Table of Contents
Introduction
Amoeba is a type of microscopic organism belonging to the kingdom Protista. It is a unicellular organism that exhibits several distinct characteristics. Amoebas are classified under the phylum Amoebozoa and are commonly found in various aquatic environments such as freshwater, soil, and marine environments.
| Amoeba Classification | |
| Domain | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom | Protista |
| Phylum | Amoebozoa |
| Class | Tubulinea |
| Order | Euamoebida |
| Family | Amoebidae |
| Genus | Amoeba |
Structure of Amoeba
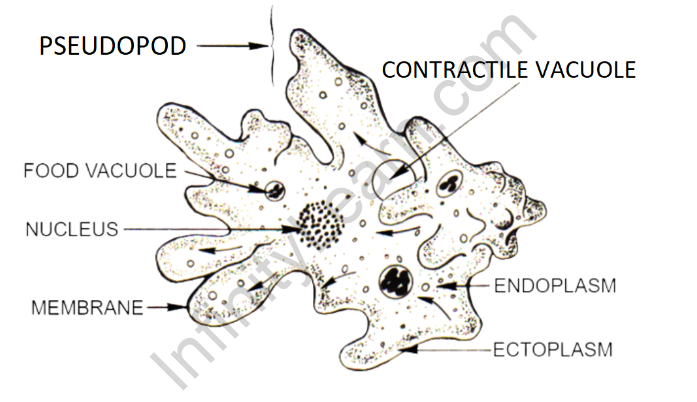
Characteristics of Amoeba
- Shape: Amoeba has a distinct shapeless or irregular shape, often resembling a blob or a droplet of water.
- Locomotion: It moves by extending finger-like projections called pseudopodia, which help in crawling and capturing food.
- Feeding: Amoeba is a heterotrophic organism and feeds on microscopic organisms like bacteria and algae. It engulfs its food by forming temporary food vacuoles.
- Respiration: Amoeba performs respiration through diffusion, where oxygen enters and carbon dioxide exits through its cell membrane.
- Reproduction: Amoeba reproduces asexually by a process called binary fission, where it divides into two identical daughter cells.
- Contractile Vacuole: Amoeba has a contractile vacuole that helps regulate water balance by collecting and expelling excess water from the cell.
- Sensory Organelles: Amoeba lacks specialized sensory organs but can sense changes in its environment, such as light and temperature.
- Adaptability: Amoeba is capable of adapting to different environments and can form cysts when conditions become unfavorable, protecting itself until favorable conditions return.
It’s important to note that while these characteristics generally apply to most Amoebas, there can be variations within the group due to the diverse species of Amoeba.
Conclusion
Amoebas are characterized by their shapeless and flexible bodies, which lack a fixed form. They have a single-celled structure, consisting of a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and a nucleus. One of the unique features of Amoebas is their ability to form temporary extensions called pseudopodia, or “false feet,” which they use for movement and capturing prey.
Amoebas are heterotrophic organisms, meaning they obtain their nutrition by ingesting other organisms or organic matter. They feed through a process called phagocytosis, in which they surround and engulf their prey, forming a temporary food vacuole. Inside the food vacuole, the prey is digested by enzymes, and the nutrients are absorbed into the Amoeba’s cytoplasm.
Reproduction in Amoebas primarily occurs through asexual means, such as binary fission, where the Amoeba divides into two identical daughter cells. Under certain conditions, Amoebas can also engage in sexual reproduction through a process called conjugation, where genetic material is exchanged between two individuals.
Amoebas play an important role in the ecosystem as decomposers, breaking down organic matter and recycling nutrients. They also serve as a food source for other organisms. However, certain species of Amoebas, such as EntAmoeba histolytica, can cause diseases in humans and animals, leading to infections and health issues.
Frequently Asked Questions on Amoeba
What is the habitat of Amoeba?
Amoebas are found in a variety of freshwater, marine, and terrestrial habitats. They are commonly found in freshwater bodies such as ponds, lakes, and streams, where they inhabit the sediment or attached to submerged surfaces.
How does Amoeba obtain its food?
Amoebas are heterotrophic organisms and obtain their food by engulfing other microorganisms and organic particles. They extend their pseudopodia around their prey, forming a food vacuole, and then release enzymes to digest the captured food.
What is the reproduction process of Amoeba?
Amoebas reproduce primarily through a process called binary fission, where the parent cell divides into two identical daughter cells. They can also engage in sexual reproduction through conjugation, where genetic material is exchanged between two individuals.
Can Amoebas cause diseases in humans?
Yes, some species of Amoebas can cause diseases in humans. For example, the species EntAmoeba histolytica can cause amoebic dysentery, a gastrointestinal infection that leads to symptoms such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fever.
Are Amoebas harmful to humans?
While most Amoebas are harmless, certain species can be harmful to humans. For instance, Naegleria fowleri is a rare but deadly Amoeba that can cause a severe brain infection called primary amebic meningoencephalitis (PAM) if it enters the body through the nose.
How do Amoebas move?
Amoebas move by extending their pseudopodia, which are temporary extensions of their cytoplasm. They can change the direction of movement by extending pseudopodia in different directions.
Can Amoebas survive in extreme environments?
Amoebas are versatile organisms and can adapt to various environmental conditions. Some species can survive in extreme environments such as hot springs, frozen tundra, and even acidic or alkaline conditions.
What is the role of Amoebas in the ecosystem?
Amoebas play a vital role in the ecosystem as decomposers. They feed on organic matter, including dead plants and animals, and help in the breakdown and recycling of nutrients, contributing to the nutrient cycle in the environment.







