Table of Contents
Financial Management Important Questions for CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Financial Decisions, Capital Structure
1.Financial Decisions
These are the decisions which are concerned with the selection of best financing alternative or best investment alternative. It is broadly concerned with three aspects, viz investment, financing and dividend.
2.Classification of Financial Decision
(i)Investment decision The investment decision relates to how the firm’s funds are invested in different assets. Investment decision may be long-term or short-term. Long-term investment decision is called capital budgeting decision and short-term investment decision is called working capital decision.
(a)Capital budgeting decisions or long-term investment decisions Factors affecting capital budgeting decisions are:
- Rate of return
- Cash flow of the projects
- Investment criteria involved
(b)Working capital decisions or short-term investment decisions They are concerned with level of inventories, cash and debtors.
(ii)Financing decision It deals with quantum of finance to be raised from long-term sources, viz debt equity. In other words, it refers to the determination as how the total funds required by the business will be obtained from various long-term sources. Factors affecting financial decisions are:
(a)Cost (g)Return on investment
(b)Risk (h)Tax rate
(c)Floatation costs (i)Flexibility
(d)Cash flow position of the company (j)Regulatory framework
(e)Fixed operating costs (k)Control considerations
(f)State of the capital market
(iii)Dividend decision This decision involves how much of the ‘after tax profits’ is to be distributed as dividends to shareholders and how much to retain in the business to meet future investment requirements.
Factors affecting dividend decisions are:
(a)Earnings (g) Taxation policy
(b)Stability of earnings (h) Stock market reaction
(c)Stability of dividends (i) Access to capital market
(d)Growth opportunities (j) Legal constraints
(e)Cash flow position (k) Contractual constraints
(f)Shareholders’ preference
3.Meaning of Capital Structure Capital structure refers to the mix between owners’ fund (equity) and borrowed funds (debt). Capital structure of a business affects both the profitability and financial risk of business. Since, use of equity and debt in the capital structure has both its merits and demerits, a judicious mix of both are used in the capital structure.
4.Optimal Capital Structure A capital structure is said to be optimal when the proportion of debt and equity is such that it results in the increase of shareholders’ wealth.
5.Factors Affecting Capital Structure
(i) Cash flow position (viii) Floatation costs
(ii) Interest coverage ratio (ix) Risk considerations
(iii) Debt service coverage ratio (x) Flexibility
(iv) Return on Investment (Rol) (xi) Control
(v) Cost of debt (xii) Regulatory framework
(vi) Tax rate (xiii) Stock market conditions
(vii) Cost of equity (xiv) Capital structure of other companies
NOTE Factors affecting capital structure Not in syllabus. Answer given from previous years will be shown to this effect.
Previous Year Examination Questions
1 Mark Questions
1.Define capital structure. (Delhi 2014)
Ans. Capital structure can be defined as the mix between the owners’ funds and borrowed funds.
Capital Structure =Debt/Equity
2.How does cost of debt affect the capital strucutre of a company? State.(Foreign 2014, Delhi 2009)
Ans. When a firm is able to borrow at a lower rate, ft increases the capacity to employ higher debt and can increase the debt component in the capital structure.
3.What is meant by financial risk? (All India 2014)
Ans. Financial risk refers to a position when a company is not able to meet its fixed financial charges namely interest, preference dividend payment and repayment obligations.
4.Name the major determinant of dividend decision. (All India 2011)
Ans. Dividends are paid out of current and past earnings. Therefore, earning is the most important determinant of dividend decision.
5.Which type of companies can declare higher dividend? (Delhi 2011 c)
Ans. A company having stable earnings is in a position to declare higher dividends.
6.Name the financial decision which will help a businessman in opening a new branch of its business. (hots; Delhi 2010)
Ans. Investment decision helps a businessman in opening a new branch of its business.
7.Cost of debt is lower than the cost of equity share capital. Give reason why even
then a company cannot work only with the debt? (hots,- All India 2010; Delhi 2010)
Ans. A company cannot work only with debt because a company cannot be formed or be in existence without equity.
