Table of Contents
Introduction to cell organelles
Cells are the fundamental units of life, and within these microscopic powerhouses, various specialized structures called organelles carry out essential functions. Each organelle plays a unique role, contributing to the overall functioning of the cell.
What are cell organelles?
Cell organelles are specialized structures or compartments within eukaryotic cells that perform specific functions essential for the cell’s survival and proper functioning. These organelles are membrane-bound and carry out various cellular processes, such as energy production, protein synthesis, waste management, and maintaining cell shape and structure. Each organelle has a distinct role and contributes to the overall efficiency and functionality of the cell. Examples of cell organelles include the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, peroxisomes, vacuoles, chloroplasts (found only in plant cells), and the cytoskeleton.
Diagram of Animal Cell with all the organelles labelled
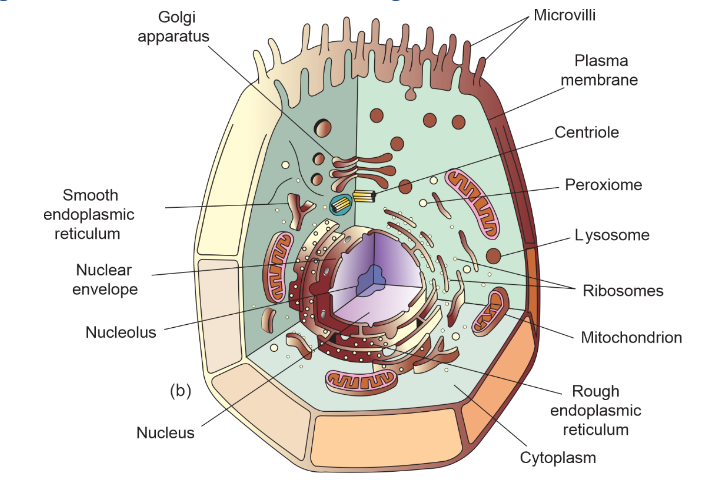
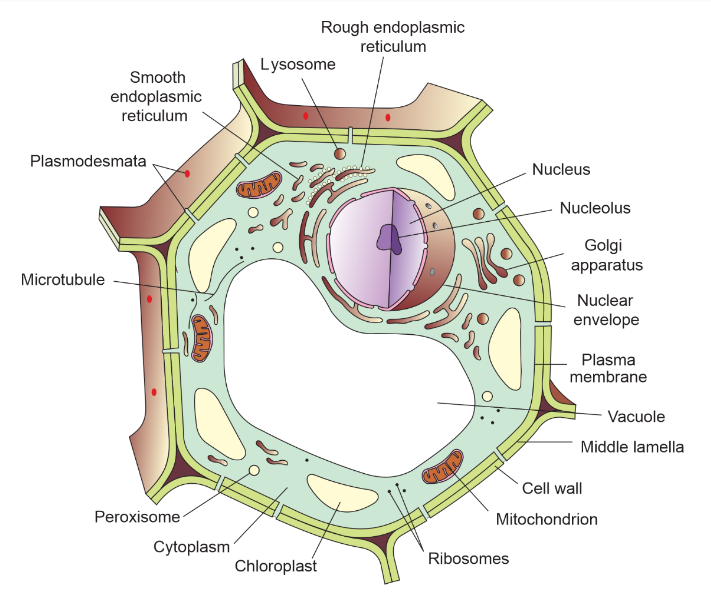
Diagram of Plant Cell with all the Organelles labelled
Various Cell Organelles and their Brief Description
Nucleus
The nucleus is often referred to as the “control centre” of the cell. It houses the cell’s genetic material, DNA, in the form of chromosomes. This organelle controls gene expression and regulates the cell’s activities. It is enveloped by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope, which contains pores allowing the exchange of substances between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are known as the “powerhouses” of the cell because they are responsible for generating energy through cellular respiration. They have their own DNA and are enclosed by a double membrane. Mitochondria produce ATP, the molecule that stores energy, and play a vital role in metabolism and cellular survival.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a network of membranous tubes and sacs involved in protein synthesis, lipid metabolism, and calcium storage. Rough ER has ribosomes on its surface, producing proteins that are either incorporated into the cell membrane or secreted. Smooth ER is responsible for synthesizing lipids and detoxifying drugs and poisons.
Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus functions as a processing and distribution centre for proteins and lipids synthesized in the ER. It modifies, sorts, and packages these molecules into vesicles for transport to their final destinations within the cell or for secretion outside the cell. It consists of flattened, membranous sacs called cisternae.
Lysosomes
Lysosomes are sac-like organelles containing digestive enzymes that break down waste materials, damaged organelles, and foreign substances. They play a vital role in cellular recycling and the removal of cellular debris.
Peroxisomes
Peroxisomes are small, single-membraned organelles involved in detoxifying harmful substances and breaking down fatty acids. They also play a role in the synthesis of certain lipids.
Vacuoles
Vacuoles are storage compartments in plant cells, responsible for storing water, ions, and nutrients. In some plant cells, the vacuole also maintains turgor pressure, which provides structural support to the cell.
Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts are exclusive to plant cells and are responsible for photosynthesis. These green, double-membraned organelles contain chlorophyll, a pigment that captures sunlight and converts it into chemical energy in the form of glucose.
Cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a network of protein filaments that provides structural support to the cell and helps maintain its shape. It also aids in cell movement, intracellular transport, and cell division.
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a semipermeable barrier that surrounds the cell, separating its internal environment from the external surroundings. It controls the passage of substances into and out of the cell, ensuring proper cellular function.
Also Check: Animal Cell
Frequently Asked Questions on Cell Organelles
What is the function of the nucleus?
The nucleus houses the cell's genetic material, controlling gene expression and regulating cellular activities.
What is the main role of mitochondria?
Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell, generating energy through cellular respiration.
What is the difference between rough ER and smooth ER?
Rough ER has ribosomes on its surface and is involved in protein synthesis, while smooth ER synthesizes lipids and detoxifies substances.
Are all organelles exclusive to eukaryotic cells?
Yes, most organelles are found only in eukaryotic cells, which include plant, animal, and fungi cells. Prokaryotic cells, like bacteria, lack membrane-bound organelles.
What is the role of chloroplasts in plant cells?
Chloroplasts conduct photosynthesis, capturing sunlight and converting it into chemical energy (glucose) for the plant's use.