Table of Contents
Introduction
Acetic acid, also known as ethanoic acid, is a widely used organic compound with the chemical formula CH3COOH.
It is a colorless liquid with a pungent vinegar-like odor. Acetic acid is characterized as a weak acid, meaning it partially dissociates in water to release hydrogen ions. This property gives it its acidity, although it is less acidic compared to strong mineral acids.
Acetic acid finds extensive applications across various industries. In the food and beverage industry, it is a primary component of vinegar, providing the characteristic sour taste and acting as a natural preservative. In the chemical industry, acetic acid serves as a versatile building block for the synthesis of numerous chemicals, solvents, and polymers. It is commonly used in the production of vinyl acetate monomer (VAM), a key ingredient in adhesives, coatings, and paints. Additionally, acetic acid has applications in the textile industry for dyeing and finishing processes, in the pharmaceutical industry for the production of medicines and disinfectants, and in laboratories for various scientific and research purposes. It can also be used as a natural cleaning agent in household applications.
However, it is important to handle concentrated acetic acid with caution due to its corrosive nature and potential irritant effects on the skin, eyes, and respiratory system.
Structural Formula of Acetic Acid
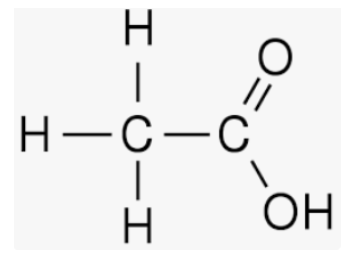
In this structure, the central carbon atom (C) is bonded to three hydrogen atoms (H) and one oxygen atom (O) through single bonds. The carbon atom is also bonded to another carbon atom through a double bond. The oxygen atom is bonded to the carbon atom through a single bond and also has two lone pairs of electrons.
Physical Properties of Acetic Acid
- State: Acetic acid is a liquid at room temperature. It appears as a clear, colorless liquid.
- Odor: Acetic acid has a pungent, vinegar-like odor. This distinctive smell is often associated with vinegar itself.
- Solubility: Acetic acid is highly soluble in water. It readily mixes with water to form a homogeneous solution. It is also miscible with many organic solvents.
- Boiling Point: The boiling point of acetic acid is approximately 118.1 °C (244.6 °F). This relatively low boiling point allows it to vaporize at a relatively low temperature.
- Density: The density of acetic acid is around 1.05 g/cm³. It is slightly denser than water.
- Viscosity: Acetic acid has a relatively high viscosity compared to water. It is more viscous, meaning it has a thicker consistency and flows less easily.
- Acidity: Acetic acid is a weak acid with a pH typically ranging between 2.4 and 2.6. It exhibits acidic properties but is less acidic than strong mineral acids such as sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid.
- Vapor Pressure: Acetic acid has a moderate vapor pressure. At room temperature, it can release vapor that is detectable by its distinct odor.
Chemical Properties of Acetic Acid
- Acidity: Acetic acid is a weak acid and can donate a proton (H+) to a base. It undergoes partial dissociation in water, releasing hydrogen ions (H+) and acetate ions (CH3COO-).
- Reactivity with Metals: Acetic acid can react with certain metals, such as zinc or aluminum, to produce hydrogen gas and corresponding metal acetates. This reaction is single displacement reaction.
- Esterification: Acetic acid can undergo esterification reactions with alcohols in the presence of an acid catalyst. This process leads to the formation of esters, with water as a byproduct. This reaction is commonly used in the production of various flavors, fragrances, and solvents.
- Oxidation: Acetic acid is prone to oxidation under certain conditions. It can be oxidized to produce carbon dioxide and water, or further oxidized to form carbon monoxide and water.
- Reaction with Bases: Acetic acid reacts with bases to form salts called acetates. For example, when reacted with sodium hydroxide (a strong base), sodium acetate and water are formed.