8.What is meant by floatation cost? (Delhi 2009 c)
Ans. Floatation costs are those expenses which are incurred while issuing securities like equity shares, preference shares, debentures, etc, e.g. underwriting commission, brokerage, stamp duty, listing charges, etc.
9.Which component of capital structure determines the overall financial risk in an organisation? (hots; Delhi 2009 c)
Ans. Proportion of debt in the total capital determines the overall financial risk.
10.What does higher business risk indicate? (All India 2009; Delhi 2009)
Ans. Higher business risk indicates high fixed operating cost.
11.What is meant by cost of equity? (All India 2009)
Ans. Equity shareholders expect a return on their investment, i.e. Earning Per Share (EPS). When a company increases debt, the financial risk faced by the equity shareholders increases and then EPS starts decreasing with inclusion of debt beyond a certain point. Thus, cost of equity may go up sharply and share price may decrease.
12.What does a firm’s lower business risk indicate? (All India 2009)
Ans. A firm’s lower business risk indicates that a firm has lowered operating cost and can raise more capital by issue of debt securities. Whereas, at the time of high business risk, it should depend upon equity.
13.’A company wants to establish a new unit in which a machinery of worth ? 10 lakh is involved’. Identify the type of decision involved here in financial management. (HOTS; Delhi 2008)
Ans. The given situation pertains to investment in fixed assets of the business. Hence, it is capital budgeting decision or fixed investment decision.
14.Name the concept which increases the return on equity shares with a change in the capital structure of a company. (Delhi 2008)
Ans. Trading on equity increases the return on equity shares with a change in the capital structure of a company.
3 Marks Questions
15.Give the meaning of ‘investment decision’ and ‘dividend decision’.(Compartment 2014)
Ans. (i) Investement decision It relates to as how the funds of a firm are to be invested into different assets, so that the firm is able to earn highest possible return for the investors. Investment decision can be long-term, also known as capital budgeting where the funds are commited into long-term basis. Short-term investment decision also known as working capital decision and it is concerned with the levels of cash, inventories and debtors.
(ii) Dividend decision It relates to decision regarding distribution of dividend. The decision taken is as to how much dividend is to be retained in business and how much should be distributed to shareholders, after taking into account various factors affecting it.
16.Explain the factors that affect capital budgeting decision. (Compartment 2014)
Ans .Factors affecting capital budgeting/long-term investment decisions are:
(i) Cash flow of the project Whenever a company is investing huge funds in an investment proposal, it expects some regular amount of cash to meet day-to-day requirements. The amount of cash flow of an investment proposal will be assessed properly before investing in the proposal.
(ii) Return on investment The most important criteria to decide the investment proposal is rate of return it will bring back for company, e.g. if project A is bringing 10% return and project B is bringing 15% return then, a businessman would prefer project B.
(iii) Risk involved With every investment proposal, some degree of risk is also involved. The company must try to calculate the risk involved in every proposal and .should prefer the investment proposal with moderate degree of risk only. .
17.Explain how the
(i)cost of debt and
(ii)cost of equity, affect the choice of capital structure. (Delhi 2010 c)
Ans. (i) Cost of debt A firm’s ability to borrow at a lower rate of interest increases its capacity to employ higher debt. Thus, more debt can be used if debt can be raised at lower rate.
(ii) Cost of equity Equity shareholders expect a return on their investment, i.e. Earning Per Share (EPS). When a company increases debt, the financial risk faced by the equity shareholders increases and then EPS starts decreasing with inclusion of debt, beyond a certain point. Thus, with the increase in risk, cost of equity may go up sharply and share prices may decrease.
18.Explain how the
(i)Risk consideration and
(ii) Tax rate affect the choice of capital structure? (All India 2010)
or
Explain any two factors that affect the capital structure of a company. (All India 2008)
Ans. (i) Risk of consideration While deciding the capital structure, risk must be analysed and considered.
