pets.
Physical Properties of Ethylene Glycol
- Appearance: Ethylene glycol is a clear, colorless, and odorless liquid at room temperature.
- Melting Point: The melting point of ethylene glycol is -13.2°C (-8.6°F).
- Boiling Point: The boiling point of ethylene glycol is 197.6°C (387.7°F).
- Density: The density of ethylene glycol is approximately 1.11 g/cm3.
- Solubility: Ethylene glycol is highly soluble in water, and it can also dissolve many organic compounds.
- Viscosity: Ethylene glycol has a relatively high viscosity, making it a thick liquid.
- Flash Point: The flash point of ethylene glycol is 111°C (232°F), indicating its flammability.
- Vapour Pressure: The vapor pressure of ethylene glycol is relatively low at room temperature.
Chemical Properties of Ethylene Glycol:
- Reactivity with Acids: Ethylene glycol reacts with acids to form esters. This reaction is commonly used in the production of polyester resins and fibers.
- Reactivity with Aldehydes and Ketones: Ethylene glycol can react with aldehydes and ketones in the presence of a catalyst, such as sulfuric acid, to form cyclic compounds known as acetals or ketals.
- Oxidation: Ethylene glycol can be oxidized to form glycolic acid, glyoxal, and other compounds under certain conditions. This property is utilized in some chemical processes and industrial applications.
Eg: 2C2H6O2 + 2KMnO4 + 3H2SO4 → 2C2H4O2 + 2MnSO4 + K2SO4 + 3H2O
In this reaction, ethylene glycol (C2H6O2) reacts with potassium permanganate (KMnO4) in the presence of sulphuric acid (H2SO4) as a catalyst. The oxidation products are acetic acid (C2H4O2), manganese(II) sulphate (MnSO4), potassium sulfate (K2SO4), and water (H2O).
- Dehydration: Ethylene glycol can undergo dehydration reactions to form polymers, such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET), which is used in the production of plastic bottles and containers.
- Combustibility: Ethylene glycol is flammable and can burn in the presence of a flame or spark. It should be handled and stored away from sources of ignition.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the formula for ethylene glycol, C2H6O2, represents the chemical composition of this organic compound. Ethylene glycol is commonly used as an antifreeze and coolant due to its ability to lower the freezing point and raise the boiling point of water. It has a wide range of applications in automotive and industrial cooling systems, heat transfer fluids, and as a solvent. The formula C2H6O2 helps to identify the specific arrangement of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms in ethylene glycol, providing a basis for understanding its chemical properties and practical uses.
Solved Examples on Ethylene Glycol Formula
Example 1: Calculate the molar mass of ethylene glycol (C2H6O2).
Solution:
The molar mass of ethylene glycol can be calculated by adding up the atomic masses of its constituent elements.
Molar mass of C = 12.01 g/mol
Molar mass of H = 1.01 g/mol
Molar mass of O = 16.00 g/mol
Molar mass of ethylene glycol (C2H6O2) = (2 * 12.01) + (6 * 1.01) + (2 * 16.00)
= 24.02 + 6.06 + 32.00
= 62.08 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of ethylene glycol is 62.08 g/mol.
Example 2: How many moles of ethylene glycol are present in 250 grams of C2H6O2?
Solution:
To calculate the number of moles, we need to divide the given mass by the molar mass.
Molar mass of ethylene glycol (C2H6O2) = 62.08 g/mol
Mass of ethylene glycol = 250 g
Number of moles = Mass / Molar mass
= 250 g / 62.08 g/mol ≈ 4.02 moles
Therefore, there are approximately 4.02 moles of ethylene glycol in 250 grams of C2H6O2.
Frequently Asked Questions on Ethylene Glycol Formula
1: What is the most common use of ethylene glycol?
Answer: The most common use of ethylene glycol is as an antifreeze and coolant in automotive and industrial applications. It is added to the cooling systems of engines to lower the freezing point and raise the boiling point of the coolant, thereby preventing freezing and overheating of the engine. Ethylene glycol-based antifreeze solutions are widely used in cars, trucks, heavy machinery, and other equipment that require efficient cooling.
2: Which form of ethylene glycol is most stable?
Answer: Gauche conformer in the most stable because of the internal hydrogen bonding between the two OH groups.
3: What is the main chemical reaction of ethylene glycol?
Answer: The main chemical reaction of ethylene glycol is its reaction with carboxylic acids or acid derivatives to form esters. This reaction, known as esterification, involves the exchange of the hydroxyl (-OH) group in ethylene glycol with the carboxyl group (-COOH) of the acid or its derivative. The reaction is typically catalyzed by an acid catalyst, such as sulfuric acid or p-toluenesulfonic acid.
The general equation for the esterification reaction of ethylene glycol with a carboxylic acid is:
HOCH2CH2OH + RCOOH -> HOCH2CH2OCOR + H2O
Where R represents the alkyl group of the carboxylic acid.
This reaction is commonly employed in the synthesis of various esters, which find applications in industries such as fragrance, flavoring, polymer production, and pharmaceuticals.
4: What is the other name for ethylene glycol?
Answer: Ethylene glycol is also commonly known by its other name, which is “ethylene alcohol.”
5: Why is it called ethylene glycol?
Answer: Ethylene glycol is called so because it is derived from ethylene, a hydrocarbon compound with a double bond between two carbon atoms. The name “glycol” is used to indicate the presence of two hydroxyl (-OH) groups in the molecule, which gives it its characteristic properties. The term “glycol” is derived from the Greek word “glykys,” meaning sweet, referring to the sweet taste of some glycols. Therefore, the name “ethylene glycol” reflects its chemical composition and origin.
6: What is the use of ethylene glycol in India?
Answer: Ethylene glycol is widely used in India for various applications. One of the primary uses of ethylene glycol is as an antifreeze and coolant in automotive engines, especially in regions with cold climates. It helps prevent the freezing of engine coolant and ensures optimal performance of the vehicle’s cooling system. Ethylene glycol is also utilized as a deicing agent for aircraft, as it can lower the freezing point of water. Additionally, it finds applications in the manufacture of polyester fibers, resins, and films, as well as in the production of various chemicals, such as solvents and intermediates. Moreover, ethylene glycol is used in the pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries as a solvent and a humectant in personal care products.
7: Is ethylene glycol used as poison?
Answer: Yes, ethylene glycol can be toxic and is sometimes used as a poison. Ethylene glycol is a clear, colorless, and sweet-tasting liquid, which can be highly dangerous if ingested. It is toxic to humans and animals, primarily affecting the central nervous system, kidneys, and cardiovascular system. Ethylene glycol poisoning can occur through accidental ingestion or intentional misuse, such as in cases of suicide or homicide. It is important to handle ethylene glycol with caution and store it securely to prevent accidental exposure. If ingested, immediate medical attention is required to minimize the harmful effects of ethylene glycol poisoning.
8: Is ethylene glycol an acid?
Answer: No, ethylene glycol (C2H6O2) is not an acid. It is a chemical compound classified as a diol or a glycol. It is neither acidic nor basic in nature. Ethylene glycol is a neutral molecule and does not exhibit acid-base properties.









