Table of Contents
Introduction to Chromic Acid Formula
Chromic acid, also known as chromium trioxide, has the chemical formula CrO3. It exists as dark red crystals and is highly soluble in water. Here are some key aspects of chromic acid.
Chromic acid has the chemical formula H2CrO4. It is a strong oxidizing agent and an important compound in the field of chemistry. Chromic acid is a versatile substance with various industrial and laboratory applications.
Chromic acid, with the chemical formula H2CrO4, is an inorganic compound that plays a significant role in several chemical processes. It is a strong oxidizing agent and a powerful acid. Chromic acid is commonly encountered in the form of its hydrate, chromic acid solution, which is a reddish-orange liquid.
Chromic acid is prepared by the reaction between sodium dichromate (Na2Cr2O7) or potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) with sulfuric acid (H2SO4). The resulting solution contains a mixture of chromic acid (H2CrO4), dichromic acid (H2Cr2O7), and water (H2O).
Structure of Chromic Acid
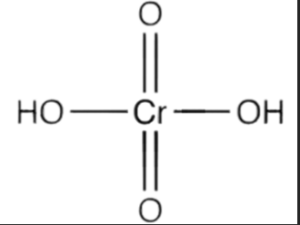
Chromic acid consists of a central chromium atom bonded to three oxygen atoms, forming a triangular planar arrangement. The oxygen atoms are single-bonded to the chromium atom.
Physical Properties of Chromic Acid
- Appearance: Dark red crystals or red-orange powder.
- Melting Point: 197 °C (387 °F)
- Boiling Point: Decomposes above 250 °C (482 °F)
- Density: 2.70 g/cm3
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water, forming a solution known as chromic acid.
Chemical Properties of Chromic Acid
- Oxidizing Agent: Chromic acid is a strong oxidizing agent and can readily donate oxygen atoms in chemical reactions.
- Acidic Nature: Chromic acid is a strong acid and can dissociate in water to release hydrogen ions (H+).
- Corrosive: It is corrosive to many metals and organic materials due to its strong oxidizing properties.
- Decomposition: Chromic acid decomposes upon heating, releasing toxic chromium fumes and oxygen gas.
Uses of Chromic Acid
- Cleaning and Etching: Chromic acid is used for cleaning and etching various materials, including glass, ceramics, and metals.
- Electroplating: It is utilized in electroplating processes, particularly for depositing chromium coatings on metal surfaces.
- Organic Synthesis: Chromic acid is employed as an oxidizing agent in organic synthesis reactions, such as the oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes or ketones.
- Laboratory Reagent: It finds application as a laboratory reagent for various analytical and synthetic procedures.
Chromic Acid Conclusion
Chromic acid finds various applications in industrial processes, such as electroplating, metal cleaning, and surface etching. It is used for the oxidation of organic compounds and acts as a powerful oxidizing agent in various chemical reactions.
However, it is important to note that chromic acid is highly corrosive and toxic. It can cause severe burns and is harmful if inhaled or ingested. Proper safety precautions, such as using protective equipment and working in well-ventilated areas, should be taken when handling chromic acid.
In summary, chromic acid (H2CrO4) is a strong oxidizing agent with a wide range of applications in industrial and laboratory settings. Its powerful oxidizing properties make it valuable for various chemical processes. However, caution must be exercised when working with chromic acid due to its corrosive and toxic nature.
It’s important to handle chromic acid with caution as it is a hazardous and toxic substance. Proper safety measures should be followed when working with it, including the use of protective equipment and working in a well-ventilated area.
Solved questions on the Chromic Acid Formula
Example 1: What is the balanced equation for the reaction between chromic acid (CrO3) and potassium iodide (KI)?
Solution:
The balanced equation for the reaction can be determined by considering the transfer of ions between the compounds. Chromic acid will donate oxygen atoms to iodide ions, resulting in the formation of iodine and chromium ions.
The balanced equation is as follows:
2CrO3 + 6KI → 3I2 + Cr2(SO4)3 + 3K2SO4
Example 2: What is the oxidation state of chromium in chromic acid (CrO3)?
Solution:
To determine the oxidation state of chromium, we can assign oxidation numbers to the atoms in the compound. Oxygen is generally assigned an oxidation number of -2, and since there are three oxygen atoms in chromic acid, they contribute a total oxidation number of -6.
The overall charge of the chromic acid compound is zero.
Let’s assume the oxidation state of chromium as x.
Therefore, the equation would be: x + (-6) = 0.
Hence, the oxidation state of chromium in chromic acid is +6.
Frequently asked questions on the Chromic Acid Formula
What is the chemical formula of carbonic acid?
The chemical formula of carbonic acid is H2CO3, meaning it's composed of two hydrogen atoms (H), one carbon atom (C), and three oxygen atoms (O).
Is carbonic acid found naturally in the environment?
Yes, carbonic acid is found naturally in the environment, especially in water. It forms when carbon dioxide (CO2) dissolves in water, creating a weak acid.
How does carbonic acid contribute to the carbon cycle?
Carbonic acid plays a role in the carbon cycle by helping to dissolve and transport carbon dioxide in water. This process aids in regulating CO2 levels in the atmosphere and oceans.
What is the significance of carbonic acid in biology?
In biology, carbonic acid is essential for processes like respiration. It helps transport carbon dioxide in the blood, regulating the body's pH and ensuring efficient gas exchange in the lungs.
What are the common sources of carbonic acid?
Common sources of carbonic acid include carbonated beverages like soda and naturally carbonated mineral waters. It's also present in the atmosphere due to the dissolution of carbon dioxide in rainwater.
Which acid is known as carbonic acid?
Carbonic acid is specifically known as H2CO3, derived from its chemical composition.
What is the formula of carbonic acid Class 10?
The formula of carbonic acid, whether in Class 10 or any other context, remains H2CO3.
Where is carbonic acid used?
Carbonic acid has various industrial uses, including in the food and beverage industry for carbonation and as a cleaning agent. It's also important in geological processes, like the dissolution of limestone in caves.