Total risk consists of two types of risks:
(a)Financial risk It refers to a position when a company is unable to meet its fixed financial charges namely, interest payment, preference dividend and payment obligations. It arises when a company borrows. Use of debt increases the financial risk of a business.
(b)Business risk It depends upon fixed operating costs. Higher fixed operating cost means higher business risk and vice-versa. If a firm’s operating risk is lower, its capacity to use debt is higher and vice-versa.
(ii) Tax rate Interest is a deductible expense. Cost of debt is affected by the tax rate. A higher tax rate
makes debt relatively cheaper and increases its attraction in relation to equity.
19.What is meant by financial management? State any two financial decisions taken by a financial manager. (Delhi 2009, All India 2009)
or
State three decisions involved in financial management. (Delhi 2008 C)
Ans. Financial management is concerned with optimal procurement as well as the usage of finance. For optimal procurement, different available sources of finance are identified and compared intermsof their costs and associated risks.
Main decisions involved in financial management are as follows:
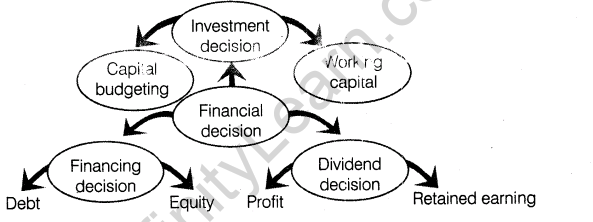
(i)Investment decision The investment decision relates to how the firm’s funds are invested in different assets. Investment decision may be long-term or short-term. Long-term investment decision is called capital budgeting decision and short-term investment decision is called working capital decision.
(ii) Financing decision It deals with quantum of finance to be raised from long-term sources, viz debt equity. In other words, it refers to the determination as how the total funds required by the business will be obtained from various long-term sources.
(iii) Dividend decision This decision involves how much of the ‘after tax profits’ is to be distributed as dividends to shareholders and how much to retain in the business to meet future investment requirements.
20.How does trading on equity affect the choice of capital structure of a company?
Explain with the help of suitable example. (Delhi 2008 c)
Ans.Trading on equity refers to the use of fixed cost sources of finance such as debentures and
preference share capital in the capital structure so as to increase the return on equity shares. There
are two conditions to use trading on equity:
(i) The rate of interest on loan/debentures should be less than the rate of Return on Investment.
(ii) The interest should be deducted from profit before tax.
For example, Let us consider two public companies X Ltd and Y Ltd.
The following calculation will show how trading on equity increases the return on equity shares
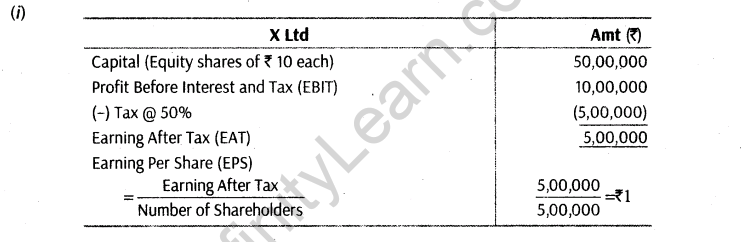
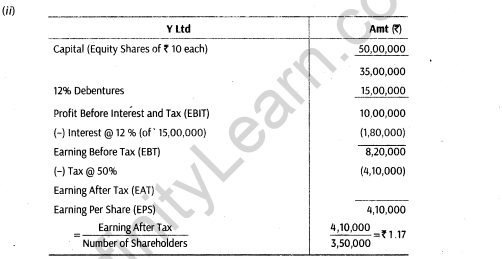
Thus, it can be concluded that Y Ltd using fixed cost sources, i.e. debentures, earn a relatively high rate of return on equity capital.
4/5 Marks Questions
21.Give the meaning of investment and dividend decisions of financial management.(Foreign 2014)
Ans. (i) Investment decision It relates to as how the funds of a firm are to be invested into different assets, so that the firm is able to earn highest possible return for the investors. Investment decision can be long-term, also known as capital budgeting where the funds are commited into long-term basis. Short-term investment decision also known as working capital decision and it is concerned with the levels of cash, inventories and debtors.
