Table of Contents
Introduction
Asexual reproduction involves the production of offspring without the involvement of gametes or the fusion of genetic material. It results in the production of genetically identical offspring, known as clones. This type of reproduction is observed in various organisms such as bacteria, fungi, plants, and some animals. Asexual reproduction is advantageous in stable and favorable environments where genetic diversity is not essential. It allows for rapid and efficient population growth, as a single parent can produce numerous offspring. Organisms capable of asexual reproduction can colonize new habitats quickly and exploit available resources efficiently.
Asexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction in which offspring are produced without the involvement of gametes (sex cells) or the fusion of genetic material from two parents. It results in the production of genetically identical or very similar offspring to the parent organism. Here’s an overview of asexual reproduction:
Characteristics of Asexual Reproduction
- Involves a single parent organism.
- Offspring are genetically identical or closely resemble the parent.
- No fusion of gametes occurs.
- Does not involve the formation of specialized reproductive cells.
- Rapid process, allowing for the production of numerous offspring in a short time.
- Commonly observed in simple organisms, such as bacteria, fungi, and some plants and animals.
Advantages of Asexual Reproduction
- Rapid reproduction allows for the colonization of new habitats or rapid population growth.
- Energy-efficient as it does not require the production of specialized reproductive cells or the search for a mate.
- Maintains the genetic traits and characteristics of successful parent organisms, ensuring the preservation of desirable traits.
- Suitable for stable or predictable environments where the offspring can thrive with traits identical to the parent.
Disadvantages of Asexual Reproduction
- Lack of genetic diversity can hinder adaptation to changing environments or make the population more susceptible to diseases or parasites.
- Limited ability to evolve and respond to environmental challenges since there is no genetic recombination or reshuffling.
- Accumulation of detrimental mutations that are not eliminated through recombination can lead to a decrease in overall fitness.
- Vulnerability to the spread of harmful traits or diseases throughout the entire population due to genetic uniformity.
Also Check
Type of Asexual reproduction
Asexual reproduction methods include binary fission, budding, fragmentation, and vegetative propagation. There are several different types of asexual reproduction observed in various organisms. Here are some common types:
Binary Fission
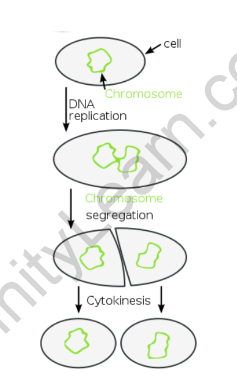
Binary fission is a form of asexual reproduction in which an organism divides into two equal-sized daughter cells. This method is commonly observed in single-celled organisms such as bacteria and protists. The parent cell duplicates its genetic material and then divides into two identical daughter cells.
Budding
Budding is a type of asexual reproduction in which a new individual develops as an outgrowth or bud on the parent organism. The bud grows and eventually detaches from the parent, becoming an independent organism. Budding is observed in organisms like yeast, hydra, and some plants.
Fragmentation
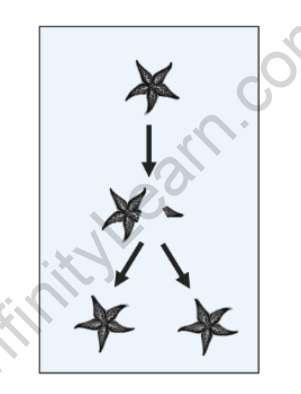
Fragmentation is a form of asexual reproduction where an organism breaks into fragments, and each fragment develops into a new individual. This method is common in organisms like flatworms and some plants. Each fragment has the ability to regenerate missing body parts and develop into a complete organism.
Vegetative Propagation
Vegetative propagation involves the production of new plants from vegetative parts such as roots, stems, and leaves. This type of reproduction is seen in plants and allows for the production of genetically identical offspring. Examples of vegetative propagation include runners in strawberry plants, rhizomes in ferns, and tubers in potatoes.
Parthenogenesis
Parthenogenesis is a form of asexual reproduction in which unfertilized eggs develop into offspring. It occurs in some insects, reptiles, and fish. In this process, the egg undergoes development without the involvement of sperm, resulting in genetically identical offspring.
Apomixis
Apomixis is a type of asexual reproduction in plants where seeds are produced without fertilization. The embryo develops from the maternal tissue, bypassing the need for pollination and the fusion of gametes. Apomixis allows for the production of offspring with the same genetic traits as the parent plant.
These are just a few examples of the different types of asexual reproduction. Each method of asexual reproduction has its advantages and adaptations, allowing organisms to reproduce efficiently and rapidly in diverse environments.
Examples of Asexual Reproduction
- Bacteria reproducing through binary fission.
- Yeast cells undergoing budding to produce new cells.
- Hydra producing new individuals through budding.
- Strawberry plants spreading through the formation of runners.
- Starfish regenerating new individuals from fragmented body parts.
- Ferns reproducing through the release and germination of spores.
FAQs on Asexual Reproduction
What is asexual reproduction?
Asexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction in which offspring are produced without the involvement of gametes or the fusion of genetic material from two parents. It results in genetically identical or closely resembling offspring to the parent organism.
What are the advantages of asexual reproduction?
The advantages of asexual reproduction include rapid reproduction, energy efficiency, preservation of desirable traits, and suitability for stable environments where offspring can thrive with traits identical to the parent.
What are the disadvantages of asexual reproduction?
The disadvantages of asexual reproduction include limited genetic diversity, reduced ability to adapt to changing environments, accumulation of detrimental mutations, and vulnerability to the spread of harmful traits or diseases.
What are the different types of asexual reproduction?
The different types of asexual reproduction include binary fission, budding, fragmentation, spore formation, and vegetative propagation. Each type has its unique mechanisms and is observed in different organisms.
How does binary fission work?
Binary fission is a type of asexual reproduction where the parent organism divides into two identical daughter cells. It is commonly observed in bacteria and other single-celled organisms.
What is budding in asexual reproduction?
Budding is a type of asexual reproduction where a new individual develops as an outgrowth or bud from the parent organism. Eventually, the bud detaches and becomes an independent organism. Yeast and hydra are examples of organisms that reproduce through budding.
How does fragmentation work in asexual reproduction?
Fragmentation is a type of asexual reproduction where the parent organism breaks into fragments, and each fragment has the potential to develop into a new individual. Regeneration in starfish and flatworms is an example of fragmentation.
What is spore formation in asexual reproduction?
Spore formation is a type of asexual reproduction where specialized cells called spores are produced. These spores can develop into new individuals. Spore formation is observed in fungi, algae, and some plants.
Can plants reproduce asexually?
Yes, plants can reproduce asexually through various methods such as vegetative propagation, runners, rhizomes, tubers, and bulbs. These methods allow plants to produce genetically identical or closely resembling offspring to the parent.