- Reaction with Carbonates and Bicarbonates: Acetic acid reacts with carbonates and bicarbonates to produce carbon dioxide gas, water, and the corresponding acetate salt. This reaction is commonly observed when vinegar (which contains acetic acid) is combined with baking soda (sodium bicarbonate).
- Polymerization: Under certain conditions, acetic acid can undergo polymerization reactions to form polymeric materials like polyvinyl acetate (PVAc), which is used in adhesives, paints, and coatings.
Also Check
Uses of Acetic Acid
- Food and Beverage Industry: Acetic acid is a key component of vinegar, which is used as a condiment, preservative, and flavoring agent in cooking, pickling, and food preservation. It provides the characteristic sour taste in various food products.
- Chemical Industry: Acetic acid is an essential chemical in the production of various chemicals, solvents, and polymers. It serves as a building block for the synthesis of vinyl acetate monomer (VAM), which is used in the production of adhesives, coatings, and paints. Acetic acid is also used in the production of cellulose acetate, a versatile material used in films, fibers, and plastics.
- Textile Industry: Acetic acid is used in the textile industry for dyeing and finishing processes. It helps fix dyes, enhance color fastness, and improve the texture of fabrics.
- Pharmaceuticals and Healthcare: Acetic acid is utilized in the pharmaceutical industry for the production of medicines, topical creams, and disinfectants. It is also used in medical laboratories as a reagent and solvent.
- Cleaning and Household Applications: Acetic acid is sometimes used as a natural cleaning agent due to its antimicrobial properties. It is effective in removing mineral deposits, lime scale, and rust from various surfaces. It is commonly used in household cleaning products and formulations.
- Agriculture: Acetic acid-based herbicides are used in agricultural practices for weed control. They help in managing weed growth in crops and agricultural fields.
- Photography: Acetic acid is used in the development process of traditional film photography. It helps in stopping the development reaction and fixing the image on the photographic film.
Conclusion
Acetic acid, or ethanoic acid, is a versatile compound with various applications across industries. Its distinct sour odor and acidic properties make it a valuable ingredient in the food and beverage industry, where it is used in the production of vinegar, a common condiment and preservative. In the chemical industry, acetic acid serves as a building block for the synthesis of chemicals, solvents, and polymers, playing a crucial role in the production of adhesives, coatings, and paints.
Acetic acid finds applications in the textile industry for dyeing and finishing processes, improving color fastness and texture of fabrics. It is also utilized in the pharmaceutical industry for the production of medicines, topical creams, and disinfectants, owing to its antimicrobial properties. Moreover, acetic acid is used in cleaning products and formulations as a natural cleaning agent, effectively removing mineral deposits, lime scale, and rust.
The agricultural sector benefits from acetic acid-based herbicides for weed control, aiding in managing unwanted weed growth in crops and agricultural fields. Additionally, acetic acid has applications in photography, where it is used in film development processes.
Overall, the diverse uses of acetic acid highlight its significance in various industries, demonstrating its versatility as a chemical compound with multiple practical applications.
Solved Example of Acetic Acid
Example 1: What is the mass of acetic acid (CH3COOH) required to prepare a 500 mL solution with a concentration of 0.2 M?
Solution:
To find the mass of acetic acid required, we need to use the molarity (M) and volume (V) of the solution.
Step 1: Convert the volume from milliliters (mL) to liters (L).
500 mL = 500/1000 = 0.5 L
Step 2: Use the formula for molarity (M) to find the number of moles (n) of acetic acid.
Molarity (M) = moles (n) / Volume (V)
0.2 M = n / 0.5 L
Rearranging the formula, we have:
n = M x V n = 0.2 mol/L x 0.5 L n = 0.1 mol
Step 3: Determine the molar mass of acetic acid (CH3COOH).
The molar mass of carbon (C) is 12.01 g/mol. The molar mass of hydrogen (H) is 1.01 g/mol. The molar mass of oxygen (O) is 16.00 g/mol.