(ii) Dividend decision It relates to decision regarding distribution of dividend. The decision taken is as to how much dividend is to be retained in business and how much should be distributed to shareholders, after taking into account various factors affecting it.
22.What is meant by long-term investment? State any three factors which affect the long-term investment decision.(Delhi 2013; All India 2013)
or
Investment decision can be long-term and short-term. Explain long-term investment decision and state any two factors affecting this decision. (All India 2012)
Ans. A long-term investment decision is also called a capital budgeting decision. It involves committing the finance on a long-term basis, e.g. making investment in a new machine to replace an existing one or acquiring a new fixed asset or opening a new branch.
Factors affecting capital budgeting/long-term investment decisions are:
(i) Cash flow of the project Whenever a company is investing huge funds in an investment proposal, it expects some regular amount of cash to meet day-to-day requirements. The amount of cash flow of an investment proposal will be assessed properly before investing in the proposal.
(ii) Return on investment The most important criteria to decide the investment proposal is rate of return it will bring back for company, e.g. if project A is bringing 10% return and project B is bringing 15% return then, a businessman would prefer project B.
(iii) Risk involved With every investment proposal, some degree of risk is also involved. The company must try to calculate the risk involved in every proposal and .should prefer the investment proposal with moderate degree of risk only.
23.Explain the following as factors affecting financing decision
(i)Cost
(ii) Cash flow position of business
(iii) Control considerations
(iv) Floatation cost (Delhi 2012)
Ans. (i) Cost The cost of raising funds through different sources are different. A prudent financial manager would normally tax for a source which is the cheapest. Debt is considered the cheapest of all sources, tax deductibility makes it still cheaper.
(ii) Cash flow position of business A stronger cash flow position may make debt financing more viable than funding through equity. Therefore, in order to take advantage of cheap finance, companies prefer debt to equity.
(iii) Control considerations The ultimate control of the company is that of the equity shareholders. Greater the number of equity shareholders, the greater will be the control in the hands of more people. This is not a good situation. Therefore, from this point of view the equity share capital should be avoided.
(iv) Floatation cost From the point of view of floating costs, higher the floatation cost, less attractive the source becomes.
24.Determining the relative proportion of various types of funds depends upon
various factors. Explain any five such factors. (hots; Delhi 2011)
or
Determining the overall cost of capital and the financial risk of the enterprise depends upon various factors. Explain any five factors. (All India 2011)
Ans. Following are the factors determining the relative proportion of various types of funds, or the capital structure:
(i) Position of cash flow Size of projected cash flow must be considered before issuing debt. Cash flow must not only cover fixed cash payment obligations but there must be sufficient cash for smooth working of the business.
(ii) Return on Investment (Rol) It refers to the earning expected from the investment. If Rol of a company is high, it can opt for trading on equity to increase the earning per share. Thus, it is an important determinant of the extent of trading on equity.
(iii) Cost of capital It may be defined as the payment made by company to obtain capital. Thus, interest is the cost of debentures or loan and dividend paid by the company is the cost of equity and preference share capital. The rate of dividend on preference shares is fixed which is generally lower than that of equity shares. The cost of debentures is generally lower and tax deductible.
(iv) Risk of consideration While deciding the capital structure, risk must be analysed and considered. Total risk consists of two types of risks:
(a)Financial risk It refers to a position when a company is unable to meet its fixed financial charges namely, interest payment, preference dividend and payment obligations. It arises when a company borrows. Use of debt increases the financial risk of a business.
(b)Business risk It depends upon fixed operating costs. Higher fixed operating cost means higher business risk and vice-versa. If a firm’s operating risk is lower, its capacity to use debt is higher and vice-versa.
(v) Flexibility To maintain flexibility, a firm should not use its debt potential in full, So that it can borrow in unforeseen circumstances.
