Table of Contents
Our planet has diverse ecosystems, species, and natural resources. However, as human activities continue to exert pressure on the environment, the need to protect and preserve these invaluable treasures becomes increasingly urgent. One of the most effective conservation initiatives on a global scale is the establishment of biosphere reserves. These reserves demonstrate how humans and nature can coexist in harmony while safeguarding our planet’s ecological integrity.
Understanding Biosphere Reserves
Biosphere reserves are internationally recognized areas that aim to reconcile biodiversity conservation, sustainable development, and the cultural heritage of local communities. These areas are designated by the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) under the Man and the Biosphere (MAB) program. The MAB program, launched in 1971, seeks to foster interdisciplinary research, monitoring, education, and capacity-building to address the complex relationship between humans and their environment.
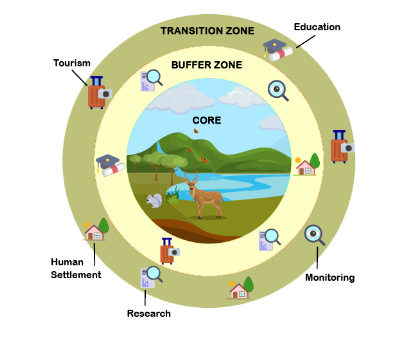
Biosphere reserves are unique because they act as living laboratories, promoting a balanced approach to conservation and development. Each reserve typically consists of three interconnected zones:
- Core Area: This is the heart of the biosphere reserve and is strictly devoted to conserving biodiversity and ecosystems. Human intervention is minimal, and the core area acts as a sanctuary for wildlife and natural processes.
- Buffer Zone: Surrounding the core area, the buffer zone serves as a transitional space where sustainable human activities can take place. Here, conservation and development can coexist, but strict guidelines ensure that activities do not harm the core area.
- Transition Area: The outermost zone, the transition area, incorporates human settlements and various economic activities. This zone encourages sustainable practices that take into account both human needs and environmental concerns.
Also, Check
The Role and Importance of Biosphere Reserves
Biosphere reserves play a crucial role in achieving a balance between environmental conservation and socioeconomic development. Here are some key reasons why these reserves are of great importance:
- Biodiversity conservation: The core areas of biosphere reserves act as sanctuaries for endangered species and critical habitats. By protecting these ecosystems, we safeguard biodiversity, which is essential for ecological stability and resilience.
- Research and monitoring: Biosphere reserves provide an opportunity for scientists and researchers to study ecosystems, monitor biodiversity trends, and conduct experiments on sustainable land-use practices. The knowledge gained in these reserves helps in conservation efforts worldwide.
- Sustainable development: The buffer and transition zones of biosphere reserves foster sustainable development models that consider the needs of the local communities, environmental protection, and economic growth. These models often serve as examples for other regions facing similar challenges.
- Environmental education: Biosphere reserves are invaluable for environmental education and awareness-raising initiatives. Visitors and local communities learn about the importance of conservation, sustainable living, and the interdependence between humans and nature.
- Cultural heritage preservation: Many biosphere reserves are home to indigenous communities with rich cultural traditions. By integrating cultural heritage preservation, these reserves celebrate the relationship between humans and nature and promote traditional knowledge and practices.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite their significance, biosphere reserves face several challenges. Pressures from population growth, unsustainable resource exploitation, climate change, and political conflicts threaten these delicate ecosystems. To address these challenges and ensure the long-term success of biosphere reserves, the following steps are crucial:
- Strengthening collaboration: Effective conservation efforts require collaboration among governments, international organizations, local communities, and NGOs. Strengthening partnerships and engaging all stakeholders in decision-making is essential.
- Sustainable livelihoods: Supporting sustainable livelihoods for local communities within and around biosphere reserves is vital. It reduces their dependence on destructive activities.
- Climate action: Biosphere reserves protect us from intense climatic changes in the future. So these ecosystems must be preserved.
- Public Awareness: Raising public awareness about the value of biosphere reserves and the urgent need for conservation is crucial. Education can mobilize support and action for their protection.
Summary
Biosphere reserves are vital areas designated for biodiversity conservation, sustainable development, and cultural heritage preservation. These reserves consist of three interconnected zones: core, buffer, and transition areas. Biosphere reserves play a critical role in protecting endangered species, supporting research, promoting sustainable practices, and raising environmental awareness. Challenges include population growth, climate change, and political conflicts. To ensure their success, collaboration, sustainable livelihoods, climate action, and public awareness are essential. Overall, biosphere reserves represent a beacon of hope for a harmonious coexistence between humans and nature, requiring global efforts to safeguard our planet’s ecological integrity.
FAQs on Biosphere Reserve
What are biosphere reserves?
Biosphere reserves are internationally recognized areas designated by UNESCO under the Man and the Biosphere (MAB) program. They aim to reconcile biodiversity conservation, sustainable development, and the cultural heritage of local communities.
What are the three zones in biosphere reserves?
Biosphere reserves typically consist of three interconnected zones: the core area, buffer zone, and transition area. The core area is strictly devoted to conserving biodiversity, while the buffer zone serves as a transitional space for sustainable human activities. The transition area incorporates human settlements and economic activities, promoting sustainable practices.
What role do biosphere reserves play?
Biosphere reserves are crucial for achieving a balance between environmental conservation and socioeconomic development. They protect endangered species and critical habitats, provide opportunities for research and monitoring, promote sustainable development models, and serve as centers for environmental education.
What challenges do biosphere reserves face?
Biosphere reserves face pressures from population growth, unsustainable resource exploitation, climate change, and political conflicts. These threats can harm the delicate ecosystems within these reserves.
How can biosphere reserves be protected for the future?
To ensure the long-term success of biosphere reserves, collaboration among governments, international organizations, local communities, and NGOs is essential. Supporting sustainable livelihoods, implementing climate action strategies, and raising public awareness are also crucial steps in safeguarding these valuable areas.
What is the significance of cultural heritage preservation in biosphere reserves?
Many biosphere reserves are home to indigenous communities with rich cultural traditions. By integrating cultural heritage preservation, these reserves celebrate the relationship between humans and nature and promote traditional knowledge and practices.
When was the Man and the Biosphere (MAB) program launched?
The MAB program was launched in 1971 with the aim of fostering interdisciplinary research, monitoring, education, and capacity-building to address the complex relationship between humans and their environment.
How do biosphere reserves contribute to biodiversity conservation?
The core areas of biosphere reserves act as sanctuaries for endangered species and critical habitats, thereby safeguarding biodiversity, which is essential for ecological stability and resilience.
What is the purpose of the buffer zone in biosphere reserves?
The buffer zone surrounding the core area allows for sustainable human activities, where conservation and development can coexist while ensuring that activities do not harm the core area.
Why are biosphere reserves considered living laboratories?
Biosphere reserves are referred to as living laboratories because they promote a balanced approach to conservation and development, offering opportunities for research, education, and sustainable practices.







