Table of Contents
Introduction
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is a chemical compound consisting of one sodium ion (Na+) and one hydroxide ion (OH-). It is commonly known as caustic soda and is a strong base. Caustic soda is highly soluble in water and has a wide range of applications in various industries.
Chemical Formula: The chemical formula of sodium hydroxide is NaOH. The subscript numbers indicate the ratio of the ions present in the compound, with one sodium ion (Na+) and one hydroxide ion (OH-).
Caustic soda is an inorganic compound that is considered a strong base. It is highly caustic and has a slippery feel. It is commonly used in chemical processes, manufacturing, cleaning agents, and in the production of various chemicals.
Equations involving Caustic soda
Dissociation in Water: When sodium hydroxide is dissolved in water, it dissociates into sodium ions (Na+) and hydroxide ions (OH-). The equation for this dissociation is:
NaOH → Na+ + OH-
Neutralization Reaction: Sodium hydroxide reacts with acids in a neutralization reaction to form water and salt. The equation for a generic neutralization reaction with hydrochloric acid (HCl) is:
NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O
Structural Formula of Caustic soda
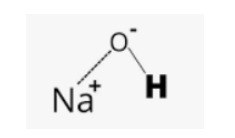
Sodium hydroxide, or caustic soda, is an ionic compound and therefore does not possess a distinct structural formula like covalent compounds. Its composition is represented by the chemical formula NaOH, indicating the arrangement of sodium ions (Na+) and hydroxide ions (OH-) within the compound. These ions are held together by ionic bonds.
The structural formula of Caustic soda can be represented as:
This structure visually demonstrates the connection between the sodium ion and the hydroxide ion in the compound.
Cautionary Note: Caustic soda is an extremely corrosive substance and requires careful handling. It is imperative to adhere to proper safety protocols when working with sodium hydroxide, including wearing protective gloves and goggles, as well as working in a well-ventilated environment.
Uses of Caustic soda
Caustic soda /Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) has various uses across different industries. Some common uses include:
- Chemical Manufacturing: Sodium hydroxide is a key ingredient in the production of various chemicals, such as detergents, soaps, bleach, and paper.
- Water Treatment: Sodium hydroxide is used in water treatment processes to adjust pH levels, neutralize acidity, and remove heavy metals and impurities.
- Food Processing: Sodium hydroxide is utilized in food processing industries for various purposes, including peeling fruits and vegetables, caramelizing sugar, and controlling acidity levels.
- Petroleum Industry: Sodium hydroxide is used in refining petroleum products and as a catalyst in the production of biodiesel.
- Cleaning and Household Products: Sodium hydroxide is a common ingredient in many cleaning products, such as oven cleaners, drain cleaners, and bathroom cleaners.
- Textile Industry: Sodium hydroxide is employed in the textile industry for various processes, including mercerization of cotton fibers to improve their strength and luster.
- Pharmaceuticals: Sodium hydroxide is used in the manufacturing of pharmaceutical products, including medicines and drugs.
- Aluminum Production: Sodium hydroxide plays a role in the extraction and refining of aluminum from bauxite ore.
Physical Properties of Sodium Hydroxide (Caustic Soda)
- State: Sodium hydroxide exists in solid form as white, crystalline flakes, pellets, or granules at room temperature. It can also be obtained as a concentrated aqueous solution.
- Melting Point: The melting point of sodium hydroxide is approximately 318°C (604°F), at which it transforms from a solid to a liquid state.
- Solubility: Sodium hydroxide is highly soluble in water, with its solubility increasing as the temperature rises. When dissolved in water, it releases hydroxide ions (OH-) and sodium ions (Na+), resulting in a strongly alkaline solution.
- Odor: Sodium hydroxide itself does not have a distinctive odor. However, its solution may have a soapy or slippery sensation when touched due to its alkaline nature.
- Density: The density of sodium hydroxide varies depending on its concentration and temperature. Solid caustic soda has a higher density than water, while its aqueous solutions typically have densities lower than that of pure water.
- Hygroscopicity: Sodium hydroxide is hygroscopic, meaning it can absorb moisture from the air. In humid conditions, it can attract water molecules, leading to the formation of concentrated solutions.
- Corrosiveness: Caustic soda is highly corrosive to various materials, including metals, organic tissues, and certain plastics. Direct contact can cause severe burns and tissue damage, necessitating careful handling and storage precautions.
Also Check
Chemical Properties of Sodium Hydroxide (Caustic Soda)
Strong Base: Sodium hydroxide is a strong base that readily dissociates in water, releasing hydroxide ions (OH-). It reacts with acids in neutralization reactions, producing water and a corresponding salt.
Neutralization Reactions: Sodium hydroxide reacts with acids, such as hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H2SO4), or acetic acid (CH3COOH), resulting in the formation of water and the respective salt.
Examples:
NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O
NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2O
NaOH + CH3COOH → CH3COONa + H2O
Alkaline Nature: Sodium hydroxide solutions exhibit high alkalinity due to the presence of hydroxide ions. They have a high pH value and can cause irritation to the skin and eyes upon contact.
Reactivity with Metals: Sodium hydroxide reacts with certain metals, such as aluminum, zinc, and tin, resulting in the production of hydrogen gas and the respective metal hydroxide.
Example: 2NaOH + 2Al → 2NaAlO2 + H2↑
Reactivity with Amphoteric Substances: Sodium hydroxide can react with amphoteric substances, which can act as both acids and bases. This reaction leads to the formation of salts.
