Table of Contents
Monohybrid cross is a basic concept in genetics where there is consideration of inheritance of one characteristic from one generation to another. It focuses on one pair of contrasting traits like tall versus short plants. A monohybrid cross is important because it can reveal some fundamental principles about heredity that are necessary for understanding more complex genetic phenomena.
Gregor Mendel, who is often regarded as the Father of Genetics, laid the foundation stone for this phenomenon through his work on peas. Mendel’s experiments with pea plants discovered the patterns of inheritance which form the basis of all modern genetics studies. His findings not only advanced scientific knowledge but also established guidelines for future studies on inherited traits.
Gregor Mendel and His Experiments
Gregor Mendel performed vital pea plant experiments in the mid-nineteenth century.
His choice of pea plants was strategic:
- They had easily observable traits
- A short generation time
- Could be cross-pollinated manually.
The seven traits that Mendel examined were controlled by him in his experiments, including plant height, seed shape and flower colour.
Mendel’s experiments involved crossing plants with different traits with one another and observing the resulting traits of their offspring.
For example, when he crossed tall plants with short ones, all the first-generation (F1) plants were tall. However, when these F1 individuals self-fertilised, the second generation (F2) produced both tall and short plants at a 3:1 ratio.
This led to the formulation of laws on inheritance by Mendel which became the classical genetics foundation.
Understanding the Monohybrid Cross
The topic of genetics revolves around Monohybrid Crosses, which is a major concept. Gregor Mendel’s work in pea plants laid the foundation for this knowledge. It leads to the principles that explains how traits are passed on from one generation to another.
So let’s understand in depth about the concept of Monohybrid Cross.
Monohybrid Cross
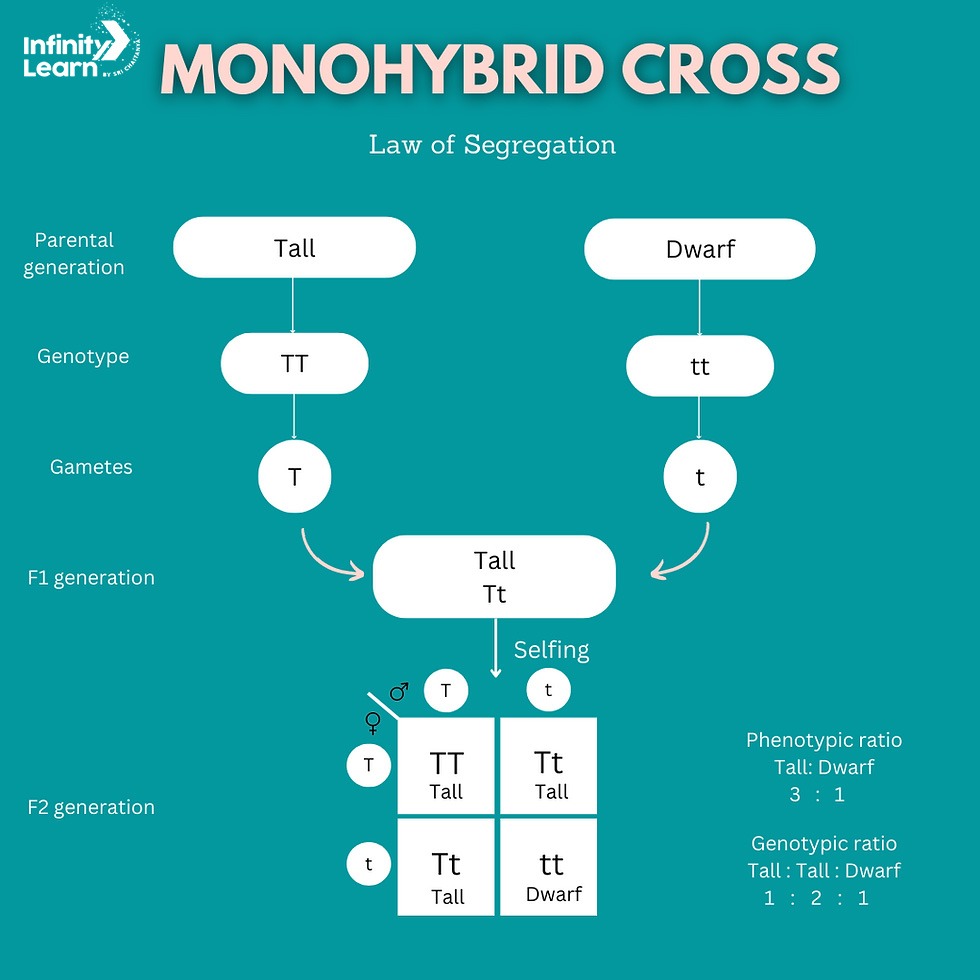
Monohybrid cross can be described as the genetic crossing of two individuals who are heterozygous for one trait.
