Table of Contents
Introduction
Fragmentation is a natural process that occurs in various organisms, including plants and animals. It involves the breaking or splitting of a parent organism into smaller pieces, which then regenerate into new individuals. This process plays a significant role in the reproduction, survival, and growth of certain species. In this article, we will explore the meaning and definition of fragmentation, its occurrence in different organisms, and the benefits associated with this regenerative phenomenon.
Fragmentation Meaning and Definition
Fragmentation refers to the breaking or separation of a parent organism into distinct fragments, each capable of developing into a complete and independent organism. This process often occurs spontaneously due to external factors or as a deliberate reproductive strategy adopted by certain organisms.
Fragmentation in Different Organisms
Fragmentation is observed in various organisms across different kingdoms of life, including plants and animals. It is a common reproductive strategy in both terrestrial and aquatic environments. Let’s explore fragmentation in plants and animals
Fragmentation in Plants
In plants, fragmentation commonly occurs in those with vegetative propagation capabilities. For example, certain grasses, ferns, and mosses reproduce through rhizomes, stolons, or other specialized structures that break off from the parent plant and give rise to new individuals. The separated fragments develop roots and shoots, establishing independent plants.
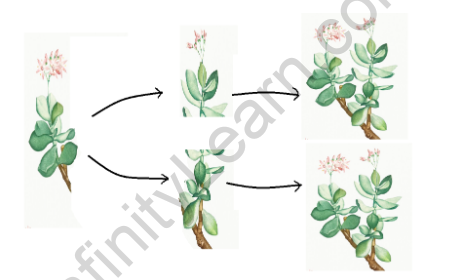
- Fragmentation is a common reproductive strategy in certain plants.
- It involves the breaking or separation of a parent plant into fragments.
- The fragments have the ability to develop into complete and independent plants.
- Plants that exhibit fragmentation often have specialized structures like rhizomes, stolons, or bulbils.
- These structures break off from the parent plant and give rise to new individuals.
- Each fragment develops roots and shoots, establishing itself as an independent plant.
- Fragmentation allows plants to efficiently propagate and colonize new areas.
- It contributes to the expansion of the plant population and genetic diversity.
- Fragmentation is advantageous in environments with limited resources, as each fragment can access necessary nutrients and space independently.
- It also increases the chances of survival and adaptation by rapidly producing new individuals.
- Examples of plants that employ fragmentation as a reproductive strategy include certain grasses, ferns, mosses, and some succulents.
- Fragmentation in plants demonstrates their remarkable ability to regenerate and perpetuate their species.
Fragmentation in Animals
In the animal kingdom, fragmentation can be observed in several organisms. Some flatworms, such as planarians, have remarkable regenerative abilities. When a planarian is cut into multiple fragments, each piece has the potential to regenerate into a complete organism. Similarly, some species of sea stars exhibit fragmentation, where a detached arm can grow into a whole new individual.
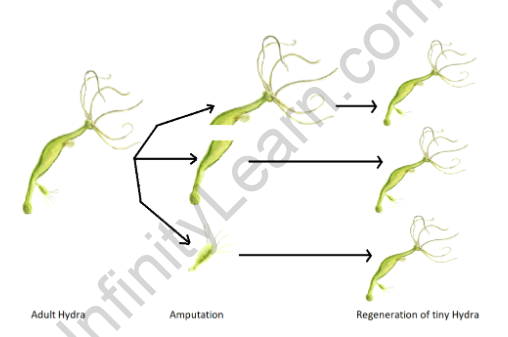
Benefits of Fragmentation
Fragmentation offers several advantages to organisms that employ this reproductive strategy. Here are some notable benefits
1. Colonization and Dispersal: Fragmentation allows organisms to colonize new habitats and expand their geographical range. The separated fragments can disperse and establish themselves in different areas, contributing to population growth and genetic diversity.
2. Regeneration and Regrowth: Fragmentation provides a means of regeneration and regrowth for organisms. By breaking into fragments, they can regenerate lost or damaged body parts, ensuring their survival and perpetuation.
3. Resource Utilization: Fragmentation enables efficient resource utilization. Each fragment can access necessary resources independently, reducing competition among the offspring and maximizing the utilization of available nutrients and space.
4. Rapid Reproduction: Fragmentation can lead to rapid reproduction and population increase. As each fragment has the potential to develop into a new individual, the process accelerates the production of offspring, facilitating the survival and adaptation of species.
Conclusion
Fragmentation is a fascinating reproductive strategy observed in various organisms. It allows organisms to reproduce, regenerate, and colonize new habitats. Whether in plants or animals, fragmentation plays a crucial role in the survival and growth of certain species. By understanding the mechanisms and benefits of fragmentation, we gain insight into the remarkable adaptability and resilience of these organisms in the face of changing environments.
Frequently Asked questions on Fragmentation
What is fragmentation in plants?
Fragmentation in plants is a reproductive process where a parent plant breaks or separates into fragments, each capable of growing into a new and independent plant.
Which plants use fragmentation as a means of reproduction?
Several plant species, including certain grasses, ferns, mosses, and succulents, use fragmentation as a means of reproduction.
How does fragmentation occur in plants?
Fragmentation can occur through various mechanisms such as the natural detachment of specialized structures like rhizomes or bulbs, the growth and separation of apical meristems, environmental factors like wind or physical disturbances, and the regeneration of plant parts.
What are the benefits of fragmentation in plants?
Fragmentation allows plants to efficiently propagate, colonize new areas, and increase genetic diversity. It ensures rapid reproduction, adaptation, and the establishment of independent individuals in environments with limited resources.
Are there any disadvantages to fragmentation in plants?
While fragmentation is generally advantageous for plants, it can lead to the loss of genetic diversity if only a few individuals contribute to the new population. It may also increase the risk of disease transmission among fragmented plants.
Can fragmentation occur in animals as well?
Yes, fragmentation can occur in certain animals, where a parent organism breaks or separates into fragments, each capable of developing into a new individual.
How is fragmentation different from other forms of reproduction?
Fragmentation is a form of asexual reproduction where new individuals are derived from fragments of the parent organism, while other forms of reproduction involve the production and fusion of gametes to form offspring.
Does fragmentation affect the genetic makeup of plant populations?
Fragmentation can impact the genetic makeup of plant populations by promoting the spread of specific genetic traits or reducing genetic diversity if only a few individuals contribute to the new population. However, genetic diversity can still be maintained through sexual reproduction or genetic exchange with other populations.








