Table of Contents
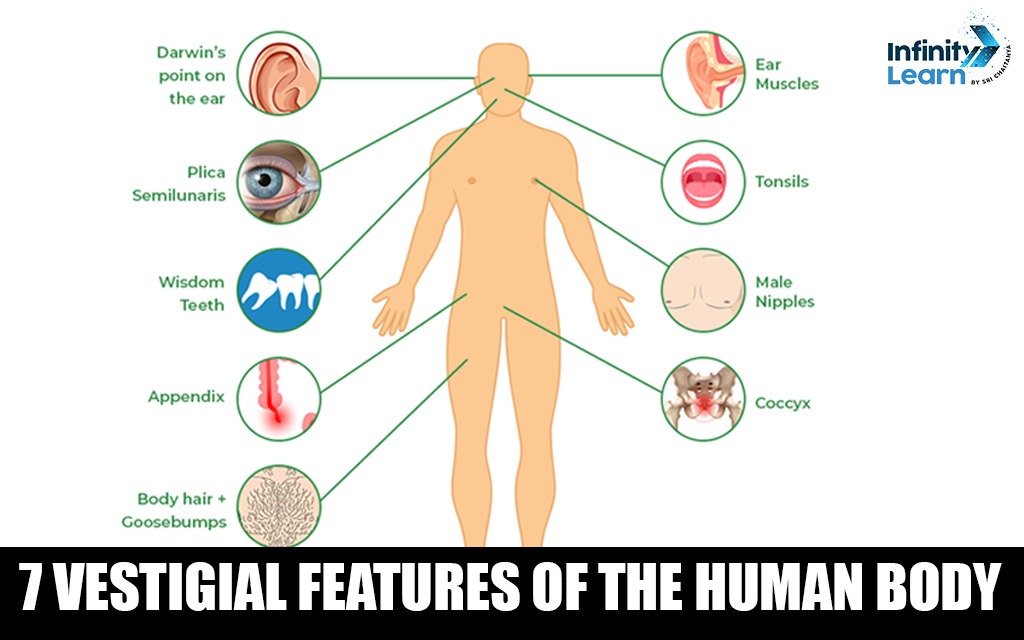
Vestiges are remnants of our evolutionary past—derived from the Latin word for “footprints” or “tracks.” All species have vestigial features, which can be anatomical, physiological, or behavioral. Humans alone exhibit over 100 vestigial traits. Here, we explore seven notable examples.
Top 7 Vestigial Features of the Human Body
Below are the following list of 7 Vestigial Features of the Human Body-
1. Pyramidalis Muscle
The pyramidalis muscle is a paired, triangular muscle located in the lower abdomen between the rectus abdominis muscle and its sheath. The presence and size of the pyramidalis muscles vary among individuals; some may have two, one, or none at all. These muscles are believed to contract the linea alba, but this function is considered insignificant to the overall function of the abdominal muscles. Researchers estimate that one or both pyramidalis muscles are present in approximately 80 percent of the human population.
2. Auricular Muscles
The auricular, or extrinsic, muscles of the human ear consist of the anterior, superior, and posterior auricular muscles, which control the pinna—the visible part of the ear. In many mammals, these muscles assist in sound localization and emotional expression through ear movements. However, in humans, they are largely nonfunctional.
Charles Darwin suggested that humans compensate for this by moving their heads to better capture sounds, reducing the necessity of auricular muscle functionality. Despite this, with practice, some people can regain a limited ability to wiggle their ears.
Also Read: Science Topics
3. Palmaris Longus Muscle
Research has shown that the palmaris longus, a slender muscle extending from the wrist to the elbow, is absent in approximately 10 percent of people. This muscle likely played a role in enhancing grip, possibly aiding in activities like hanging. However, its absence does not affect grip strength in modern humans. Nowadays, the palmaris longus is often used as a source of tissue for tendon grafts in reconstructive surgeries due to its redundancy in function.
4. Nictitating Membrane
The plica semilunaris is a small fold of conjunctiva located at the inner corner of the human eye. It resembles the nictitating membrane, or third eyelid, found in many animals, suggesting it may be a vestigial remnant of this structure. While some primates, like gorillas, retain a functional nictitating membrane, in chimpanzees—close relatives of humans—the plica semilunaris is also vestigial.
The nictitating membrane in various animals serves protective roles, such as keeping the eye clean and moist or hiding the iris from predators. In certain species, it is transparent enough to allow vision underwater or underground. The loss of the nictitating membrane in humans is not well understood, but changes in habitat and eye physiology may have made this structure unnecessary.
5. Tails
During the sixth week of gestation, a human embryo develops a tail, containing several vertebrae. However, within a few weeks, this tail diminishes, and the vertebrae fuse to form the coccyx, or tailbone, in adults. Humans and their ape relatives are unique among primates for their lack of a tail, though the reason for this evolutionary trait remains unclear.
Occasionally, a human infant is born with a vestigial tail, which generally lacks vertebrae and is harmless, though it can sometimes be linked to spina bifida, a condition where the vertebrae do not completely encase the spinal cord. These tails are usually removed surgically without complications.
6. Wisdom Teeth
As humans migrated out of Africa and settled in diverse habitats, their diet shifted towards softer, processed foods. This dietary change reduced the need for large, powerful jaws, leading to a decrease in jaw size. Consequently, molars, especially third molars or wisdom teeth, often became impacted and are now frequently absent at birth. Due to these changes, wisdom teeth are considered a vestigial feature of the human body.
7. Palmar Grasp Reflex
The palmar grasp reflex is a notable behavior in human infants, developing as early as 16 weeks into gestation when the fetus starts grasping the umbilical cord in the womb. Research has shown that newborns can support their weight for at least 10 seconds using this reflex by gripping a horizontal rod. In contrast, monkey infants, who also exhibit this behavior, can hang from one hand for over half an hour.
This reflex is vital for monkey infants to cling to their mother’s fur. Humans, having evolved away from an arboreal lifestyle and losing body fur, do not require such a strong grasp. Typically, human infants begin to lose this reflex around three months of age. Despite its early loss, some researchers believe that the grasp reflex may still serve important functions in humans.
FAQs on 7 Vestigial Features of the Human Body
What are the vestigial parts of the human body?
Vestigial parts of the human body include the appendix, wisdom teeth, coccyx (tailbone), ear muscles, and the palmar grasp reflex. These structures are remnants of our evolutionary past .
Which 3 are vestigial structures?
Three well-known vestigial structures are the appendix, wisdom teeth, and the tailbone (coccyx).
Is hair a vestigial organ?
Human body hair is considered vestigial because it no longer serves the same function of insulation and protection that it did for our fur-covered ancestors.
What are examples of vestigial organs?
Examples of vestigial organs include the appendix, wisdom teeth, coccyx, palmar grasp reflex, and ear muscles .