Example: 2NaOH + Al2O3 → 2NaAlO2 + H2O
Saponification: Sodium hydroxide is involved in the saponification process, where it reacts with fats or oils to produce soap. The hydroxide ions break down the ester bonds in fats or oils, resulting in the formation of soap molecules and glycerol.
Dehydration: Sodium hydroxide is capable of dehydrating certain compounds by removing water molecules. It can react with alcohols to form alkoxides and water. For example: NaOH + C2H5OH → C2H5ONa + H2O
Solved Examples on Caustic soda:
Example 1: Calculation of Molar Mass Calculate the molar mass of sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
The molar mass of sodium is 22.99 g/mol, the molar mass of oxygen is 16.00 g/mol, and the molar mass of hydrogen is 1.01 g/mol.
To calculate the molar mass of sodium hydroxide (NaOH), we add the molar masses of sodium, oxygen, and hydrogen.
Molar Mass = (Number of sodium atoms × Molar mass of sodium) + (Number of oxygen atoms × Molar mass of oxygen) + (Number of hydrogen atoms × Molar mass of hydrogen)
Molar Mass = (1 × 22.99 g/mol) + (1 × 16.00 g/mol) + (1 × 1.01 g/mol)
Molar Mass = 22.99 g/mol + 16.00 g/mol + 1.01 g/mol
Molar Mass = 40.00 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is 40.00 g/mol.
Example 2: Stoichiometry in a Reaction Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) reacts with hydrochloric acid (HCl) to form sodium chloride (NaCl) and water (H2O). If you mix 10 grams of sodium hydroxide with excess hydrochloric acid, what is the theoretical yield of sodium chloride?
The balanced chemical equation for the reaction is:
NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O
According to the stoichiometry of the balanced equation, 1 mole of sodium hydroxide reacts with 1 mole of hydrochloric acid to produce 1 mole of sodium chloride.
First, we calculate the number of moles of sodium hydroxide using its molar mass:
Moles of NaOH = (Mass of NaOH ÷ Molar mass of NaOH) = (10 g ÷ 40.00 g/mol)
= 0.25 moles
Since the ratio of moles of sodium hydroxide to moles of sodium chloride is 1:1, the number of moles of sodium chloride produced is:
Moles of NaCl = Moles of NaOH = 0.25 moles
Finally, we convert the moles of sodium chloride to grams using its molar mass:
Mass of NaCl = (Moles of NaCl × Molar mass of NaCl)
= (0.25 moles × 58.44 g/mol) = 14.61 grams
Therefore, the theoretical yield of sodium chloride in the reaction is 14.61 grams.
Frequently Asked Questions on Caustic Soda
What is Caustic soda used for?
Sodium hydroxide has numerous applications across various industries. It is commonly used in the production of soaps, detergents, and cleaning agents. It is also used in water treatment, paper and pulp industry, textile industry, and as a pH regulator in various chemical processes. Sodium hydroxide is also employed in the manufacturing of food products, petroleum refining, and as a drain cleaner.
Can Caustic soda be used for unclogging drains?
Yes, Caustic soda can be used as a drain cleaner. It is a strong base that reacts with fats, oils, and other organic matter in the clogged drains, breaking them down and clearing the blockage. However, it should be used carefully and following the instructions provided, as it can cause damage to certain types of pipes or fixtures.
Can Caustic soda be used for skin care?
Sodium hydroxide is used in small quantities in certain skincare products, such as soaps and cleansers. However, it is important to note that sodium hydroxide is a caustic substance, and direct contact with concentrated solutions can be harmful to the skin. In skincare products, sodium hydroxide is used in controlled amounts and is neutralized during the manufacturing process to ensure it is safe for use.
What is the difference between sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide?
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and potassium hydroxide (KOH) are both strong bases, but they differ in their chemical compositions. Sodium hydroxide contains sodium (Na+) ions, while potassium hydroxide contains potassium (K+) ions. They have slightly different properties and applications, although they can both be used in similar ways, such as in the production of soaps and cleaning agents.
Can Caustic soda react with acids?
Yes, Caustic soda reacts with acids in a neutralization reaction. The hydroxide ions (OH-) from sodium hydroxide combine with the hydrogen ions (H+) from the acid to form water, while the remaining components form a salt. This reaction helps to neutralize the acidic properties of the acid.
What are Caustic soda hazards?
Caustic soda (NaOH) is a highly corrosive and caustic substance that can cause severe burns to the skin and eyes upon contact. Inhalation of sodium hydroxide dust or aerosols can irritate the respiratory system. It is also reactive and can release heat, toxic gases, or cause explosions when mixed with incompatible materials. Sodium hydroxide is harmful to aquatic life and should be handled with caution, following proper safety protocols and using appropriate protective equipment to minimize the risks associated with its use.
What are Sodium hydroxide crystals?
Sodium hydroxide crystals are solid, white, and highly caustic compounds composed of sodium, oxygen, and hydrogen. They are extremely corrosive and can cause severe burns if they come into contact with the skin or eyes. Sodium hydroxide crystals readily dissolve in water, releasing hydroxide ions that make it a strong base. They are commonly used in various industries, such as chemical manufacturing, cleaning products, and soap production. However, due to their hazardous nature, proper precautions must be taken when handling, storing, and using sodium hydroxide crystals, including wearing protective equipment and ensuring adequate ventilation to minimize the risks associated with their use.
Why is NaOH called caustic soda?
NaOH is called caustic soda because it is a highly corrosive substance that can cause severe chemical burns and tissue damage upon contact with the skin or other materials. The term caustic refers to its ability to burn or destroy organic tissues. The word soda is used to indicate its alkaline nature as it is a strong base. So, the name caustic soda is derived from its corrosive and alkaline properties.