25.How are the shareholders likely to gain with loan components in capital employed? Explain with suitable example. (hots; All India 2011)
Ans. With a debt component in the total capital, shareholders are likely to have the benefit of a higher rate of return on the share capital. This is because debt/loan carry a fixed charge and the amount of interest paid is deductible from the earnings before tax payment. The benefit to the shareholders will be realised only if the average rate of return on total capital invested is more than the rate of interest payable on loan/debt.
For example,Trading on equity refers to the use of fixed cost sources of finance such as debentures and
preference share capital in the capital structure so as to increase the return on equity shares. There
are two conditions to use trading on equity:
(i) The rate of interest on loan/debentures should be less than the rate of Return on Investment.
(ii) The interest should be deducted from profit before tax.
For example, Let us consider two public companies X Ltd and Y Ltd.
The following calculation will show how trading on equity increases the return on equity shares


Thus, it can be concluded that Y Ltd using fixed cost sources, i.e. debentures, earn a relatively high rate of return on equity capital.
26.Name the decision taken by a financial manager which determines the overall cost of capital and the financial risk of the enterprise. Explain any two factors which affect this decision. (hots; All India 2011)
Ans. Financing decision determines the overall cost of capital and the financial risk of the enterprise.
The two main factors which affect financing decisions are:
(i) Cost The costs of raising funds through different sources are different. A prudent financial manager would normally tax for a source which is the cheapest. Debt is considered the cheapest of all sources, tax deductibility makes it still cheaper.
(ii) Control consideration The ulitmate control of the company is that of the equity shareholders. Greater the number of equity shareholders, the greater will be the control the hands of more people. This is not a good situation. Therefore, from this point of view the equity share capita! should be avoided.
27.Name the decision which financial manager will take, keeping in view the overall objective of maximising shareholders’ wealth. Explain any two factors which affect this decision. (HOTS; All India 2011)
Ans. Dividend decision A financial manager takes decision in three broad areas, viz, investment, financing and dividend, for maximising shareholders’ wealth. Wealth maximisation is possible with increase in price of shares. A good dividend policy will enhance the market value of shares thus, meeting the objective of wealth maximisation. It also influences the financing decision of the firm, since the firm will not require funds to the extent of re-invested retained earnings. So, it should be taken keeping in view the overall objective of maximising shareholders’ wealth.
The two factors which affect diviednd decisions are:
(i) Earnings Dividends are paid to the shareholders either from the past earnings or from the current earnings or from both. Therefore, ‘earnings’ is a major factor which affects dividend decision.
(ii) Stability of earnings It also affects the dividend decision. A company having stable earnings can declare higher dividend whereas, a company having unstable earnings is likely to pay smaller dividend.
6 Marks Questions
28.Explain the following as factors affecting dividend decision (All India 2014; Delhi 2014)
(i)Stability of earnings
(ii)Growth opportunities
(iii)Cash flow position
(iv)Taxation policy
Ans. Dividend decision relates to how much of the company’s net profit is to be distributed to the
shareholders and how much of it is to be retained in the business.
Factors affecting dividend decision are:
(i) Stability of earnings Stability of earnings of a business unit also affects the dividend decision. A company having stable earnings can declare higher dividend whereas a company having unstable earnings is likely to pay smaller dividend.
(ii) Growth opportunity Companies which are intended to grow, generally pay less dividend and retain more money out of profits to invest in profitable projects. On the contrary, companies which are not intended to grow and have enough earnings and cash, can pay higher dividends.
(iii)Cash Flow position Dividend involves an outflow of cash. Availability of enough cash is necessary for payment of declaration of dividends.
(iv)Taxation policy The decision is affected by tax treatment of dividends and capital gains. For a company, it is better to pay less by dividends when the tax rate on dividend is higher and pay more as dividends when tax rate is lower. This is because however dividends are tax fall in the hands of shareholders, dividends distribution tax is levied on the company.
29.Explain the following as factors affecting ‘dividend decision’.
(i)Stability of dividend
(ii)Shareholders’ preference
(iii)Legal constraints .
(iv)Access to capital market (Delhi 2014)
Ans. Dividend decisions relate to how much of the company’s after tax profit is to be distributed to the
share holders and how much of it should be retained in the business for future requirements.