Molar mass of acetic acid (CH3COOH) = (12.01 x 2) + (1.01 x 4) + 16.00 + 1.01 + 16.00
= 60.05 g/mol
Step 4: Calculate the mass of acetic acid using the number of moles and molar mass.
Mass = moles x molar mass
Mass = 0.1 mol x 60.05 g/mol
Mass = 6.005 g
Therefore, 6.005 grams of acetic acid is required to prepare a 500 mL solution with a concentration of 0.2 M.
Example 2: A chemist needs to prepare 250 mL of a 0.5 M acetic acid solution. How many grams of acetic acid (CH3COOH) should be dissolved in the solution?
Solution:
To find the mass of acetic acid required, we need to use the molarity (M) and volume (V) of the solution.
Step 1: Convert the volume from milliliters (mL) to liters (L). 250 mL = 250/1000 = 0.25 L
Step 2: Use the formula for molarity (M) to find the number of moles (n) of acetic acid.
Molarity (M) = moles (n) / Volume (V) 0.5 M = n / 0.25 L
Rearranging the formula, we have:
n = M x V n = 0.5 mol/L x 0.25 L n = 0.125 mol
Step 3: Determine the molar mass of acetic acid (CH3COOH).
The molar mass of carbon (C) is 12.01 g/mol.
The molar mass of hydrogen (H) is 1.01 g/mol.
The molar mass of oxygen (O) is 16.00 g/mol.
Molar mass of acetic acid (CH3COOH) = (12.01 x 2) + (1.01 x 4) + 16.00 + 1.01 + 16.00 = 60.05 g/mol
Step 4: Calculate the mass of acetic acid using the number of moles and molar mass.
Mass = moles x molar mass
Mass = 0.125 mol x 60.05 g/mol
Mass = 7.51 g
Therefore, 7.51 grams of acetic acid should be dissolved in 250 mL of the 0.5 M acetic acid solution.
Frequently Asked Questions on Acetic Acid
Why is CH3COOH called acetic acid?
CH3COOH is called acetic acid because it is the systematic name based on the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) nomenclature system. Acetic refers to its origin from vinegar, which contains acetic acid.
What is acetic acid common name?
Acetic acid is commonly known as vinegar, which is its most well-known and widely used form. Vinegar is a diluted solution of acetic acid, typically containing around 5-8% acetic acid by volume.
How is acetic acid made?
Acetic acid can be produced through various methods. The most common method is the fermentation of carbohydrates, such as sugars or ethanol, by certain bacteria of the genus Acetobacter or by yeast. The bacteria convert the carbohydrates into acetic acid in the presence of oxygen. Another method is the oxidation of ethanol using chemical processes.
Is acetic acid a base or acid?
Acetic acid is an acid, specifically a weak acid. It donates a proton (H+) in aqueous solutions, making it acidic. Acetic acid does not behave as a base.
What is the difference between CH3COO and CH3COOH?
The difference between CH3COO and CH3COOH lies in the presence of an additional hydrogen ion (H+). CH3COO- is the acetate ion, which is the conjugate base of acetic acid (CH3COOH). Acetic acid can lose a hydrogen ion to form the acetate ion (CH3COO-) in an acidic solution.
What is the pH of acetic acid?
The pH of acetic acid depends on its concentration. A 0.1 M solution of acetic acid has a pH of approximately 2.4-2.6, indicating its acidic nature. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with values below 7 considered acidic.
Is vinegar an acid?
Vinegar, which contains acetic acid, is indeed an acid. It has a sour taste and exhibits acidic properties. However, it is a weak acid compared to stronger mineral acids like sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid.
Is acetic acid soluble in water?
Acetic acid is highly soluble in water. It readily mixes with water to form a homogeneous solution. This solubility is one of the reasons why acetic acid, in the form of vinegar, can be easily diluted and used in various applications.