In other words, it includes only one gene with two alleles, that includes:
- One dominant
- One recessive.
For instance, in pea plants, the height gene has two alleles which are tall (T) or short (t).
When a Tt plant is crossed with another Tt plant that is referred to as monohybrid cross.
How is a Monohybrid Cross Conducted?
The first step in doing a monohybrid cross involves identification of alleles responsible for the trait in question.
We will assume that we have crossed two tall heterozygous pea plants (Tt).
- The alleles during formation of gametes are separated producing either t or T genotype cells.
- As these cells combine during fertilisation; their possible genotypes include:
- TT
- Tt
- tt.
- Offspring resulting from this cross during fertilisation will produce phenotypes like those of its parents since they inherited them through genetics:
- TT for Tall
- Tt for heterozygous short
- tt for homozygous short
This shows the typical 3:1 ratio that is seen in F2 generation of monohybrid crosses.
Mendel’s Law of Inheritance
Mendel’s experiment introduced the fundamental laws of inheritance. His works helped us to understand how one trait is passed from one generation to another. Below is the brief discussion about Mendel’s Law of Inheritance.
Mendel proposed two key inheritance law:
- Law of Segregation
- Law of Independent Assortment
Law Of Segregation
- This law states that in gamete formation, the two alleles for a trait segregate so that each gamete obtains only one allele.
- For example, in a Tt plant – T and t segregate resulting in either T or t-carrying gametes.
- It ensures that an individual inherits one allele from each parent.
Law of Independent Assortment
- While this law is more associated with dihybrid cross, it is still an important part of inheritance.
- This means that alleles for different traits are independently distributed into gametes.
- In monohybrid cross we focus on single trait
- Hence this law plays an important role in this cross.
Punnett Square and Monohybrid Cross
A Punnett Square is a simple grid that is used to forecast the genotypes and phenotypes of offspring in a genetic cross. There are some steps to follow in order to use a Punnett Square for a monohybrid cross:
- It begins by drawing a square with four compartments. On top of it, alleles are listed from one parent while on its side consists of the other parent’s.
- All the alleles are merged in every box that predicts possible genotypes for offspring.
- This will involve an analysis of genotypes, which will help to determine their phenotypic manifestations.
- For instance, when you have Tt x Tt cross we see that TT, Tt and tt are likely outcomes as shown by Punnett Square. It gives 3 tall plants per short plant.
Punnett square can be used to predict offspring gene frequencies and also demonstrate how alleles segregate during gamete formation.
FAQs on Monohybrid Cross
What is a monohybrid cross in simple terms?
A Monohybrid Cross is the inheritance pattern observed when there is a cross between two individuals. It is done between a homozygous recessive and heterozygous alleles.
What are the steps of a monohybrid cross?
It includes identifying the traits, setting up the punnett square, filling it up by genotypes and then observing the possible phenotypic outcomes.
What is the typical ratio in a monohybrid cross?
The typical ratio in a monohybrid cross is 3:1. It consists of 3 dominant traits and one recessive trait.
What is an allele?
A pair of contrasting genes of a trait present on the same loci of a homologous chromosome is called an allele.
What is a homozygous trait and a heterozygous trait?
The organism having two identical alleles for a particular gene expressing a character is called a homozygous trait. For example,TT, tt. Whereas the individual having two dissimilar alleles of a gene expressing a character is called a heterozygous trait. For example Tt.