Factors affecting dividend decisions are:
(i) Stability of dividend Companies generally have a policy of stabilising dividends, i.e. increase in dividend is only done when the earning potential of the company has gone up and not just the current year’s earnings. Thus, dividend per share is not altered when the change is small or temporary in nature.
(ii)Shareholders’ preference While declaring dividends, management must keep in mind the preferences of the shareholders in this regard. If the shareholders in general desire that at least a certain amount is paid as dividend, the companies are likely to declare the same. There are always some shareholders who depend upon a regular income from their investments.
(iii)Legal constraints Certain provisions of The Companies Act place restrictions on payouts as dividend. Such provisions must be adhered while declaring the dividend.
(iv) Access to capital market Large and reputed companies generally have easy access to the capital market and, therefore, may depend less on retained earning to finance their growth. These companies tend to pay higher dividends than the smaller companies.
30.Explain any four factors which affect the ‘dividend decision’ of a company.(Compartment 2014, All India 2013)
or
What is meant by ‘dividend decision’? Explain any four factors which affect the dividend decision of a company. (Delhi 2013)
or
What is meant by ‘dividend decision’? State any four factors affecting the dividend decision. (Delhi-2010)
Ans. This decision involves how much of the ‘after tax profits’ is to be distributed as dividends to shareholders and how much to retain in the business to meet future investment requirements.
Various factors affecting dividend decision
Trading on equity refers to the use of fixed cost sources of finance such as debentures and
preference share capital in the capital structure so as to increase the return on equity shares. There
are two conditions to use trading on equity:
(i) The rate of interest on loan/debentures should be less than the rate of Return on Investment.
(ii) The interest should be deducted from profit before tax.
For example, Let us consider two public companies X Ltd and Y Ltd.
The following calculation will show how trading on equity increases the return on equity shares


Thus, it can be concluded that Y Ltd using fixed cost sources, i.e. debentures, earn a relatively high rate of return on equity capital.
Dividend decisions relate to how much of the company’s after tax profit is to be distributed to the
share holders and how much of it should be retained in the business for future requirements.
Factors affecting dividend decisions are:
(i) Stability of dividend Companies generally have a policy of stabilising dividends, i.e. increase in dividend is only done when the earning potential of the company has gone up and not just the current year’s earnings. Thus, dividend per share is not altered when the change is small or temporary in nature.
(ii)Shareholders’ preference While declaring dividends, management must keep in mind the preferences of the shareholders in this regard. If the shareholders in general desire that at least a certain amount is paid as dividend, the companies are likely to declare the same. There are always some shareholders who depend upon a regular income from their investments.
(iii)Legal constraints Certain provisions of The Companies Act place restrictions on payouts as dividend. Such provisions must be adhered while declaring the dividend.
(iv) Access to capital market Large and reputed companies generally have easy access to the capital market and, therefore, may depend less on retained earning to finance their growth. These companies tend to pay higher dividends than the smaller companies.
31.Explain any four factors which determine the choice of the capital structure of a company. (Compartment 2014; All India 2012,2011,2008; Delhi 2011,2008)
or
Exaplain the following as factors affecting the choice of capital structure.
(i)Return on Investment (Rol) (ii) Flexibility
(iii) Risk consideration (iv) Control (Foreign 2014)
or
Explain the following factors affecting the choice of capital structure.
(i)Cash flow position (ii) Cost of equity
(iii) Floatation tests (iv) Stock market condition (Foreign 2014)
or
Determination of capital structure of a company is influenced by a number of factors. Explain any four of them. (All India 2009; Delhi 2009)
Ans. Various factors influencing capital structure are:
(i) Position of cash flow Size of projected cash flow must be considered before issuing debt. Cash flow must not only cover fixed cash payment obligations but there must be sufficient cash for smooth working of the business.
(ii) Return on Investment (Ro!) It refers to the earning expected from the investment. If Rol of a company is high, it can opt for trading on equity to increase the earning per share. Thus, it is an important determinant of the extent of trading on equity.
(iii) Cost of capital It may be defined as the payment made by company to obtain capital. Thus, interest is the cost of debentures or loan and dividend paid by the company is the cost of equity and preference share capital. The rate of dividend on preference shares is fixed which is generally lower than that of equity shares. The cost of debentures is generally lower and tax deductible.
(iv) Risk Consideration While deciding the capital structure, risk must be analysed and considered. Total risk consists of two types of risks:
(a)Financial risk It refers to a position when a company is unable to meet its fixed financial charges namely, interest payment, preference dividend and payment obligations. It arises when a company borrows. Use of debt increases the financial risk of a business.
(b)Business risk It depends upon fixed operating costs. Higher fixed operating cost means higher business risk and vice-versa. If a firm’s operating risk is lower, its capacity to use debt is higher and vice-versa.
(v)Flexibility To maintain flexibility, a firm should not use its debt potential in full, So that it can borrow in unforeseen circumstances.
(vi)Cost of Equity Equity shareholders expect a return on their investment, i.e. Earning Per Share (EPS). When a company increases debt, the financial risk faced by the equity shareholders increases and then EPS starts decreasing with inclusion of debt, then beyond this point, cost of equity may go up sharply and share price may decrease.
(vii) Control If the firm wants more control, it will choose to raise funds through debt.
(viii) Floatation cost Raising funds through debt or equity involves same cost. Loan from bank may not cost too much. Thus, the floatation costs may also affect choice of capital structure.
(ix) Stock market consideration During the bullish phase, it is easy to raise funds through equity. Vice-versa, during a bearish phase the raising of equity capital becomes diffcult and thus, the firm may opt for debt.
32.What is meant by financing decision? State any four factors affecting the financing
decision. (All India 2010; Delhi 2010)
Ans. Financial decision deals with quantum of finance to be raised from long-term sources, viz debt equity. In other words, it refers to the determination as how the total funds required by the business will be obtained from various long-term sources. There should be a proper balance between debt and share capital as it influences the market price of the shares and cost of capital.
Factors affecting financing decisions
(i) Cost The cost of raising funds through different sources are different. A prudent financial manager would normally tax for a source which is the cheapest. Debt is considered the cheapest of all sources, tax deductibility makes it still cheaper.
(ii) Cash flow position of business A stronger cash flow position may make debt financing more viable than funding through equity. Therefore, in order to take advantage of cheap finance, companies prefer debt to equity.
(iii) Control considerations The ultimate control of the company is that of the equity shareholders. Greater the number of equity shareholders, the greater will be the control in the hands of more people. This is not a good situation. Therefore, from this point of view the equity share capital should be avoided.
(iv) Floatation cost From the point of view of floating costs, higher the floatation cost, less attractive the source becomes.
33.What is meant by financial structure cr capital structure of an organisation?
Explain any two advantages and two limitations of it. (Delhi 2009)
Ans. Meaning of capital or financial structures Capital structure refers to the mix between owners’ fund (equity) and borrowed funds (debt).
Advantages of capital structure are: (Any two)
(i) Return The capital structure should give maximum return to the shareholder.
(ii) Risk The use of debt adds to the risk of the company and shareholder. Therefore, it should be used cautiously with equity.
(iii) Flexibility If a firm uses its debt potential to the full, it loses flexibility to issue further debt. To maintain some borrowing power to take care of unforseen circumstances.
Disadvantages of capital structure are: (Any two)
(i) Debt and equity differ in cost and risk. As the debt involve less cost, but it is very risky whereas, equity are expensive securities, but these are safe securities from the company’s prospects.
(ii) Debt is risky because payment of regular interest on debt is a legal obligation of the business. In case, they fail to pay debt security holders can claim over the assets of the company and if firm fails to meet return of principal amount, it can even go to liquidation u.id at the stage of insolvency.
(iii) Equity securities are safe securities from company’s point of view as company has no legal obligation to pay dividend to equity shareholders if it is running in loss.









